1-click AWS Deployment 1-click Azure Deployment 1-click Google Deployment
Overview
What is SharePoint?
SharePoint is a document management and collaboration tool developed by Microsoft. It’s basically an intranet and content management system that is used for internal purposes to assist with bringing an organisation together.SharePoint is comprised of a multipurpose set of technologies that has tight integration with Office 365 as well as handy document management capabilities.In short, SharePoint is a browser-based collaboration, content management, and extensible platform from Microsoft. The latest release of the product is SharePoint 2013.

Previous versions of SharePoint 2013
The previous two versions are MOSS 2007 and SharePoint 2010.

Concepts
The logical result of SharePoint Server 2013’s flexibility and richness can be a high degree of complexity around installing and configuring SharePoint Server 2013 correctly. A fundamental understanding of the following key structural elements in a SharePoint Server 2013 environment is required in order to correctly deploy and support SharePoint Server 2013:
Server farm: The top-level element of a logical architecture design for SharePoint Server 2013.
Web application: An IIS Web site that is created and used by SharePoint Server 2013.
Content database: Provides storage Web application content. You can separate content into multiple content databases at the site collection level.
Site collection: A set of Web sites that have the same owner and share administration settings.
Site: One or more related Web pages and other items (such as lists, libraries, and documents) that are hosted inside a site collection.
In addition to understanding the elements of a SharePoint Server 2013 environment and how they have to be configured for your solution, you must consider the following additional factors: physical architecture, installation and configuration, and the various stages of deployment.
Physical architecture
The physical architecture, which consists of one or more servers and the network infrastructure, enables you to implement the logical architecture for a SharePoint Server 2013 solution. The physical architecture is typically described in two ways: by its size and by its topology. Size, which can be measured in several ways, such as the number of users or the number of documents, is used to categorize a farm as small, medium, or large. Topology uses the idea of tiers or server groups to define a logical arrangement of farm servers.
Size
Size uses the number of users and number of content items as a fundamental measure to indicate whether a server farm is small, medium, and large, as follows:
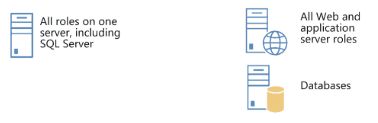
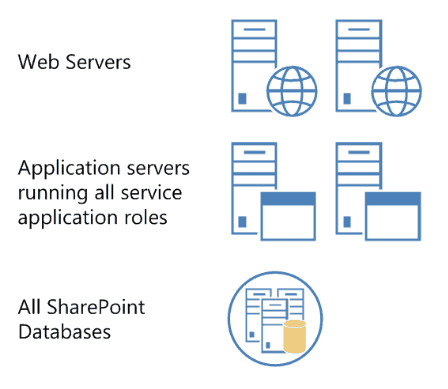
A small server farm typically consists of at least two Web servers and a database server. One of the Web servers hosts the Central Administration site and the other handles additional farm-related tasks, such as serving content to users.A small farm usually used in the development or testing environments where it can have only one or maximum of two servers. You have to install everything in one server if there is only one server. If you two servers you can separate your database server.
One server farm can server to less than 100 users.
Two servers small farm can serve up to 10,000 users.
The small farm can be scaled out to three tiers using a dedicated application server in response to the number of users, the number of content items, and the number of services that are required.
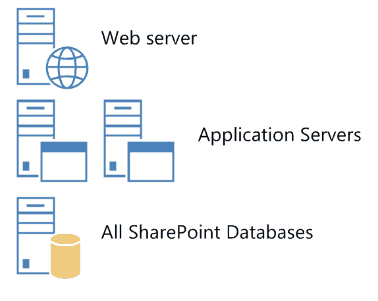
A medium server farm typically consists of two or more Web servers, two application servers, and more than one database servers. We recommend that you start with the preceding configuration and then scale out to accommodate the workload placed on the servers.In scenarios where services are known to use a disproportionate amount of resources, you can scale out the application tier. Performance data will indicate which services you should consider off-loading to a dedicated server.If you have a larger number of users then you can create a medium farm which will have 3 to 4 servers. If you have 3 servers then one can be used for a web server, one can be used as an application server and one can be used as a database server.The can server users between 10,000 to 20,000 users.If you have 4 servers, depending on your usage 2 can be a web server, one can be application server and one can be a database server. Or you can also build like one web server, two application server, and one database server.
A large server farm can be the logical result of scaling out a medium farm to meet capacity and performance requirements or by design before a SharePoint Server 2013 solution is implemented. A three-tier topology environment typically uses dedicated servers on all the tiers. Additionally, these servers are often grouped according to their role in the farm. For example, all client-related services can be grouped onto one or two servers and then scaled out by adding servers to this group as needed in response to user demand for these services.In a large farm, there can be 6 or more than 6 servers. You can use 2 servers as a web server, 2 as application server and 2 for the database server.In an 8 server farm, you can use two servers as web servers, 2 dedicated servers for query processing components and index components and 2 as application servers for other application services and 2 can be used as database server.You can also optimize your database server: you can put your content database in one server and other databases into another database server.
SharePoint 2013 is a collaboration environment that organizations of all sizes can use to increase the efficiency of business processes.
SharePoint 2013 sites provide secure environments that administrators can configure to provide personalized access to documents and other information.
SharePoint 2013 introduces new ways to work together in today’s cloud, social, mobile business environment. With SharePoint 2013, you can share, build, organize, manage and discover better.
Applications can be developed for the SharePoint 2013 platform in different ways, for example, as:
- Apps for SharePoint
- SharePoint Publishing Sites
- SharePoint Farm Solutions
- Mobile Apps for SharePoint
- Reusable Components for SharePoint
Adding these capabilities to your application (of any type mentioned alongside) helps users do things better and faster:
- Workflows
- Social & Collaboration Features
- Location & Mapping Features
- Search
- Business Connectivity Services
- Office 2013 & SharePoint 2013 Application Services
Assign Permission
The SharePoint 2013 setup administrator is the only account where you need to assign permission by yourself.
SQL Server Service Account
Permission are assigned automatically during installation of SQL Server 2012.
The SQL Server service account should be a domain account and is used to run SQL Server.
If you have an existing SQL Server instance provided by your SQL Server team you don’t need this account.
SharePoint Setup Administrator
You need to manually assign permissions.
The setup administrator is used to install SharePoint 2013.
The SharePoint 2013 setup administrator has to be a member of the administrators group on every server SharePoint should be installed.
