1-click AWS Deployment 1-click Azure Deployment
Overview
SQL Server is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft. It is widely used for storing, managing, and retrieving data in various applications and systems. SQL Server supports the Structured Query Language (SQL) for managing databases and offers a range of features for data storage, manipulation, and analysis.
Here are some key aspects and features of SQL Server:
- Data Storage: SQL Server allows you to create and manage databases, tables, and other database objects to store your data efficiently. It supports different data types, such as integers, strings, dates, and binary data.
- Data Retrieval and Manipulation: SQL Server provides a comprehensive set of SQL statements for querying and modifying data. You can use SELECT statements to retrieve data from tables, and UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE statements to modify the data.
- Transaction Management: SQL Server supports transactions to ensure data integrity and consistency. You can group multiple database operations into a single transaction and ensure that they either all succeed or all fail.
- Security: SQL Server offers various security features to protect your data. You can define user roles and permissions to control access to the database objects. It also provides encryption capabilities for securing sensitive data.
- Scalability and Performance: SQL Server is designed to handle large amounts of data and support high-performance applications. It offers features like indexing, query optimization, and partitioning to enhance performance and scalability.
- High Availability: SQL Server provides features for ensuring high availability of your databases. It supports database mirroring, failover clustering, and Always On Availability Groups for maintaining database availability in case of hardware or software failures.
- Business Intelligence: SQL Server includes tools and features for business intelligence and data analysis. It supports data warehousing, reporting, and integration with other Microsoft BI tools like Power BI.
- Integration Services: SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) is a powerful ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool that allows you to integrate data from various sources, perform transformations, and load data into SQL Server databases.
- Analysis Services: SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) enables online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining capabilities. It allows you to create multidimensional data models and perform complex analysis on large datasets.
- Reporting Services: SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) is a reporting platform that enables the creation, management, and delivery of paginated and interactive reports.
SQL Server has different editions, including the Enterprise, Standard, and Express editions, each with varying features and limitations. It also integrates with other Microsoft technologies and development tools, making it a popular choice for building applications that require a robust and scalable database backend.
Main Editions of SQL Server
- Enterprise Edition: This edition provides the most comprehensive set of features and capabilities for large-scale enterprise deployments. It includes advanced features like high availability, online transaction processing (OLTP), data warehousing, advanced analytics, and business intelligence. Enterprise Edition is suitable for mission-critical applications that require maximum performance, scalability, and high availability.
- Standard Edition: Standard Edition is designed for smaller to medium-sized businesses. It offers a basic set of database management features, including core database engine functionality, security features, and basic business intelligence capabilities. While it lacks some of the advanced features found in the Enterprise Edition, it still provides reliable performance and scalability for most common database applications.
- Express Edition: Express Edition is a free, lightweight version of SQL Server. It has limitations on database size (10 GB maximum per database) and hardware utilization (limited to a single processor and 1 GB of RAM). Express Edition is suitable for small-scale applications or development and testing purposes.
- Developer Edition: Developer Edition has the same features as the Enterprise Edition but is licensed for development and testing purposes only. It provides all the functionalities of the Enterprise Edition, making it an excellent choice for developers and development teams to build and test applications without the cost of the Enterprise license.
- Web Edition: Web Edition is specifically designed for hosting websites and web applications. It offers the necessary database management features for web-based workloads at a lower cost compared to other editions. Web Edition has limitations on CPU utilization and memory usage and is licensed based on the number of cores used by the server.
- Business Intelligence Edition: This edition is tailored for business intelligence and data warehousing scenarios. It includes features like advanced analytics, data integration, and reporting capabilities. Business Intelligence Edition provides a cost-effective solution for organizations focused on data analysis and reporting.
Key Components / Services of SQL Server
- Database Engine: The Database Engine is the core component responsible for storing, processing, and managing data. It includes the SQL Server Database Services, which handle query processing, data storage, and transaction management.
- SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS): SSMS is a graphical user interface (GUI) tool used for administering and managing SQL Server. It allows database administrators and developers to perform tasks such as creating databases, writing queries, managing security, and monitoring server performance.
- Integration Services (SSIS): Integration Services is an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool that enables data integration and workflow management. It provides a platform for building and managing data integration solutions, including data extraction, transformation, and loading processes.
- Analysis Services (SSAS): Analysis Services is a component of SQL Server used for creating and managing online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining solutions. It allows users to build multidimensional data models and perform complex analysis on large datasets.
- Reporting Services (SSRS): Reporting Services is a server-based reporting platform that enables the creation, management, and delivery of paginated reports, interactive reports, and mobile reports. It provides a wide range of reporting capabilities and supports data-driven subscriptions and report distribution.
- Full-Text Search: Full-Text Search is a service that enables advanced text-based search capabilities in SQL Server. It allows users to perform complex searches on text and unstructured data stored in the database and retrieve relevant results efficiently.
- Machine Learning Services (formerly R Services): Machine Learning Services integrate the R and Python programming languages into SQL Server. It allows users to run machine learning and data analytics algorithms directly within the database engine, leveraging the power of SQL Server for scalable and high-performance analytics.
- Replication: Replication is a feature that enables data synchronization and distribution across multiple SQL Server instances. It allows you to replicate data from one database to another, maintaining consistency between multiple copies of the database.
- Always On Availability Groups: Always On Availability Groups is a high-availability and disaster recovery feature that provides database-level redundancy and failover capabilities. It allows you to create groups of databases that can failover to a secondary replica in case of a primary replica failure.
