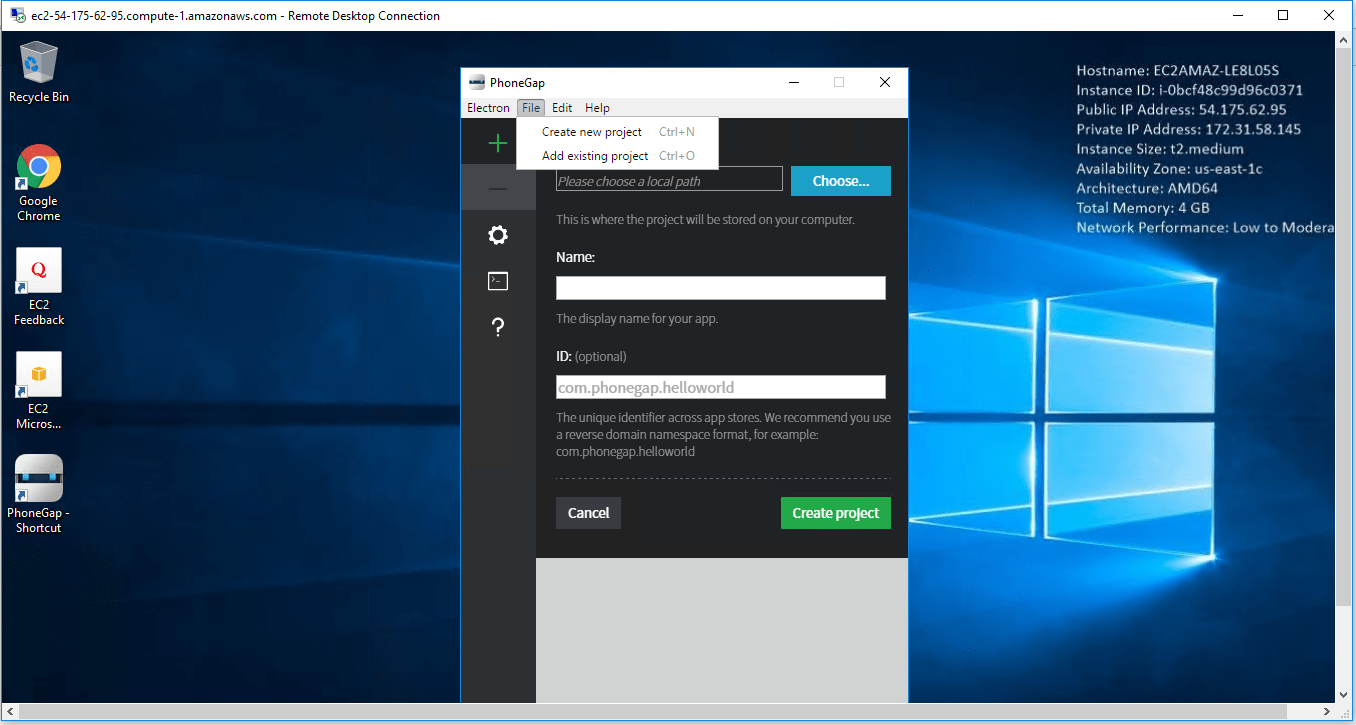
1-click AWS Deployment 1-click Azure Deployment
Overview
Building applications for each platform–iPhone, Android, Windows and more–requires different frameworks and languages. PhoneGap solves this by using standards-based web technologies to bridge web applications and mobile devices. Since PhoneGap apps are standards compliant, they’re future-proofed to work with browsers as they evolve. Read an in-depth post explaining PhoneGap visually.
PhoneGap has been downloaded millions of times and is being used by hundreds of thousands of developers. Thousands of apps built using PhoneGap are available in mobile app stores and directories. Check out some of them here.
The PhoneGap code was contributed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under the name Apache Cordova and graduated to top-level project status in October 2012. Through the ASF, future PhoneGap development will ensure open stewardship of the project. It will always remain free and open source under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
Phonegap is owned by Phonegap(https://phonegap.com/) and they own all related trademarks and IP rights for this software.
Phonegap on Cloud runs on Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Azure and is built to provide a way for users to create mobile applications using technologies such as HTML, CSS and Javascript.
PhoneGap Tutorial
PhoneGap is a software development framework by Adobe System, which is used to develop mobile applications. To develop apps using PhoneGap, the developer does not require to have knowledge of mobile programming language but only web-development languages like, HTML, CSS, and JScript. PhoneGap produces apps for all popular mobile OS platforms such as iOS, Android, BlackBerry, and Windows Mobile OS etc. In this tutorial we will focus on developing App for Android platform. This tutorial will give you adequate information about how to produce apps quickly using PhoneGap services.