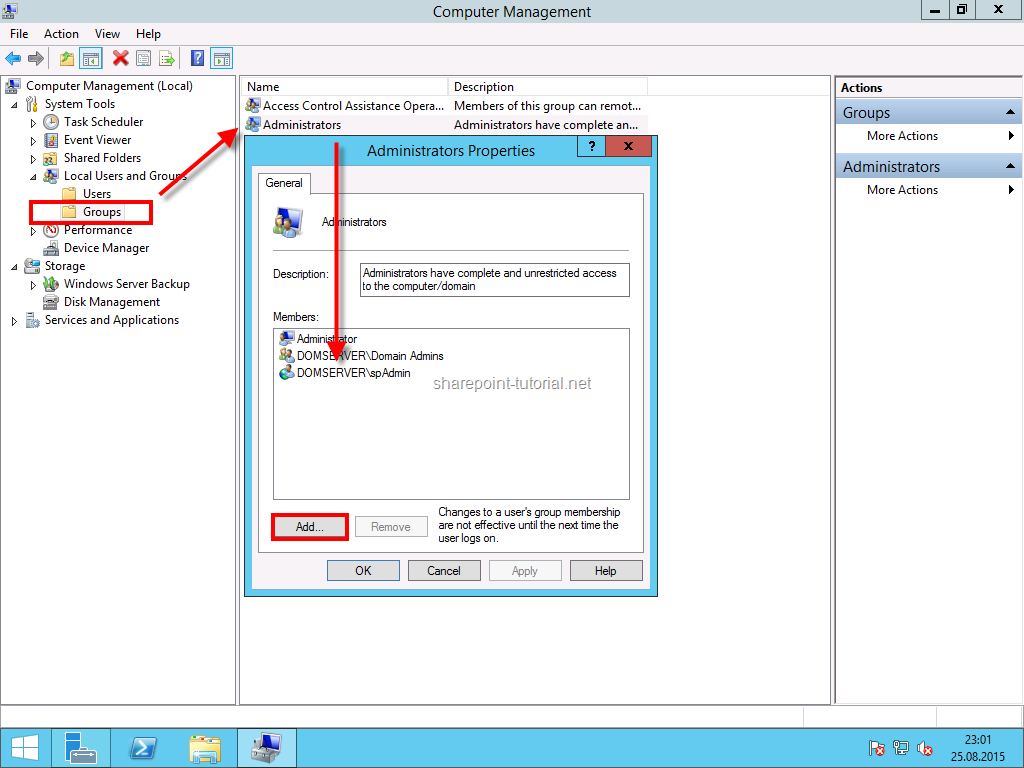
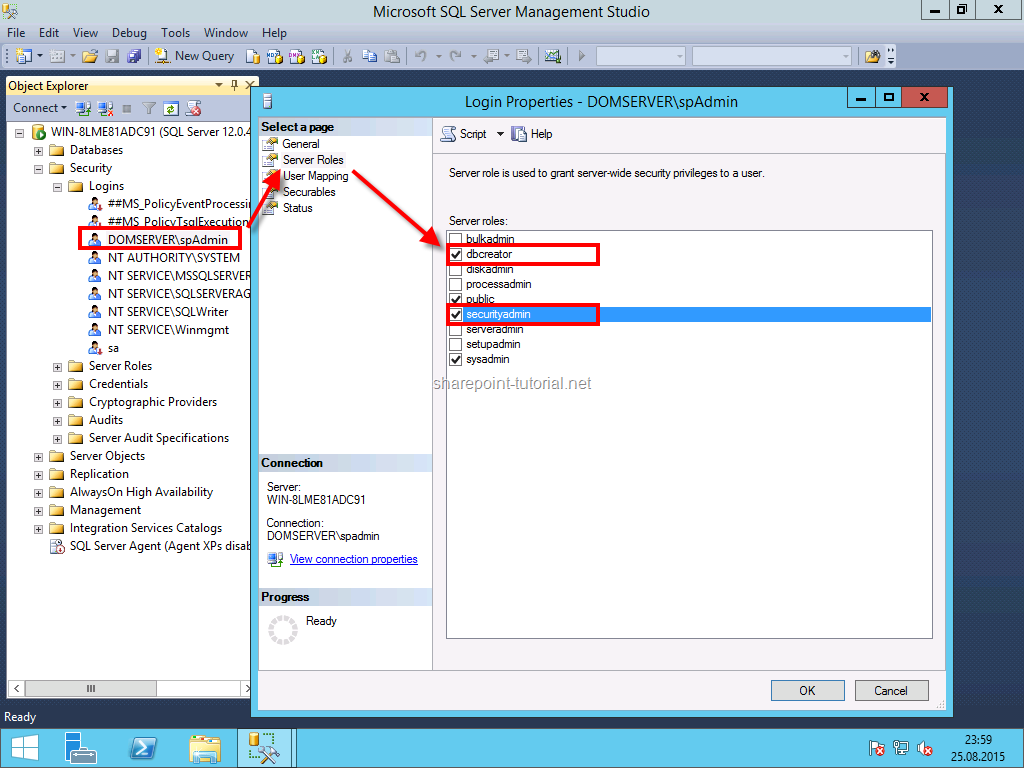
This account also needs the securityadmin and dbcreator role in SQL Server
If you run Windows PowerShell cmdlets that affect a database, this account must be a member of the db_owner fixed database role for the database.
If we create a development environment we shoild also assign the sysadmin role during the setup of SQL Server 2012 sowe have only one accoun that we need to administrate Windows Server, SQL Server and SharePoint.
SharePoint 2013 Farm Account
Permissions are automatically assigned if you use the SharePoint 2013 setup administrator during installation.
The farm account is used for the following things
Configure and manage the server farm.
Act as the application pool identity for the SharePoint Central Administration website.
Run the Microsoft SharePoint Foundation Workflow Timer Service.
Installing SharePoint Foundation 2013:
1.First, log in with your spfarm account, and then run the install file you downloaded, and you’ll get the lovely blue splash screen.

Click Install software prerequisites, under the Install section. This installs all the stuff SharePoint needs to run
Just accept defaults and walk through this wizard. This wizard will probably require your server to restart. It may need to reboot a couple of times depending on how many updates it has to do.
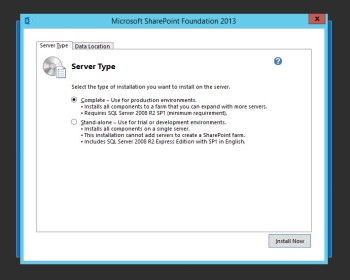
Log back in and rerun the installer. Back at the blue screen, press Install SharePoint Foundation. Most of the installation will be pretty basic: accept the terms, press continue. For Server Type, select Complete and press Install Now.
When done, you can go ahead and press Close.
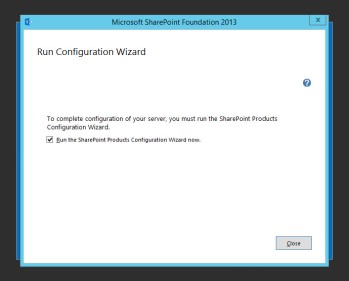
The SharePoint Products Configuration Wizard will appear next. Click Next then Yes to the warning. On the next page, select Create a new server farm.

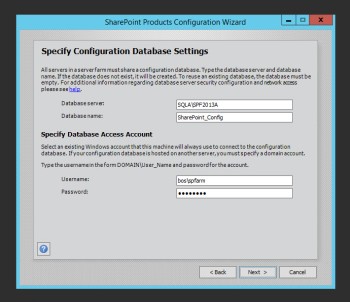
On the next screen, enter your details for the SQL server, and use your spfarm account for its credentials.Here we are showing the \SPF2013A because we installed SQL with another instance, so we can probably leave ours as the server name.
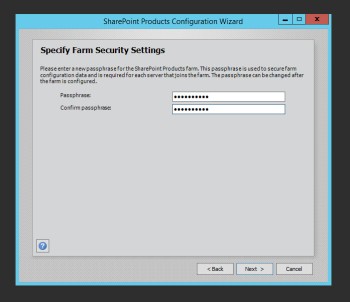
Specify a passphrase. Important! This passphrase will be needed if you want to add another server to your farm in the future. Keep it safe!
On the next screen, you can leave it as default, or specify a port number. If you decide to specify your own port, do not specify any of the standard web ports like 80, 443, 8080, etc. This should be a unique port number as central administration is the core of SharePoint, all configuration, permissions and such occurs here.

Click Next a couple more times and the configuration will run. It may take a while depending on hardware and what not. Let it run. It will error if there’s a problem, otherwise, no news is good news.
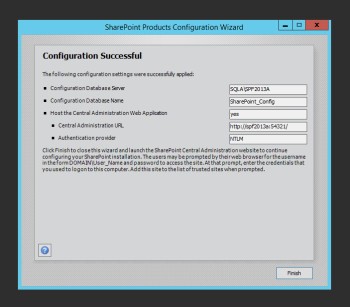
Success! Click Finish and Central Administration will open.
Recent Changes in SharePoint
The 2013 version of SharePoint has added some useful functions and features for business implementations:
-Improved integration of Microsoft Office publishing and document management features using the ribbon toolbar present in Word, Excel and other Microsoft applications
-Addition of social networking features to integrate these marketing and communications tools into the workplace environment more organically
-Feature parity for cloud computing services; this functionality was promised in SharePoint 2010 but failed to deliver the true parity expected by most business enterprises
-Improved support for mobile access to allow true anytime, anywhere connectivity with workplace applications and data
These new features will provide even more functionality for businesses in the increasingly digital world of the modern workplace. However, some of the shortcomings present in previous versions of SharePoint persist in the 2013 version.
Drawbacks of SharePoint
Microsoft SharePoint offers an easy-to-use solution for corporate networking needs. However, it has its own set of failings that may limit its utility in the modern corporate environment:
-The high cost of SharePoint in comparison to other solutions can be an insurmountable obstacle for smaller companies.
-In most cases, third-party applications and customizations are required and must be integrated to fulfill internal company needs.
-The social networking functions incorporated in the new version still do not include all elements of the SharePoint system.
-Many users find the search function clunky and inelegant compared to more advanced search engines available online and through other applications.
-Microsoft’s branding requirements reduce the degree of customization allowable for many intranet and Internet home and landing pages.
-These shortcomings have not significantly affected SharePoint’s popularity in the business world; it is estimated that nearly half of all intranet implementations use the SharePoint platform.
SharePoint Online is a collection of Web-based tools and technologies that help your organization store, share and manage digital information. Built on Microsoft SharePoint Server 2013, this hosted service is ideal for working on projects, storing data and documents in a central location and sharing information with others.
Cognosys Provides Hardened images of SharePoint on the cloud ( AWS marketplace, Azure and Google Cloud Platform).