- Security and Authentication: SQL Server provides robust security features to protect data. It includes mechanisms for authentication, authorization, and encryption to ensure data privacy and prevent unauthorized access to the database.
SQL Server Instances
SQL Server instances play a crucial role in the efficient and organized management of databases. Here are some key reasons highlighting the importance of SQL Server instances:
- Database Isolation: SQL Server instances allow for the isolation of databases and their resources. Each instance functions as a separate and independent environment, enabling multiple databases to run concurrently on the same server without interfering with one another. This isolation ensures better resource allocation, performance optimization, and simplified management.
- Security and Access Control: Instances provide a boundary for security and access control. Each instance can have its own authentication, authorization, and security settings, allowing administrators to define and enforce fine-grained access controls for specific databases within an organization. This enhances data security and mitigates the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Resource Allocation and Management: Instances enable efficient utilization and allocation of server resources. By segregating databases into separate instances, administrators can allocate resources such as CPU, memory, and disk I/O according to the specific requirements of each instance. This ensures optimal performance and prevents resource contention between different databases.
- Version and Patching Flexibility: Instances allow flexibility in managing different versions and patch levels of SQL Server. Organizations may have multiple applications or databases that rely on specific SQL Server versions or require different patch levels due to compatibility or stability reasons. Instances provide a means to maintain and manage these diverse environments effectively.
- Application and Service Isolation: Instances enable the isolation of applications or services that rely on SQL Server. By deploying different instances for different applications or services, administrators can ensure that changes or issues in one application or service do not affect others. This isolation enhances the stability and reliability of applications and services running on SQL Server.
- Scalability and Performance: Instances offer scalability options to handle growing database workloads. Administrators can add additional instances or distribute databases across multiple instances to distribute the load and improve performance. This scalability approach allows organizations to accommodate increased data volumes, user concurrency, and processing requirements.
- High Availability and Disaster Recovery: Instances are instrumental in implementing high availability and disaster recovery solutions. Organizations can configure instances as primary and secondary replicas in an availability group or configure database mirroring between instances. This ensures continuous availability of critical databases and minimizes downtime in the event of a failure.
- Application Testing and Development: Instances provide a dedicated environment for application testing and development. Developers can have separate instances to work on new features, test database changes, or experiment without affecting the production environment. This isolation facilitates a controlled and independent testing and development process.
Operation and SQL Server Architecture
We have two types of servers such as the OLTP server(OnLine Transactional Processing) which allows us to write transactional queries(exemple: SELECT “colonne1, colonne2 …, n” FROM “table” WHERE “condition1, condition2,. ., n)on the one hand and on the other hand we have the OLAP server (OnLine Analytical Processing) which a decisional server or a Datawarehouse. In other words, it’s thanks to the OLAP serevr it can be possible to make business intelligence(create multidimensional cubes,make report…)
MS SQL Server contains several software that run as services or have graphical interfaces or are accessible through a command line. MS SQL Server is composed of 5 main services such as:
- TSQL SERVER : It’s the database engine service that corresponds to a SQL Server instance. This component runs as a Windows service and is named as MSSQLSERVER for a default instance and MSSQLSERVER$instanceName for a named instance. An instance name is defined when installing a new instance
- SSIS (Sql Server Integration Service) : It’s the tool for Importing and exporting data,transfering and transforming data.It includes wizards for creating ETL (Extraction Transformation Loading).
- SSAS(Sql Server Analysis Service) : It’s the right component for making decisional projects. This component is an OLAP analysis tool and Microsoft’s Data Mining tool for building OLAP Cube.
- SSRS (Sql Server Reporting Service) : It’s thanks to this component it possible to return our data coming from our Datawarehouse in a form report (table, chart etc …), dashboard, on various support and easily understood by third persons.This component also makes it possible to create interactive, tabular, graphical reports from XML, relational, or multidimensional data sources
- Agent SQL :In charge of SQL Serve monitoring, this component also manages the execution of scheduled tasks and the monitoring of alerts. It runs as a Windows service and is directly linked to a SQL Server instance. It is referenced by default in the Windows Service Manager as SQL Server Agent and by SQL Server Agent (instance name) in the case of a named instance.
[] To this list of main components we can add others such as:
- Microsoft Full Text Search : Manages the indexing of text documents and word-based searches
- CLR : It permit you to develop stored procedures and functions using C# and VB.NET
- Composant de Replication de données : Allows the data to be positioned closer to the users and to reduce processing times. The replication is the duplication of data from one server to another server for the purpose of spreading the workload between the two server
We can find different tools in MS SQL SERVER such as:
- SQL Server Management Studio to Allow you performing all operations at the Database Engine level
- SQL Server Configuration Manager to Manage All Services Related to SQL Server
- SQL Server Profiler to track and analyze the workload of a SQL Server instance
- The Database Engine Tuning Wizard allows for optimizing the operation of the Database Engine
- The SqlCmd tool is used to execute approved queries, execute Command scripts, establish a dedicated administration connection (DAC)
SQL Server Login Database
SQL Server login database is a simple creadential which is used to access SQL Server.
What is credential?
Credentials are simply a username and a password that you provide your username and password when logging on to Windows or even your e-mail account. This username and password builds up the credentials.
There are four types of logins provided by SQL Server:
- A login based on Windows credentials.
- A login specific to SQL Server.
- A login mapped to a certificate.
- A login mapped to asymmetric key.
Logins based on Windows credentials facilitates you to log in to SQL Server using a Windows username and password. If you want to create your own credentials (username and password,) you can create a login specific to SQL Server.
To create, alter, or remove a SQL Server login, you can take one of two approaches:
- Using SQL Server Management Studio.
- Using T-SQL statements.
Using SQL Server Management Studio
Open SQL Server management studio
Go to Security:
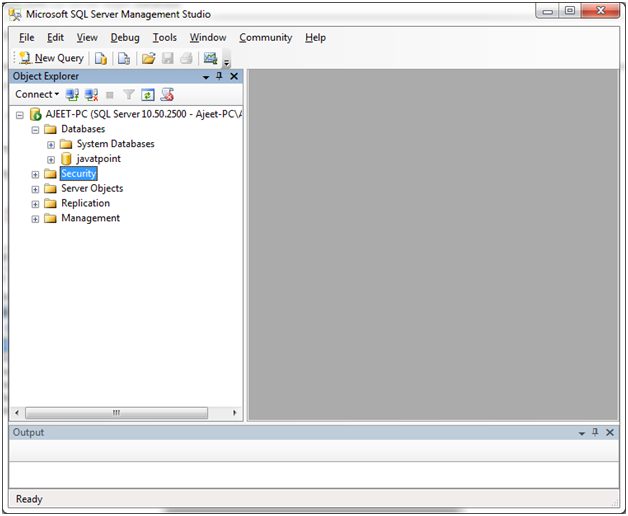
Open Security. You will see “Logins”. Right click on Logins and you will get “New Login”?
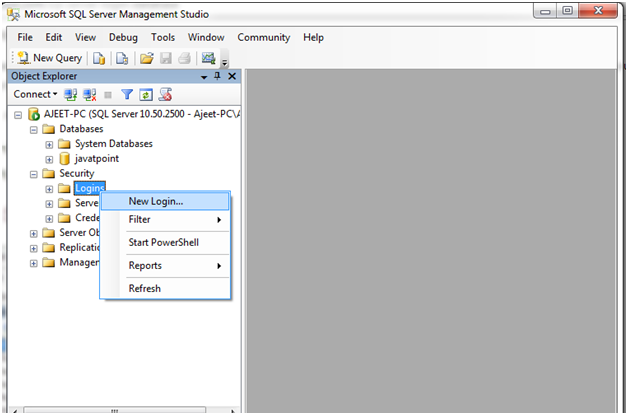
It will open a new page:
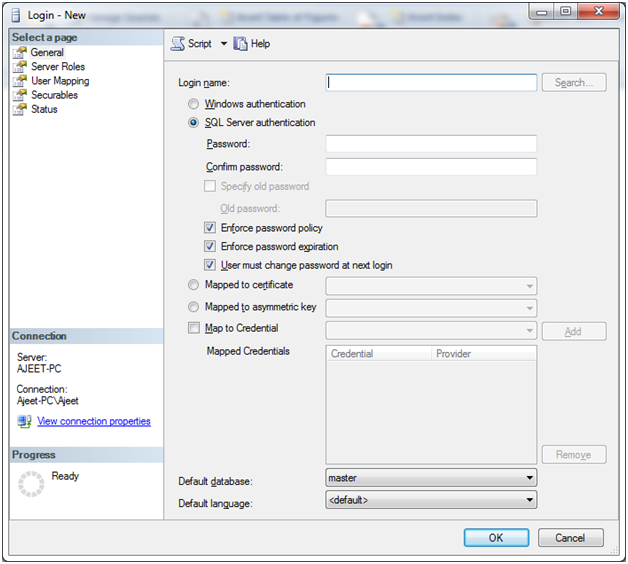
Here you can set a login name and password.
SQL Server Create Datatabase
In SQL Server, you have to create a database first before creating a table.
Go to SQL Server Management Studio. You will see a Database.
Right click on the databases and you will see new database. Create a new database.
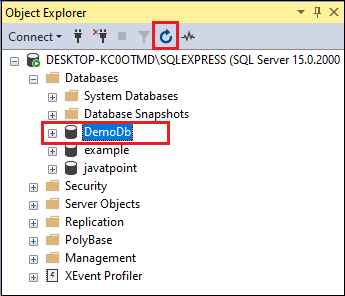
Name your database.
For example:
Create a database “javatpoint”.
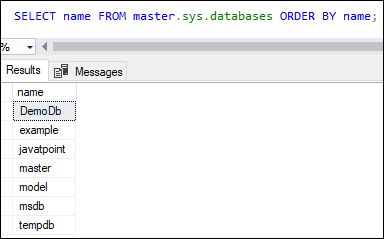
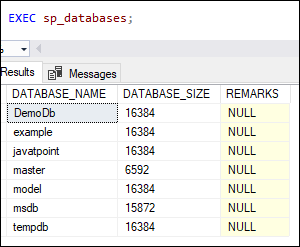
You can see that a database is created as “javatpoint”.
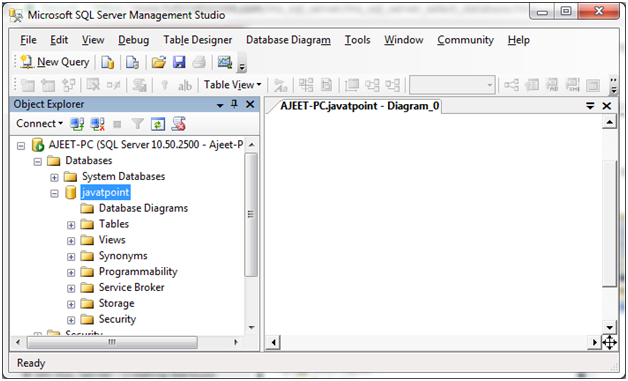
MS SQL Server Select Database
SQL Server select database specifies your database in which you want to create your table and further operations.