Deploy SharePoint securely on cloud i.e. AWS marketplace, Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Secured Sharepoint 2013 Standard on Windows 2012 R2
Sharepoint 2013 Standard on Cloud for AWS
Features
SharePoint Functionality
Microsoft SharePoint has evolved significantly from its first iteration as SharePoint Portal Server 2001. SharePoint 2013 offers a number of functions that can be categorized as follows:
1.Storage of data can be managed to create tiered levels of access and archival-level document management for easy access throughout the corporate management and staffing structure.
2. Internal communities can be established to manage various projects, data resources and other vital elements of the corporate operations plan.
3.Website creation can be facilitated from within SharePoint to allow specific intranet groups to share resources and exchange information in a collaborative environment. Additionally, outward-facing sites can be created that allow limited and controlled interactions by customers and vendors with the internal structure of the SharePoint platform.
4 Advanced search features allow staff members to retrieve necessary documents and data quickly and accurately.
The new version of SharePoint incorporates composite application capability for added functionality from existing applications and tools in the workplace.
5.Analytics and reports can be compiled from data stored in the SharePoint platform.
These categories of functions can deliver added connectivity for business operations and provide a working platform for office intranet and extranet activities.
1. Authentication
OAuth support. This web authorization protocol means that a user or web app can request authorization to get temporary access to specific network resources.
Default claims-based authentication for new web apps. A new Windows PowerShell cmdlet, Convert-SPWebApplication, helps you migrate from Windows classic-mode authentication to claims-based authentication.
Distributed Cache Service for login tokens. A dedicated cache helps avoid the need for additional configuration and makes for less memory utilization in the web front-ends.
.
2. Business Connectivity Services (BCS)
OData support. With this web protocol, you can now connect to an external data source.
Event listener. This includes an event subscriber, enabling SharePoint users and custom code to receive notifications of events that occur in the external system.
Support for apps for SharePoint. Lets you add self-contained apps for SharePoint that don’t make any changes to the underlying code on the computer running SharePoint Server, enhancing safety and easing installation and removal.
External list enhancements. Users can now filter, sort, or export external lists that display content from BCS content types; performance improvements reduce the load on SharePoint farm database servers.
3. eDiscovery
SharePoint eDiscovery Center. Site template creates a new portal for managing holds and cases, including abilities to search, place holds, and export content.
Improvements to in-place holds. Includes site-level preservation, Exchange mailbox preservation, ability to set permissions for users to access original versions of preserved content.
eDiscovery export. Ability to export the results of an eDiscovery search for later import into a review tool.
Enterprise-wide eDiscovery. Ability to manage eDiscovery across multiple SharePoint farms, Exchange servers, and file shares.
4. Mobile
Optimized viewing across different mobile platforms.
One site, multiple renderings. Ability to render a single published SharePoint site in multiple designs to accommodate different devices.
Push notifications. Works for Windows Phones.
Geolocation field type. For mobile app development.
Ability to view business intelligence content.
Office Web Apps. Ability to view Word, Excel, and PowerPoint documents.
5. Records Management
Site-level retention policies. Ability to create and manage retention policies in SharePoint Server 2013 that apply to SharePoint sites and any associated Exchange Server 2013 team mailboxes.
6. Business Intelligence
In-Memory BI Engine (IMBI) or Vertipaq engine. Near instant analysis of millions of rows.
Power View Add-in for Excel. Visualize and interact with modeled data via visualizations, animations, and smart querying.
PivotChart reports. Create them without having to include a PivotTable report on the same page.
Ability to explore and analyze data in Excel Services reports. For reports that use SQL Server Analysis Services data or PowerPivot data models.
View and display items in PivotChart and PivotTable reports. Support for users in Excel Services to view and change display of items in Excel Services-published PivotChart reports and PivotTable reports.
Calculate measures and members. Support for Excel-created calculated measures and members in Excel Services.
Timeline controls. Improved Excel Services timeline controls.
Dashboard migration. PerformancePoint Services dashboard migration.
PerformancePoint Services filters. Enhanced PerformancePoint Services filter UI and filter search.
Cleaner BI Center.
Support for Analysis Services Effective User.
PerformancePoint support on Apple iPad.
Visio Services Maximum Cache Size.
Updated Visio Health Analyzer rules.
Windows PowerShell cmdlets. Updated PowerShell cmdlets for Visio.
Visio commenting. Ability to add comments to a Visio drawing on the web in full page rendering mode.
7. Social Computing
New and updated policy settings. For the User Profile service application and My Sites in Central Administration.
Privacy and people. New privacy settings and updated people settings.
Microblogging. New microblogging ability on Newsfeed page in My Site.
My Sites. Improved My Sites saving, synchronization, sharing, and moving of content.
New site templates. Community Site and Community Portal. Community Site offers a forum-like experience. Community Portal is a page that surfaces SharePoint site collections and sites.
8. Web Content Management
Word to HTML. Ability to copy content from Word, paste it into a Web Part, and obtain an HTML-correct display.
Drag and drop. Ability to drag and drop menu items directly to a page.
Video upload. Improved video upload process.
Dynamic content. Ability to insert an iframe element to embed dynamic content from other sites.
Support for image renditions. Allows display of different-sized versions of an image on different pages.
Integrated translation service.
Language detection. Ability to redirect visitors to a site in an appropriate language based on the language setting of their web browser.
Cross-site publishing. When you make changes to content, those changes are displayed on all site collections that are reusing this content.
Catalog. Designate any library or list as a catalog. Enables content to be reused on publishing site collections.
Managed navigation. Ability to define and maintain navigation on a site by using term sets, in addition to site structure-based navigation.
Category pages. Page layouts that are used for displaying structured content such as catalog data.
User-friendly URLs.
New Web Part. Content Search Web Part displays crawled and indexed content.
Refiners and faceted navigation. Enables users to refine and narrow searches while browsing different pages.
New analytics processing component. Ability to analyze user actions for content managers. Ability to make recommendations and offer choices to users.
Branding changes. SharePoint Designer or Visual Studio knowledge no longer necessary. Can design a site by using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, in tools such as Adobe Dreamweaver, Microsoft Expression Web, or other HTML editors.
Device-specific publishing. Ability to create channels that allow a single publishing site to be rendered in multiple ways on multiple devices.
9. Workflow
New SharePoint Designer 2013 workflow functionality includes the following:
Visual workflow. Develop workflow visually using Visio 2013 add-in.
No-code web service calls. New action enables no-code web service calls from within a workflow.
Task actions. New actions for creating a task and starting a task process
Coordination actions. New coordination actions between workflows built on SharePoint 2010 and SharePoint 2013
New dictionary type.
Stage, Loop, and App Step workflow building blocks.
New enterprise features in Workflow Manager.
New PowerShell cmdlets. Cmdlets that manage workflow via Workflow Manager service.
10. Search
Search UI improvements.
Search result relevancy improvements.
Continuous crawl.
Improved flexibility of search schema.
New search architecture.
Major Features of Sharepoint 2013 Standard
- App Deployment : Cloud-hosted apps for SharePoint include at least one remote component and may also include SharePoint-hosted components.
- Custom Site Definitions : Not available to SharePoint Online customers. SharePoint Server 2013 customers can create their own site definitions that customize and extend standard SharePoint site templates.
- SharePoint Design Manager : The Design Manager enables a step-by-step approach for creating design assets that you can use to brand sites. Upload design assets—images, HTML, CSS and so on—and then create your master pages and page layouts.
- Client Object Model : SharePoint 2013 has three client object models for managed code: .NET, Silverlight and mobile. In addition, SharePoint includes a JavaScript client object model
- Remote Event Receiver : To handle events in an app for SharePoint, developers can create remote event receivers and app event receivers. Remote event receivers handle events that occur to an item in the app, such as a list, a list item, or a web.
- Access Services : Build web databases and publish them to a SharePoint site. SharePoint visitors can use your database application in a web browser by using SharePoint permissions to determine who can see what. And you can start with a template so that you can start collaborating immediately.
- App Management Services : The App Management Service database stores licensing information for all of the apps for SharePoint.
- Browser-based customizations : You can customize your site without any special tools or coding expertise just by using the site settings. For example, you can change the look, title and logo, change the navigation links, change the contents of a page, or change the appearance of views for lists and libraries.
- Client Object Model (OM) : SharePoint 2013 has three client object models for managed code: .NET, Silverlight and mobile. In addition, SharePoint includes a JavaScript client object model.
- Custom Site Provisioning Page : Not available to SharePoint Online customers. SharePoint Server 2013 customers get a quick and easy way for users to make their site requests and to start using their sites quickly.
- Developer Site : Use an Office 365 Developer Site as a development and testing environment to shorten your setup time and start creating, testing and deploying your apps for SharePoint.