SQL Server Installation Prerequisites
For our SQL Server Installation steps, we will be first downloading the Developer edition
- Click on Download now and the downloading of will start

- • Once downloading is finished, the file will be available in the downloads folder, or in any folder you have specified, as SQLServer2017-SSCI-Dev
SQL Server Installation
- Click on the file SQLServer2017-SSCI-Dev, and you will find a window with three options: Basic, Custom, and Download Media

- Select Custom, as we want the Developer edition, and you will find a path for it below Media Location. You can either retain the default one or you can specify a customized path

- In the snapshot, the default path is retained as is in Media Location
- Once the path is selected, click on Install and the installation begins
- A message appears as Your SQL Server Installation will begin shortly… and you will find a pop-up screen of SQL Server Installation Center
How to Install SQL Server?
- A pop-up window, SQL Server Installation Center, appears and it contains two columns
- Select Installation from the left-side column, and once you select it, you will find multiple options on the right-side column

- Select the first option from the right-side column, which is New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation
- Wait for it to process and you will have a window SQL Server 2017 Setup in which click on Next

- Select Perform a new installation of SQL Server 2017 and click on Next
- Select the free edition from Specify a free edition and click on Next
- Accept the license terms
- The display screen takes you to the features of the SQL Server 2017
- There are many options available, but in this blog we will be selecting Database Engine Services
- Click on Next

- The next setup is the Instance Configuration
- Give the details in Named instance and Instance ID fields and click on Next
- Here in the snapshot, I have given the Name instance as SPARATA and the same appears for the Instance ID

- The Server Configuration screen is displayed in which click on Next
- Now on the screen, you will find two authentication modes
- Windows authentication mode
- Mix Mode
- Select the Mix mode and enter the desired password and confirm the password
- Select the user by clicking on Add Current User, and the current user has been added now