- Forms Based Applications : A form view is basically a view that contains controls. A Forms Based Application lets the user create and use one or more forms within the application.
- List and Library APIs : SharePoint provides APIs for accessing list and library data in the server object model, managed and JavaScript client object models and the REST web service.
- REST API : SharePoint 2013 provides an implementation of a Representational State Transfer (REST) web service that uses the OData protocol to perform CRUD operations on SharePoint list data. Use this when you must access SharePoint data from client technologies that do not use JavaScript and are not built on the .NET Framework or Microsoft Silverlight platforms.
- Sandboxed Solutions : A sandboxed solution, compared to a farm solution, enables site collection administrators to install custom solutions in SharePoint Foundation 2013 without the involvement of a higher-level administrator.
- SharePoint Design Manager : The Design Manager enables a step-by-step approach for creating design assets that you can use to brand sites. Upload design assets—images, HTML, CSS and so on—and then create your master pages and page layouts.
AWS
Installation Instructions for Windows
Step 1) RDP Connection: To connect to the deployed instance, Please follow Instructions to Connect to Windows instance on AWS Cloud
Connect to virtual machine using following RDP credentials :
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 3389
Username: To connect to the operating system, use RDP and the username is Administrator.
Password : Please Click here to know how to get password .
Step 2) Application Access Instructions:-
Note: Users need to reach out to us for CAL license providing number of CAL required.
If you face any issue in running this image or activating license, Please reach out to support@secureanycloud.com.
- Sharepoint Server has already been installed.
- Sharepoint configuration should be completed by the user.
- Please join a domain and have a SQL Server instance ready before starting the Sharepoint Configuration.
1. Default Login Credentials for SharePoint Access are same as your RDP Credentials,
- User Name: Administrator
- Password: Retrieved from Console
Step 3) Other Information:
1.Default installation path: will be in your root folder “C:\Program Files\Common Files\microsoft shared\Web Server Extensions\15\BIN”
2.Default ports:
- Windows Machines: RDP Port – 3389
- Http: 80
- Https: 443
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link
Installation Step by Step Screenshots
Step 1. Open SharePoint 2013 Application using desktop icon
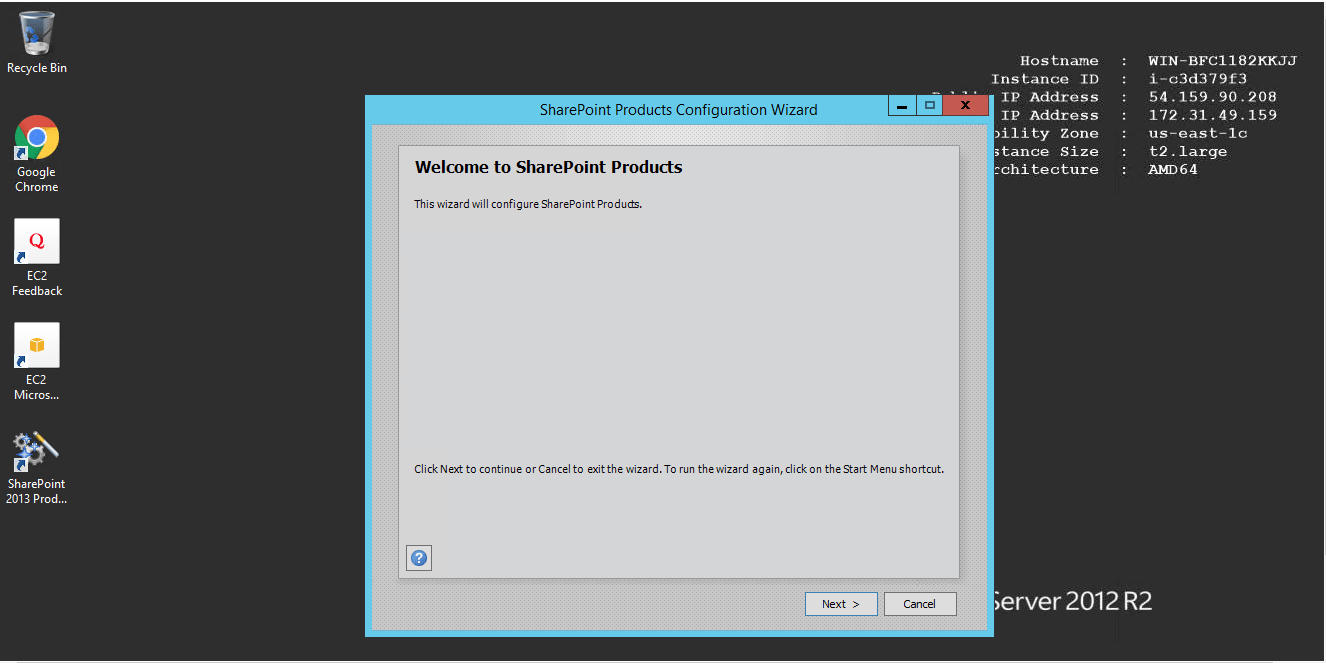
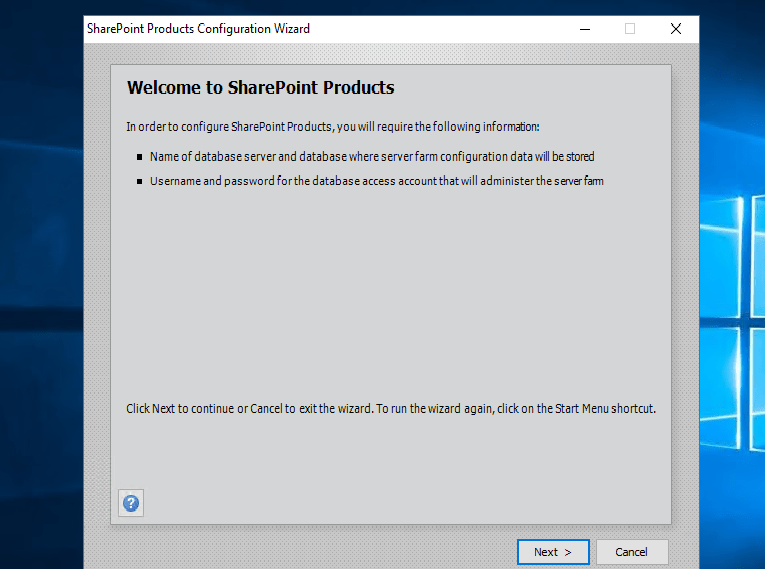
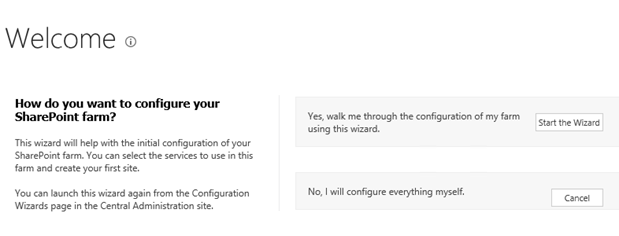
Step 2.Welcome Page sharepoint
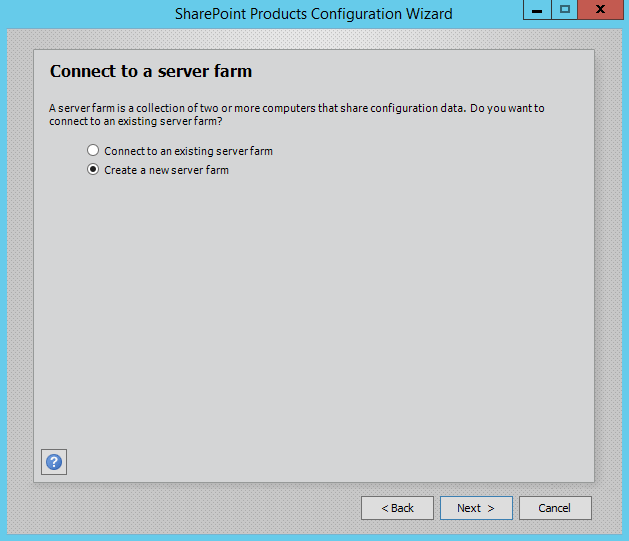
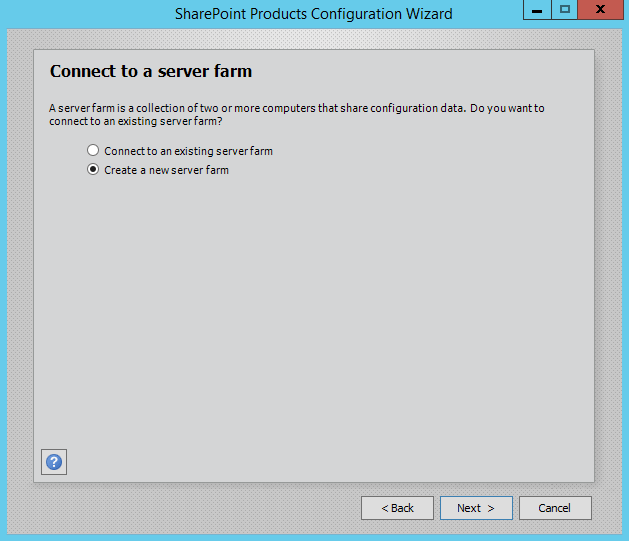
Step 3.Select Create a new server farm option from the next step as shown in below screen, if you are already have installed a new farm and doing a MinRole installation then select the first option to connect to an existing server farm.
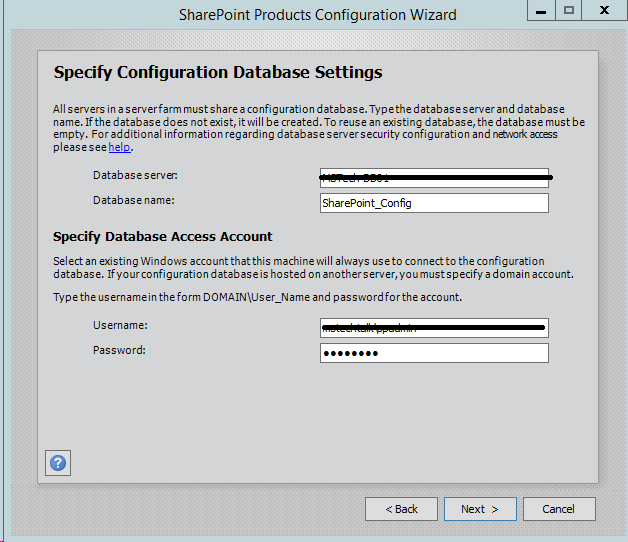
Step 4.Enter the database server details and database access account details, use a separate user for this but I am using the same SPAdmin user for the preview installation. I have assigned it below rights in DB server:
- Dbcreator
- SecurityAdmin
- SysAdmin
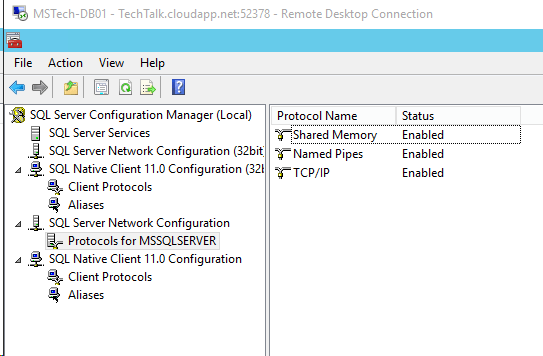
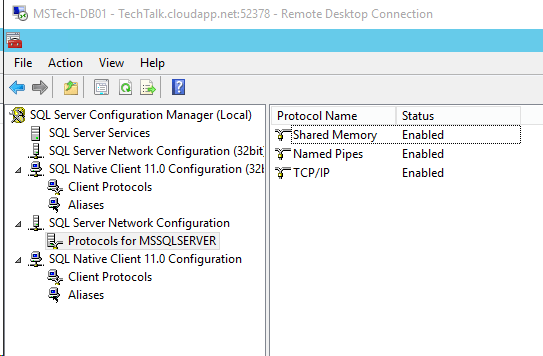
Step 5.If you are facing issues in connecting to SQL Server then make sure TCP/IP is enabled in SQL Server Configuration Manager. If you still getting the error then turn off the firewall on SQL server machine.
Step 6. After completing the database settings, press next which will take to you on Farm security settings page. Enter passphrase here which is required to secure the farm configuration data and is required for each server that joins the farm.
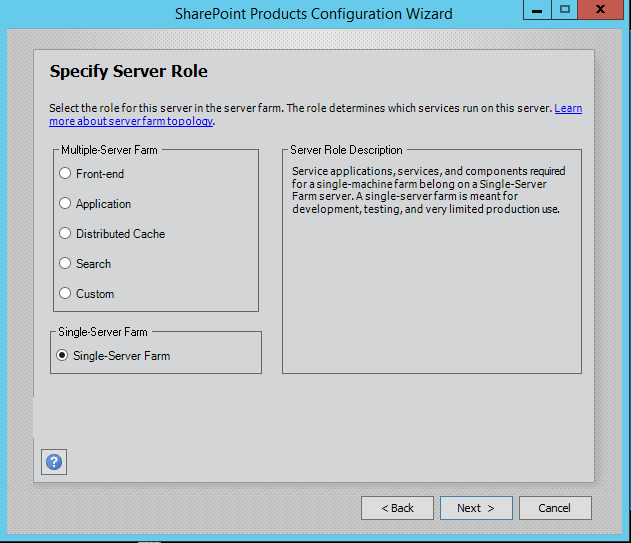
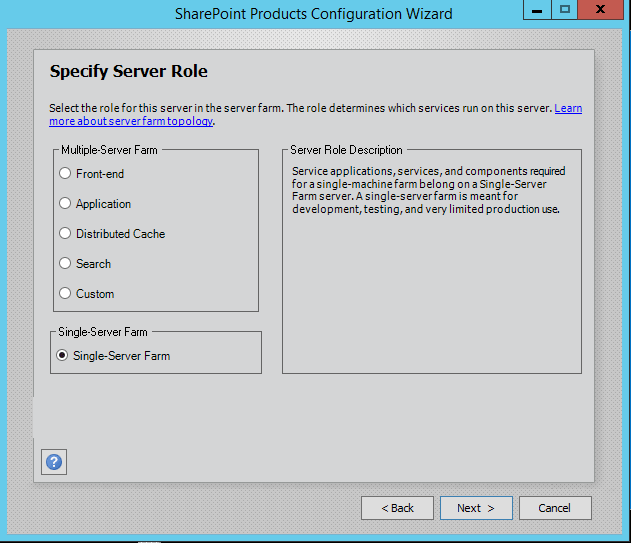
Step 7. Server Roles or the MinRoletopology
Here comes the MinRoles, SharePoint Server 2013 has six types of server roles:
- Front-end
- Application
- Distributed Cache
- Search
- Custom
- Single-Server Farm
You can either select single-server farm or can do a multi-server installation using MinRolestopology. If you have selected Single-Server Farm then you cannot extend to Multi-Server environment, so if you plan to extend to multi-Server farm in future then select the Custom MinRole or Application.
I am using single-server farm installation so will go with the last option.
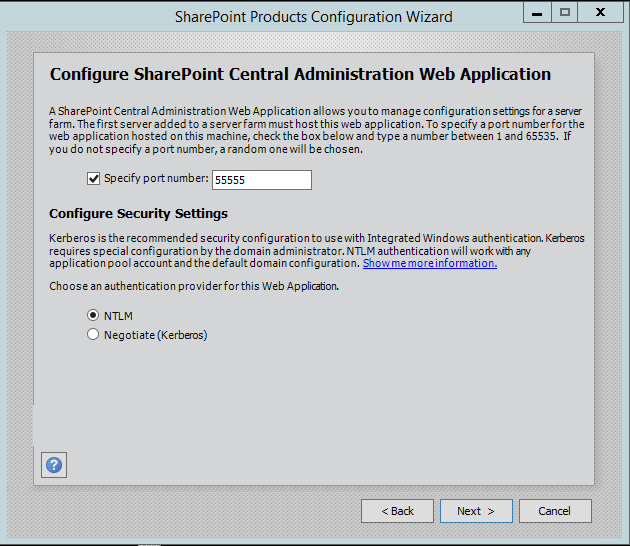
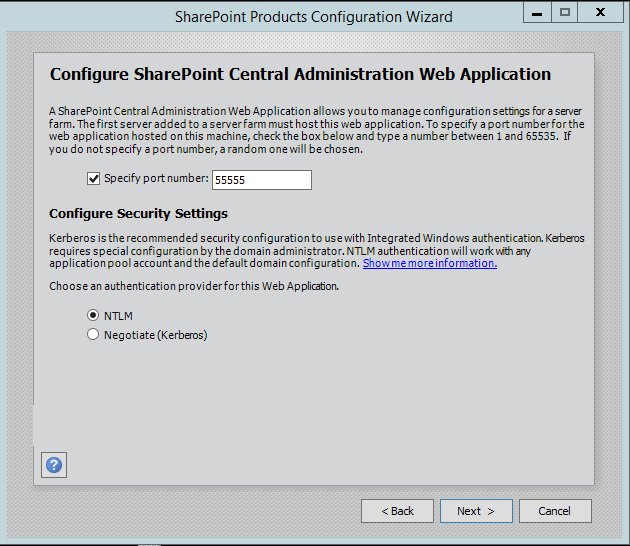
Step 8.On next screen, you can specify port for Central Admin or can use the default which is selected randomly. I have never used the default port, I always an easy one which I can remember like 5555. Select NTLM installation mode at this phase and press next.