- Click on Next
- Once the Current User is added, the SQL Server is ready to install
- Now, click on Next and the installation process takes place
- Once the installation process is completed, you’re back to SQL Server Installation Center

Now, you will also have to install the SQL Server Management Tools; this tool will help you connect with the database.
- Click on Install SQL Server Management Tools and it will redirect you to Microsoft web page
- Download the latest version of SQL Server Management Studio and you will find the downloaded file in your folder as SSMS-Setup-ENU

- Click on the file and install the studio
- Once the installation is completed, search for Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
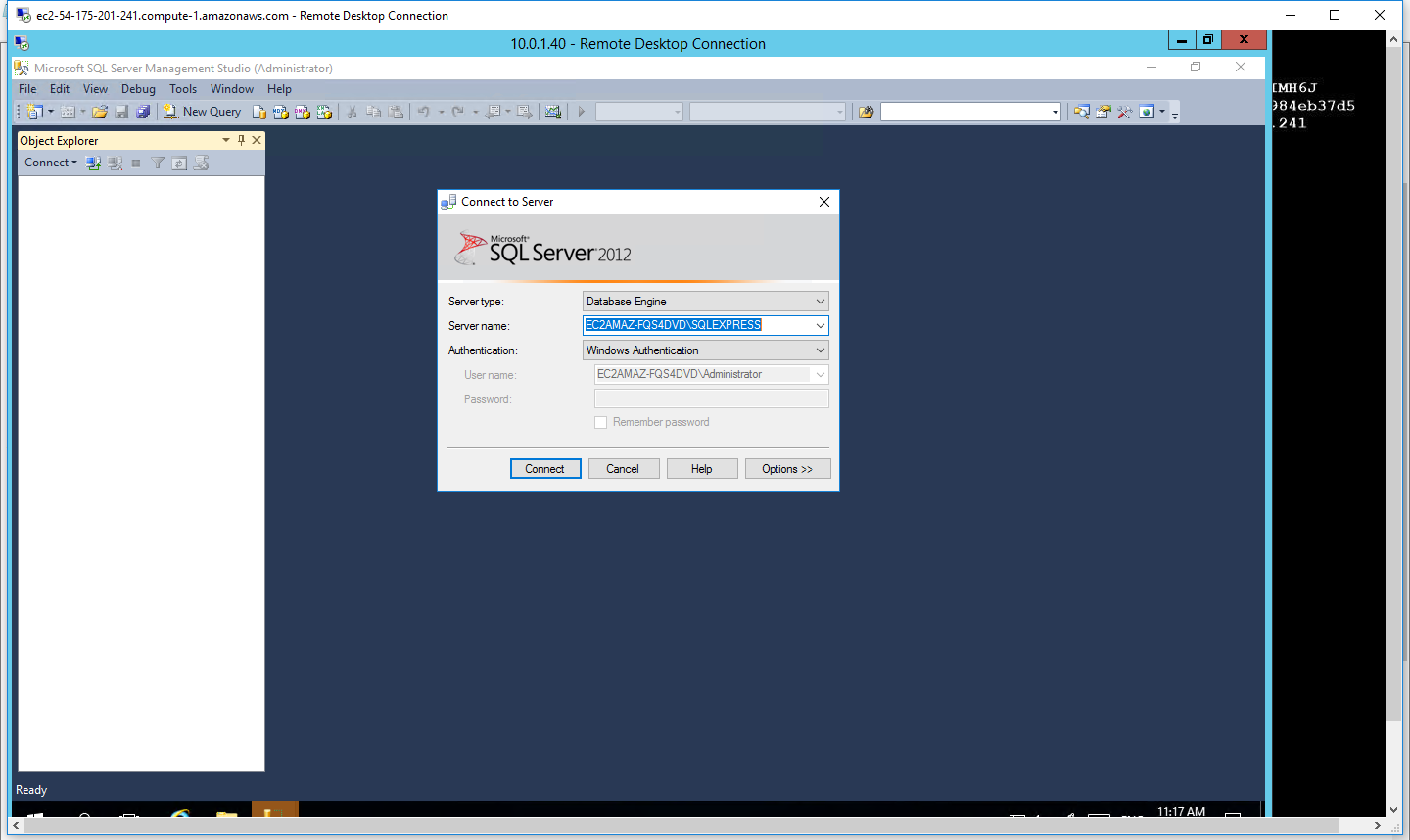
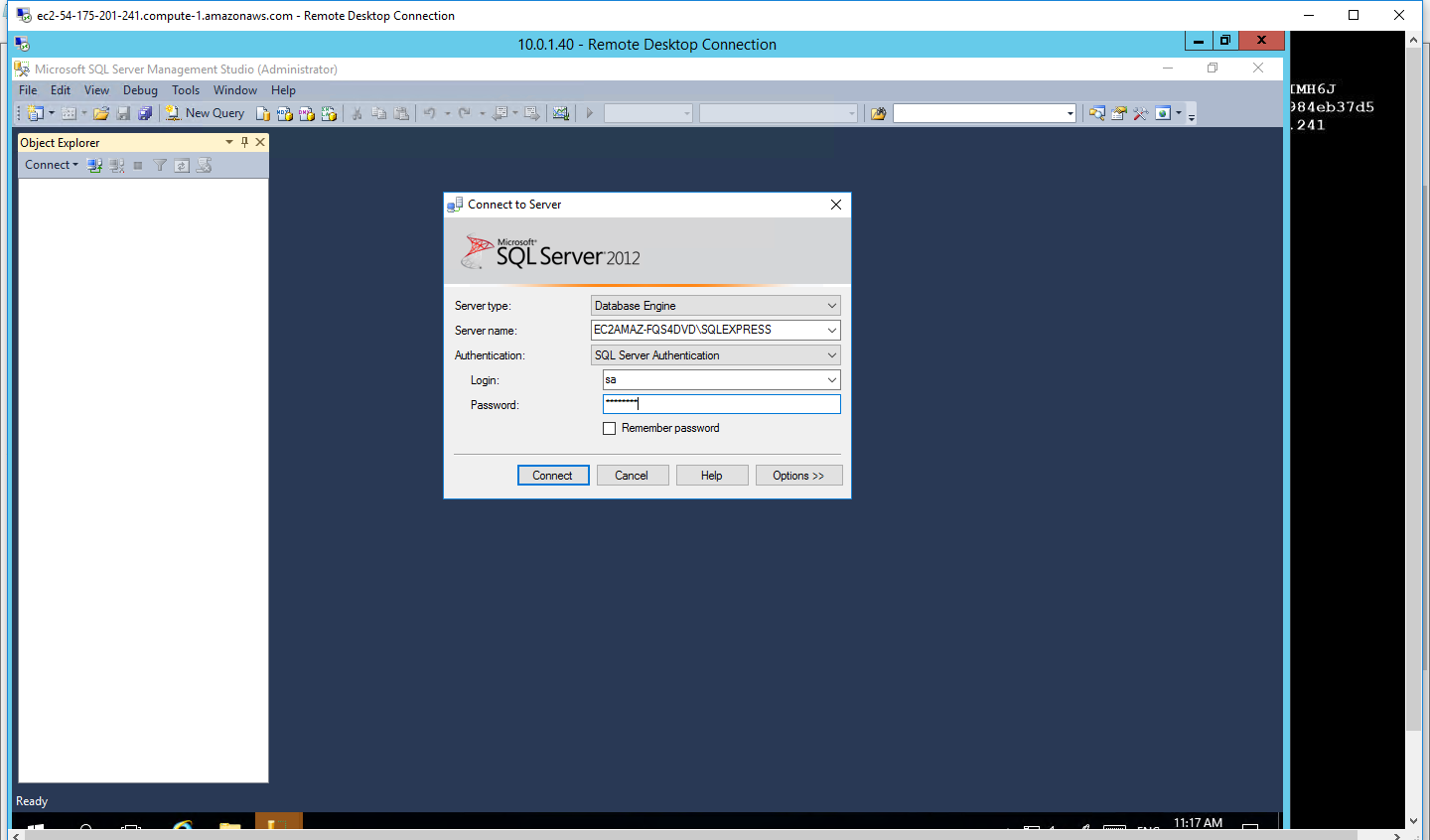
- The SQL Server Management Studio is launched, and you will find a pop up, Connect to Server
- Enter the password which you had entered before with Login as sa and click on Connect

—Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Express is a powerful and reliable free data management system that delivers a rich and reliable data store for lightweight Web Sites and desktop applications. Microsoft SQL Server 2012 is a relational database management system (RDBMS) designed for the enterprise environment. Like its predecessors, SQL Server 2012 comprises a set of programming extensions to enhance the Structured Query Language (SQL), a standard interactive and programming language for getting information from and updating a database.SQL Server 2012’s new features and enhancements include
Always On SQL Server Fail-over Cluster Instances and Availability Groups which provides a set of options to improve database availability, Contained Databases which simplify the moving of databases between instances, new and modified Dynamic Management Views and Functions, programmability enhancements including new spatial features,metadata discovery, sequence objects and the THROW statement, performance enhancements such as Column Store Indexes as well as improvements to OnLine and partition level operations and security enhancements including provisioning during setup, new permissions, improved role management, and default schema assignment for groups.