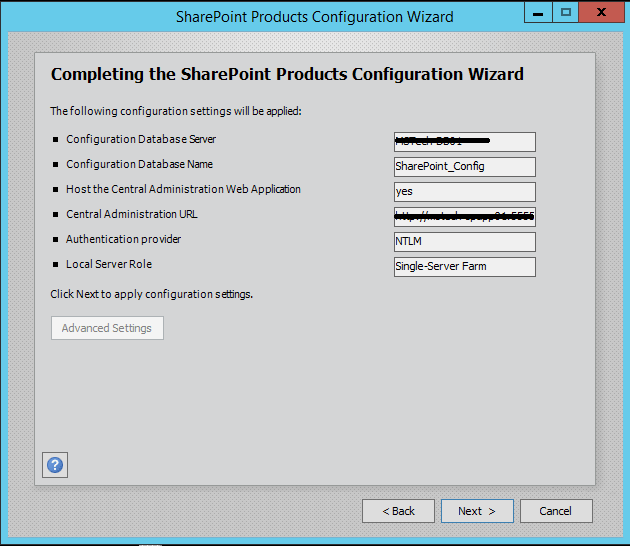
Step 9. Verify the settings in configuration wizard, press next to start the wizard. Advance option is not enabled for Single-Server installation.
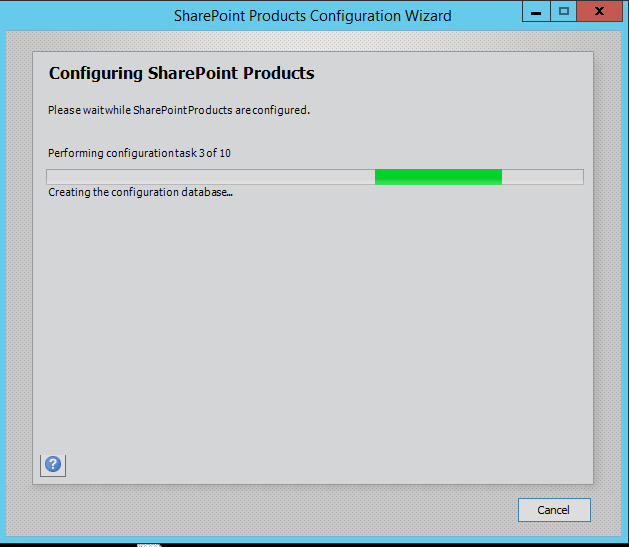
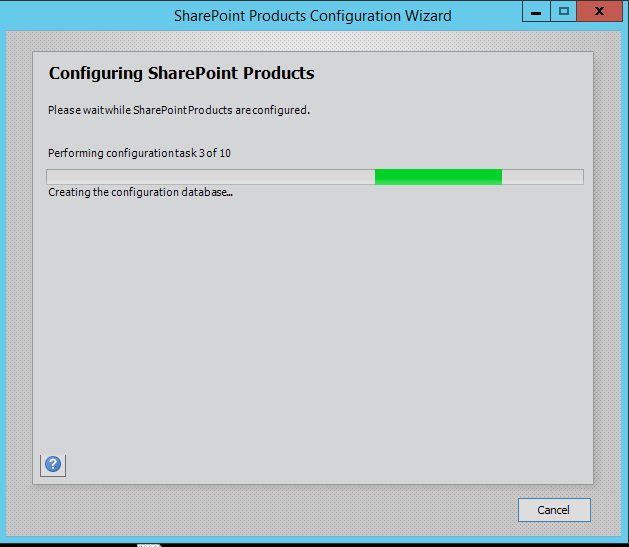
Step 10. Press Next button, it will start the configuration of SharePoint farm. This is similar to what we do in past with MOSS 2007, SharePoint 2010 and SharePoint 2013 or even with SharePoint Foundation which is no more part of SharePoint 2016.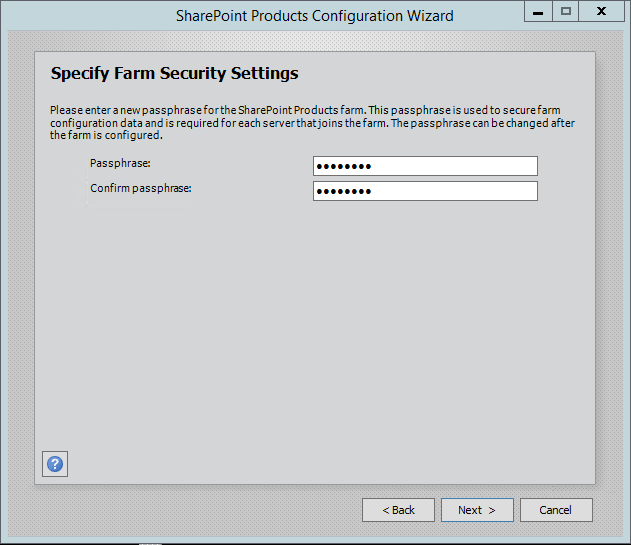
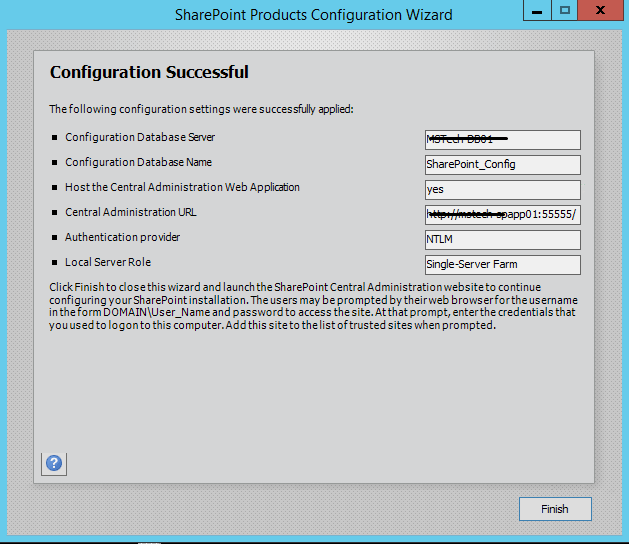
Step 11. The wizard can take some time and if you get some errors then you have to verify the roles of the user in SQL Server.
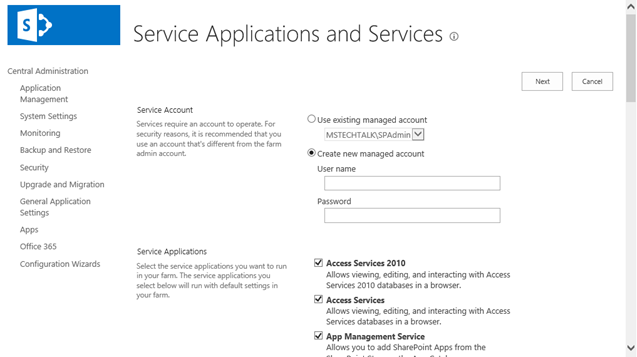
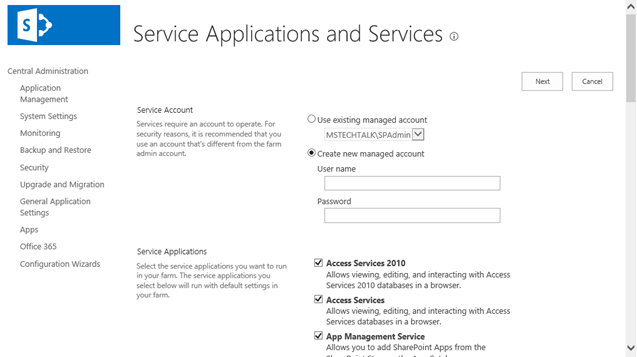
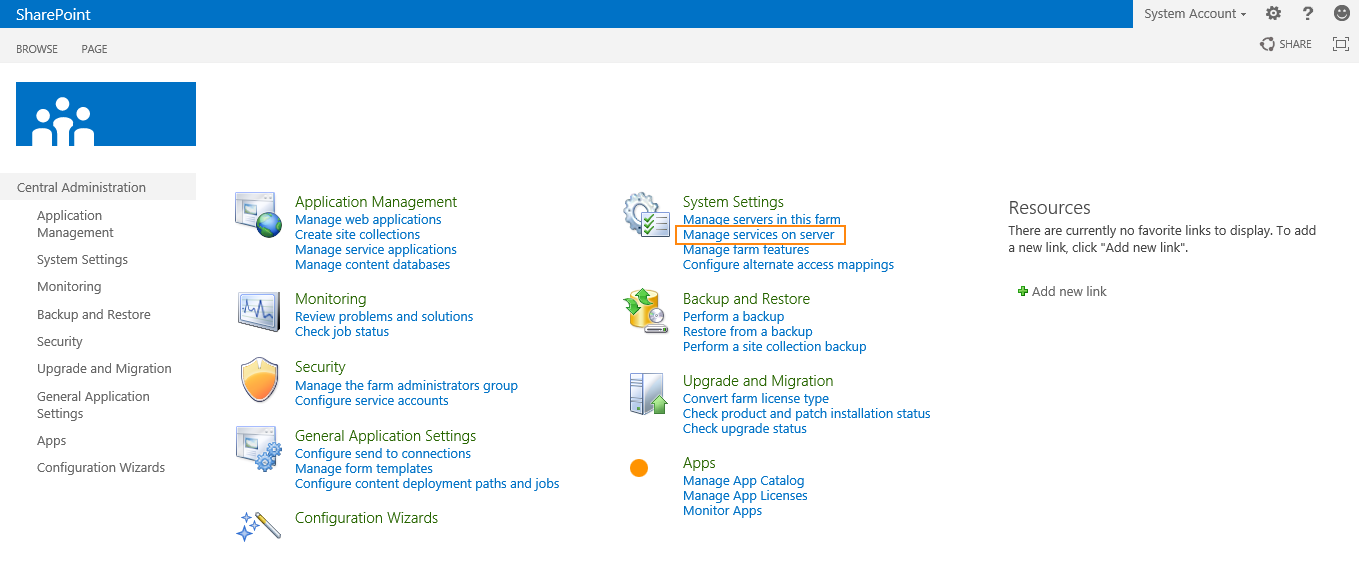
Step 12. After the installation, run the services wizard from Central Administration, setup will take you to the service configuration wizard page, you can either configure them through wizard and can also configure them manually.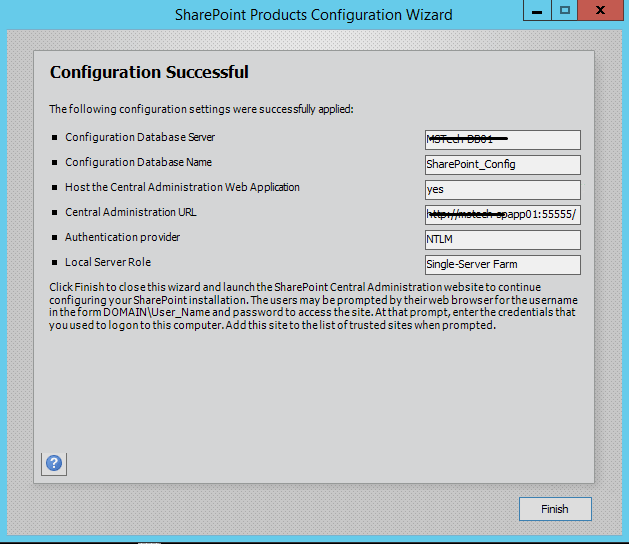
Step 13.As this is test environment, so I will prefer configuring services using wizard. We can define a separate account for services but I am using the same SharePoint Admin account for all services.
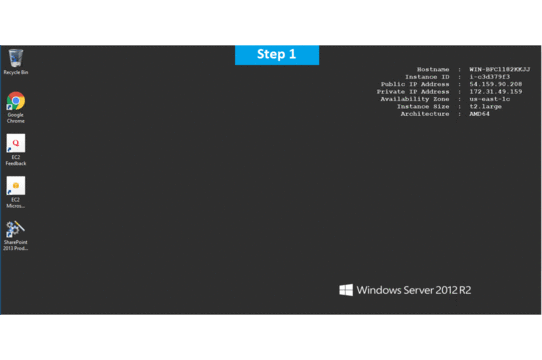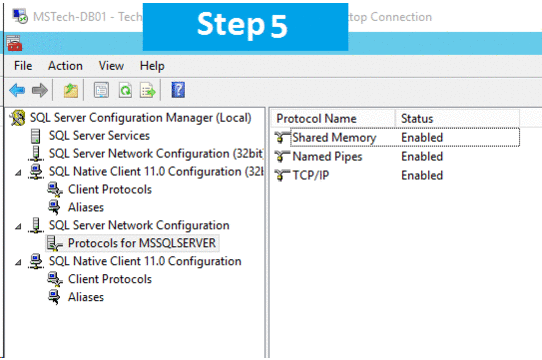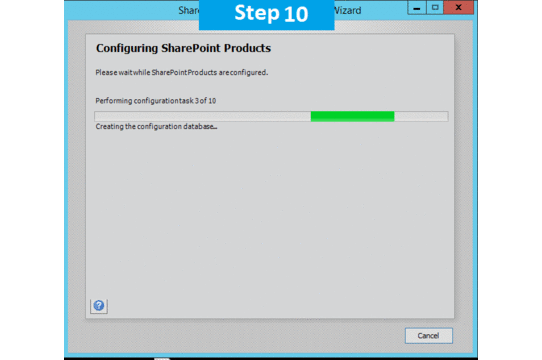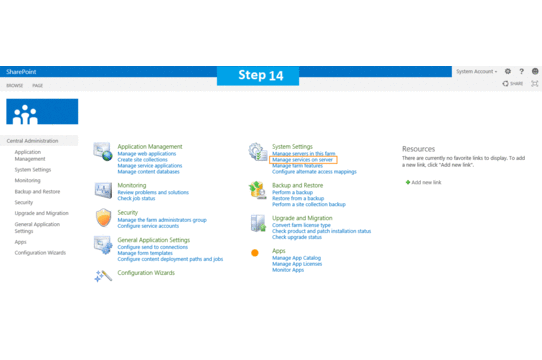
Step 14.This will complete the services wizard for me and now I am ready to explore SharePoint.
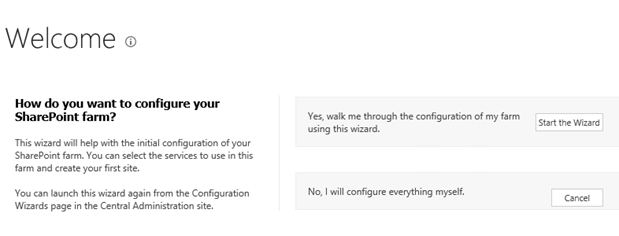
Installation Instructions for Windows
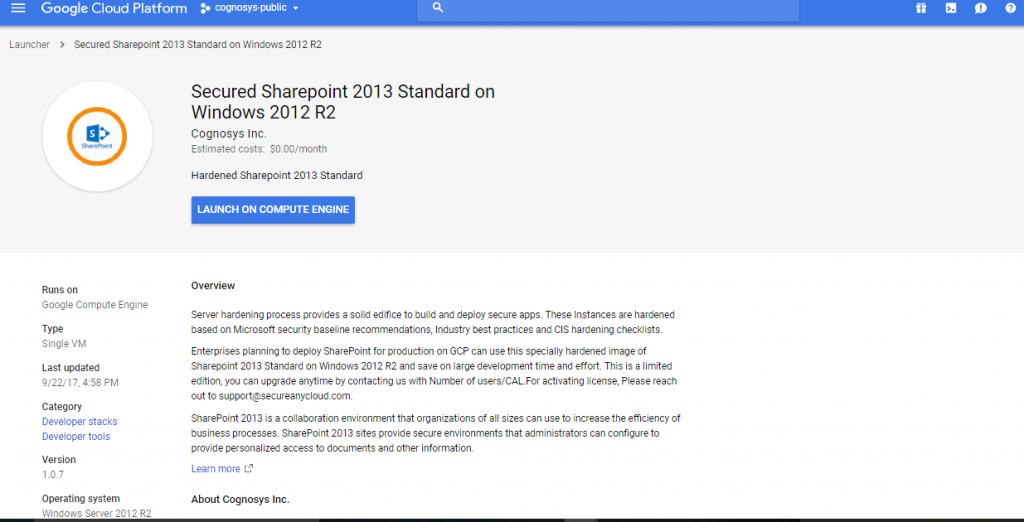
Step 1) VM Creation:
- Click the Launch on Compute Engine button to choose the hardware and network settings.