Features
There are the following features of SQL:
High speed
Using the SQL queries, the user can quickly and efficiently retrieve a large amount of records from a database.
No coding needed
In the standard SQL, it is very easy to manage the database system. It doesn’t require a substantial amount of code to manage the database system.
Well defined standards
Long established are used by the SQL databases that are being used by ISO and ANSI.
Portability
SQL can be used in laptop, PCs, server and even some mobile phones.
Interactive language
SQL is a domain language used to communicate with the database. It is also used to receive answers to the complex questions in seconds.
Multiple data view
Using the SQL language, the users can make different views of the database structure.
Microsoft SQL Server 2019 New Features
Big Data Clusters
The latest version of SQL Server simplifies big data analytics for users. It combines Apache Spark and HDFS (Hadoop Distributed Filing System) and provides one integrated system. The new SQL server allows you to build “Big Data Clusters” using a blend of SQL Server and Apache Spark containers over Kubernetes utilizing SQL Server’s current PolyBase features. With the help of local Kubernetes, which is supported by public clouds, you’ll be able to deploy Big Data Clusters on AWS, on Azure, on GCP, and also on your own infrastructure.
Always On Availability Groups
For the first time, Always On Availability Groups were introduced in SQL Server 2012. Since then, Microsoft has made some improvements to this feature in each new release. In the same way, in SQL Server 2019, has made improvements to the high availability and disaster recovery feature. In the new version, the Always On Availability Group can have 5 synchronous replicas (1 primary copy and 4 secondary ones) for failover purposes, whereas there were 3 limitations in previous SQL Server 2017.
One of the great things about this feature is that it enables numerous duplicates of a database to be reproduced on different servers. SQL Server 2019 can redirect connections for customer applications from a secondary replica to the primary one. This means that a customer can be redirected to the primary replica without using the accessibility group listener, which is a virtual system name used to interface customers to databases in replicas.
UTF-8 Support
This feature provides significant storage savings. The new version supports the widely used UTF-8 encoding as an export or import encoding, or column-level or as a database-level grouping for text data. Thus, Unicode string data will take up much less storage space than the previous UTF-16.
UTF-8 is permitted in VARCHAR and CHAR and extends capabilities when creating or changing an object’s collation with UTF-8. And you can use the familiar CHAR data type rather than NCHAR, as CHAR requires only 10 bytes, whereas NCHAR requires 20 bytes for the same Unicode string data storage.
Resumable online index
The most exciting capabilities are related to indexing. Probably many database administrators face a terrible situation when an indexing operation goes wrong. Finally, SQL Server 2019 has come up with the new features to cope with these situations. When resumable online index is created, we can pause the indexing process and then resume from where we left off. We don’t need to start again from the very beginning.
New SQL Server 2019 supports the recovery of indexing failure. The process may fail due to many factors, such as after running out of disk space or after a database failure. You can resume the indexing process, once you have corrected the error that caused the index operation to crash without having to start over.
New SQL Server 2019 also reduces the amount of log space required when you create a large index, compared to the previous SQL Server 2017.
Additionally, SQL Server 2019 has a new feature for online conversion of conventional row storage tables to columnstore indexes. In the previous SQL Server 2017, such conversions could only be performed offline. But, with the latest version of SQL Server 2019 and Azure SQL Database, we can create or re-create Creating clustered columnstore indexes (CCI) online.
Intelligent Query Processing
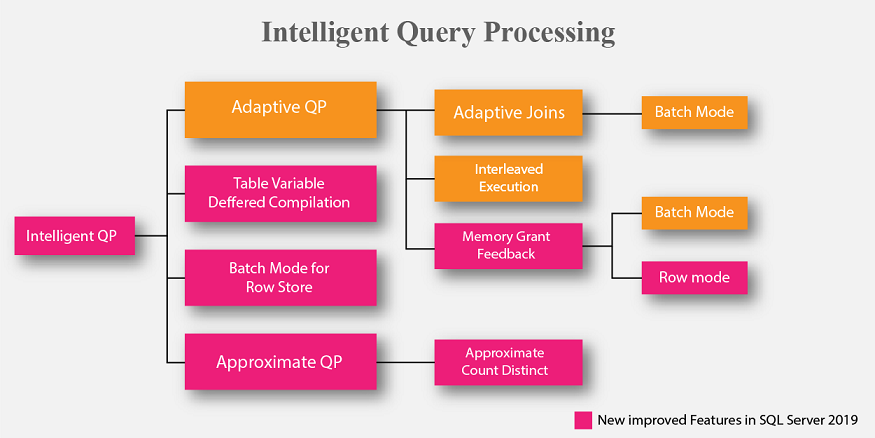
The new Intelligent Query Processing suite is developed to fix some of the common query execution issues by adopting some automatic corrective strategies at runtime. It uses feedback data insights gathered from past executions. Microsoft has also started leveraging some of these features in Azure SQL DB and plans to keep expanding this region for SQL Server 2019. The image above shows the new and improved areas in the Intelligent Query Processing features.
Added features for SQL Server on Linux
Microsoft has added plenty of new features to its Linux edition. Perhaps the most exciting update is support for data replication which enables you to build distributed SQL databases effectively, especially those related to the Linux version of the Distributed Transaction Coordinator.
Another significant expansion of the Linux version is the ability to set up Always On Availability Groups in Docker containers arranged with Kubernetes. Additionally, for Linux, Microsoft makes certified container images available and places all of its windows and container images for SQL Server 2019 and SQL Server 2017 into the Microsoft Container Registry.
Another significant added feature – SQL Server 2019 on Linux supports OpenLDAP. It is an open source form of the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. Although OpenLDAP can work autonomously of Microsoft’s Active Directory, the new support for OpenLDAP allows Linux-based SQL Server databases to join Active Directory.
In addition, another important part of SQL Server 2019, Microsoft has included integrated tools for building and testing machine-learning models on Linux. Thus, it enables SQL Server on Linux users to run machine learning applications written in Python and R languages.
Master Data Services (MDS)
Silverlight controls are replaced with HTML: Silverlight support for MDS portal is no longer needed. HTML controls will now perform the same function.
Security
The new version has come up with advanced security support. It encrypts the data using secure enclave technology. Certificate management is now integrated into the SQL Server Configuration Manager. A widely used SSL/TLS certificates are integrated to secure access to SQL Server instances.
-Major Features of SQL Server :
- New storage features—Column-store indexes, File-table storage.
- New Transact-SQL (T-SQL) constructs—Sequence objects, THROW statement, new conversion, logical, string, and date and time functions, and adhoc query paging.
- New scalability and performance features—Indirect checkpoints, FORCESCAN table hint, number of table partitions increased to 15,000.
- New security features—Database Audit, user-defined server roles, contained databases.
- New availability features—A number of high-availability enhancements known as AlwaysOn, which include AlwaysOn Availability Groups and AlwaysOn Failover Cluster Instances.