2. You can see at this page, an overview of Cognosys Image as well as some estimated costs of VM.
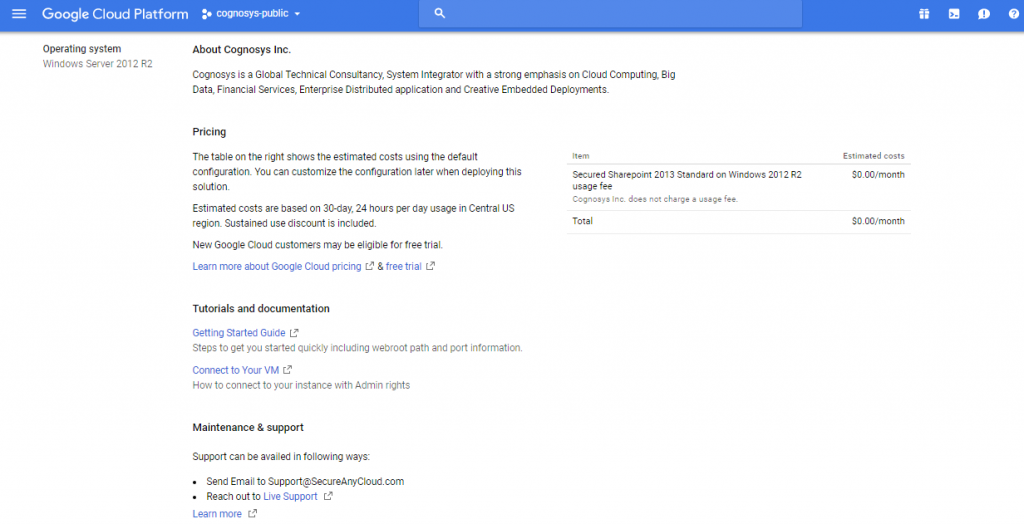 3.In the settings page, you can choose the number of CPUs and amount of RAM, the disk size and type etc.
3.In the settings page, you can choose the number of CPUs and amount of RAM, the disk size and type etc.
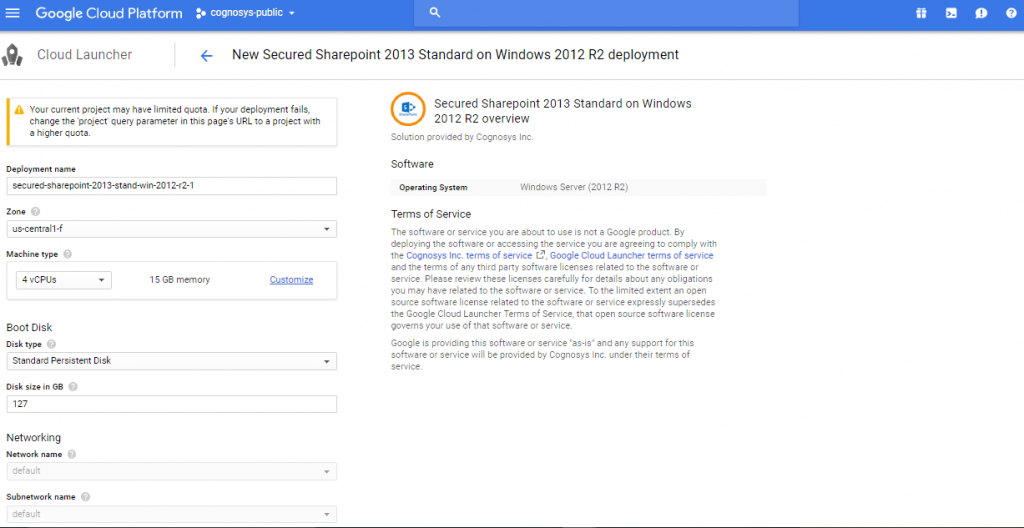 Step 2) Application Access Instructions:-
Step 2) Application Access Instructions:-
Click the Windows “Start” button and select “All Programs” and search for Sharepoint
Step 3) Other Information:
1.Default ports:
- Windows Machines: RDP Port – 3389
- Http: 80
- Https: 443
Installation Step by Step Screenshots
Step 1. Join the Computer to Active Directory and with Domain login open SharePoint Product Configuration
Step 2.Welcome Page SharePoint
Step 3.Select Create a new server farm option from the next step as shown in below screen if you are already have installed a new farm and doing a MinRole installation then select the first option to connect to an existing server farm.
Step 4.Enter the database server details and database access account details, use a separate user for this but I am using the same SPAdmin user for the preview installation. I have assigned it below rights in DB server:
- Dbcreator
- SecurityAdmin
- SysAdmin
Step 5.If you are facing issues in connecting to SQL Server then make sure TCP/IP is enabled in SQL Server Configuration Manager. If you still getting the error then turn off the firewall on SQL server machine.
Step 6. After completing the database settings, press next which will take to you on Farm security settings page. Enter passphrase here which is required to secure the farm configuration data and is required for each server that joins the farm.
Step 7. Server Roles or the MinRoletopology
Here comes the MinRoles, SharePoint Server 2016 has six types of server roles:
- Front-end
- Application
- Distributed Cache
- Search
- Custom
- Single-Server Farm
You can either select single-server farm or can do a multi-server installation using MinRolestopology. If you have selected Single-Server Farm then you cannot extend to Multi-Server environment, so if you plan to extend to multi-Server farm in future then select the Custom MinRole or Application.
I am using single-server farm installation so will go with the last option.
Step 8.On next screen, you can specify the port for Central Admin or can use the default which is selected randomly. I have never used the default port, I always use an easy one which I can remember like 5555. Select NTLM installation mode at this phase and press next.
Step 9. Verify the settings in configuration wizard, press next to start the wizard. The advance option is not enabled for Single-Server installation.
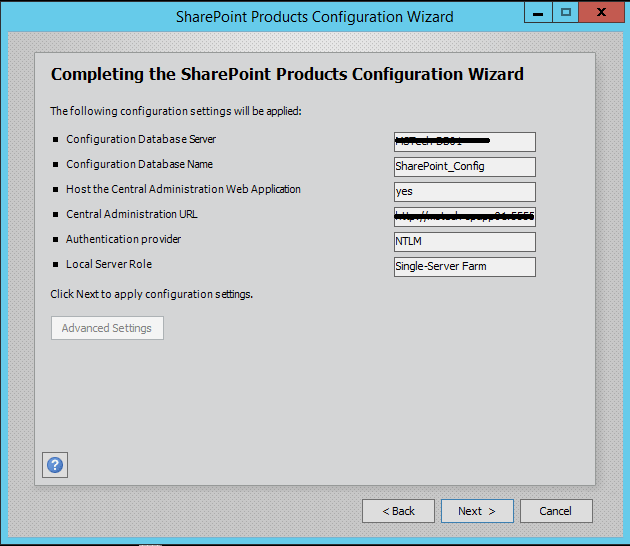
Step 10. Press Next button, it will start the configuration of SharePoint farm. This is similar to what we do in past with MOSS 2007, SharePoint 2010 and SharePoint 2013 or even with SharePoint Foundation which is no more part of SharePoint 2016.
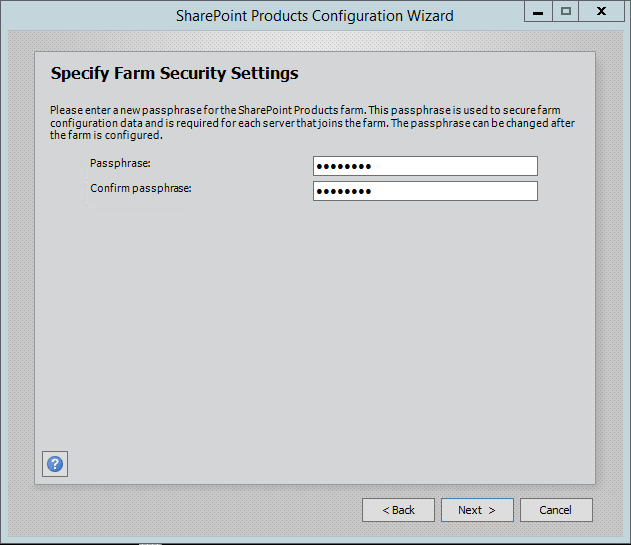
Step 11. The wizard can take some time and if you get some errors then you have to verify the roles of the user
Step 12. After the installation, run the services wizard from Central Administration, setup will take you to the service configuration wizard page, you can either configure them through the wizard or you can also configure them manually.
Step 13.As this is test environment, so I will prefer configuring services using the wizard. We can define a separate account for services but I am using the same SharePoint Admin account for all services.
Step 14.This will complete the services wizard for me and now I am ready to explore SharePoint.
Videos
Secured Sharepoint 2013 Standard on Windows 2012 R2