- Statistical Semantic Search—Statistical Semantic Search builds upon the existing full-text search feature in SQL Server by querying the contextual meaning of terms within a document repository.
- Data Quality Services—This new feature allows you to build a knowledge base of data rules and use those to perform a variety of critical data quality tasks, including correction, enrichment, standardization, and de-duplication of your data.
AWS
Installation Instructions for Windows
A) Click the Windows “Start” button and select “All Programs” and then point to SQL Server
B) RDP Connection: To connect to the operating system,
1) Connect to virtual machine using following RDP credentials :
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 3389
Username: To connect to the operating system, use RDP and the username is Administrator.
Password : Please Click here to know how to get password .
C) Other Information:
1.Default ports:
- Windows Machines: RDP Port – 3389
- Http: 80
- Https: 443
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link
AWS Step by Step Screenshots
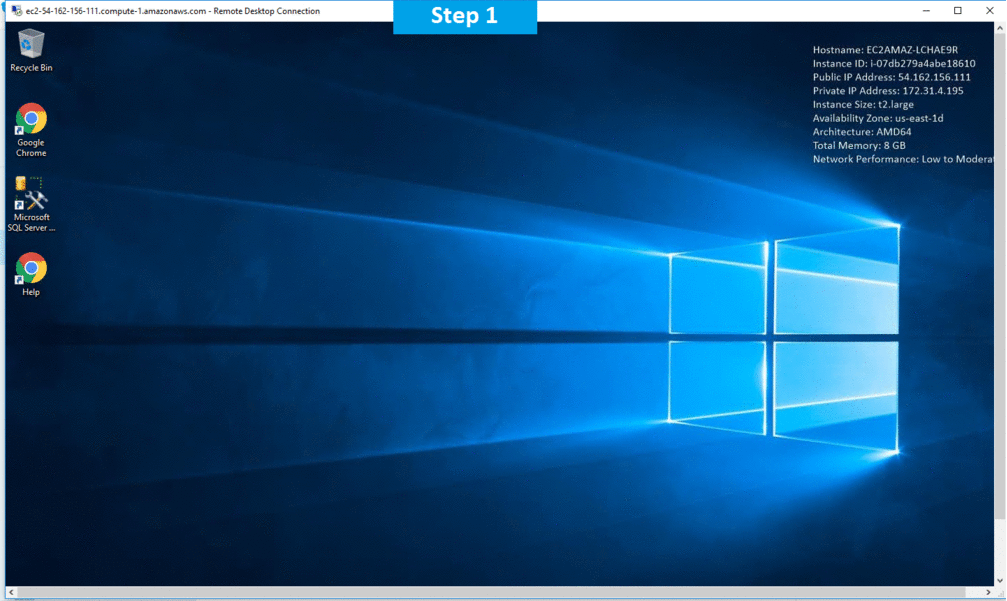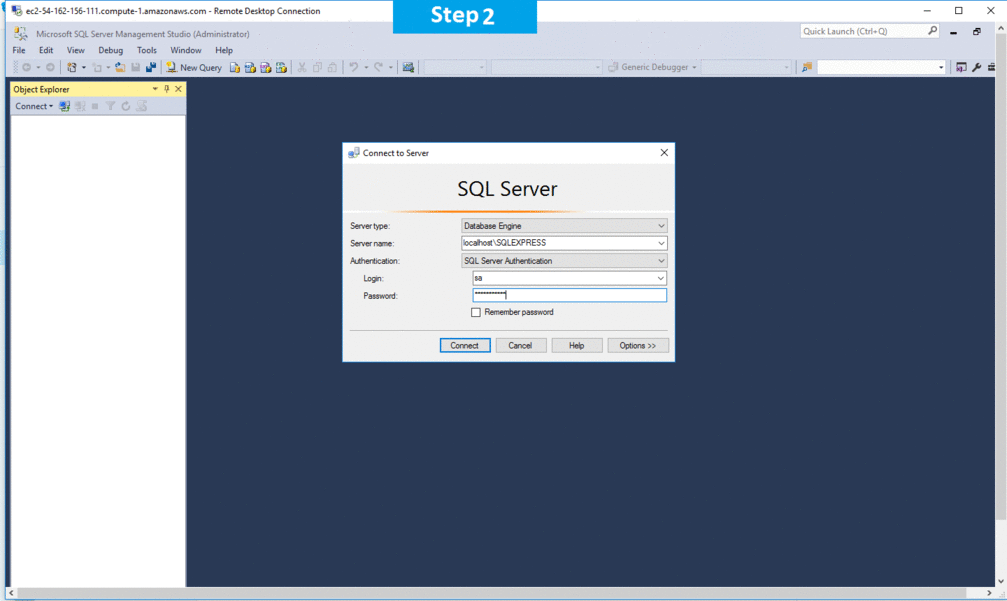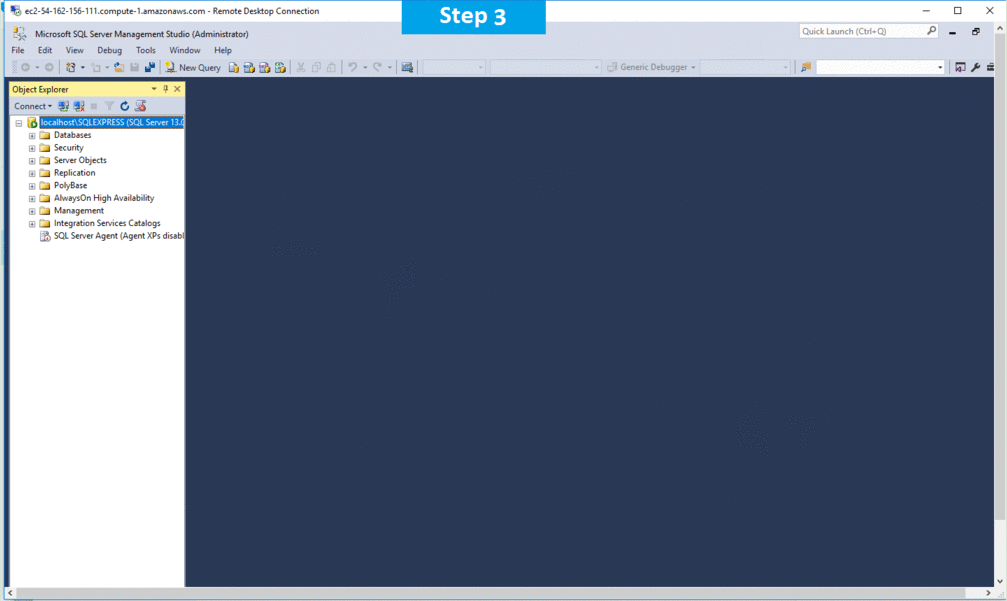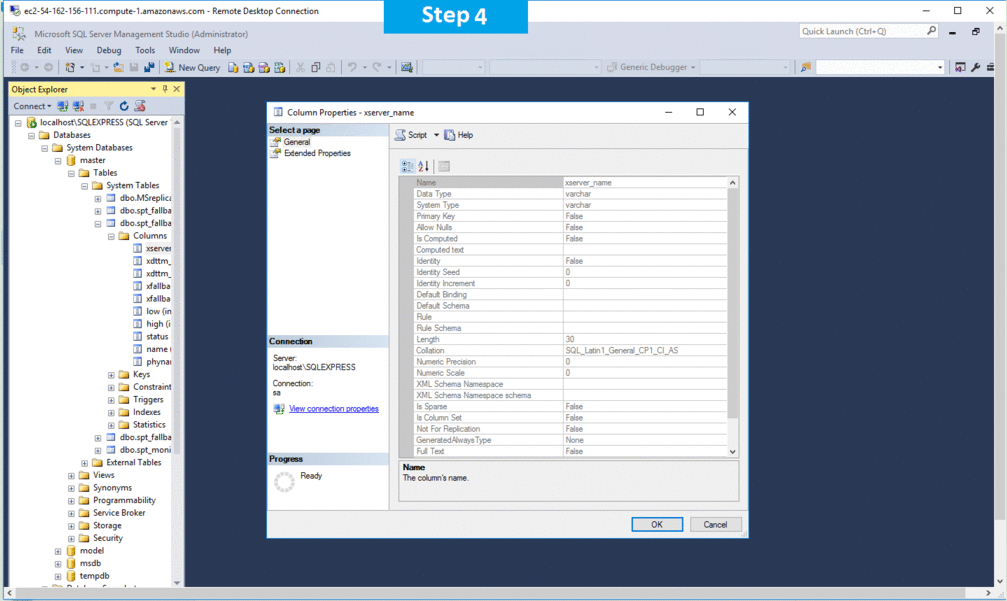
Azure
Installation Instructions for Windows
A) Click the Windows “Start” button and select “All Programs” and then point to SQL Server
B) RDP Connection: To connect to the operating system,
1) Connect to virtual machine using following RDP credentials :
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 3389
Username: Your chosen username when you created the machine ( For example: Azureuser)
Password : Your Chosen Password when you created the machine ( How to reset the password if you do not remember)
C) Other Information:
1.Default ports:
- Windows Machines: RDP Port – 3389
- Http: 80
- Https: 443
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link
Azure Step By Step Screenshots
Videos