Audience
Programmers who want their website to be available on app either offline or online, may take advantage of this tutorial. This tutorial is designed to give a general view of App building using web technologies. Anybody who is interested to know how to develop Apps using web technologies may use this tutorial.
Prerequisites
It is mandatory that you have knowledge of HTML, CSS and JScript to create website that you might want to put on App. No other programming language is required to use PhoneGap.
Overview:
Mobile, handhelds and easy-to-carry devices have started a new revolution in software engineering. These small but efficient devices are capable to run applications created with high-end programming languages. People who own these devices tend to use them at their maximum as these devices such as mobile phones, are very convenient to use anytime, anywhere.
The architecture of a mobile device is similar to that of a computer system. It has custom built hardware, firmware, and operating systems.
These three items are mostly proprietary and are engineered, developed, and assembled under one flagship organization. Apps (Application Software) are developed both by flagship organization and developers from outside the organization.
A number of well-recognized mobile operating systems are available in the market in both proprietary and open-source categories. Most widely used mobile operating systems are −
Android
IOS
BlackBerry
Windows
Every mobile operating system provides their own set of tools and environments to develop apps that will run on them. Application made for one operating system cannot run on any other platform as they are entirely different. Developers tend to cover all major mobile operating systems in order to increase reachability among their users.
Thus it becomes a tedious task to develop an application program that may run on all major OS platforms, keeping its look, feel, and functionality identical on all platforms. For this work, a developer needs to understand all platforms and should have a good understanding of major development tools for different operating systems.
PhoneGap may be seen as a solution to all problems mentioned above. PhoneGap is a framework that makes the developers develop their apps using standard web APIs for all major mobile operating systems. It is open-source and free.
Developers only need to know web development using HTML, CSS and JavaScript. PhoneGap takes care of rest of the work, such as look and feel of the app and portability among various mobile operating systems.
Using PhoneGap, one can create apps for all major mobile operating systems like Apple iOS, Android, BlackBerry, Windows etc. This does not require the developer to have an expertise over any of the above mentioned platforms, neither the developer is required to know programming to code the app from scratch.
PhoneGap allows its users to upload the data contents on website and it automatically converts it to various App files.
In this tutorial, we shall see how to create an app for Apple, android, and windows platform online without using any offline tool.
PhoneGap – Environment Setup
In this chapter, we will learn how to set up basic environment in order to make apps effortlessly. Though PhoneGap supports offline creation of apps using Cordova command line interface and Github repository mechanism, we shall concentrate on minimum effort procedure.
We assume that you are well versed with web technologies and have your web application ready to be shipped as an app. Because PhoneGap supports only HTML, CSS and JavaScript, it is mandatory that the application should be created using these technologies only.
From a developer’s perspective, an app should have the following items included in its package −
- Configuration files
- Icons for app
- Information or content (built using web technologies)
Configuration
Our web app will need only one configuration file that should be adequate to configure all its necessary settings. Its name is config.xml. This file contains all the necessary information required to compile the app.
Let us see config.xml for our example −
<?xml version = “1.0” encoding = “UTF-8”?> <widget xmlns = “http://www.w3.org/ns/widgets” xmlns:gap = “http://phonegap.com/ns/1.0” id = “com.tutorialspoint.onlineviewer” version = “1.0”> <name>Tutorials Point</name> <description> Tutorials Point Online Viewer </description> <author href = “http://tutorialspoint.com” email = “contact@tutorialspoint.com”> Tutorials Point </author> <preference name = “permissions” value = “none”/> <icon src = “res/icon/android/drawable-ldpi/tp_icon.png” gap:platform = “android” gap:qualifier = “ldpi” /> <icon src = “res/icon/android/drawable-mdpi/tp_icon.png” gap:platform = “android” gap:qualifier = “mdpi” /> <icon src = “res/icon/android/drawable-hdpi/tp_icon.png” gap:platform = “android” gap:qualifier = “hdpi” /> <icon src = “res/icon/android/drawable-xhdpi/tp_icon.png” gap:platform = “android” gap:qualifier = “xhdpi” /> <icon src = “res/icon/android/drawable-xxhdpi/tp_icon.png” gap:platform = “android” gap:qualifier = “xxhdpi” /> <icon src = “res/icon/ios/Icon-72.png” gap:platform = “ios” gap:qualifier = “”/> <icon src = “res/icon/ios/icon-57.png” gap:platform = “ios” width = “57” height = “57” /> <icon src = “res/icon/ios/icon-72.png” gap:platform = “ios” width = “72” height = “72” /> <icon src = “res/icon/ios/icon-57-2x.png” gap:platform = “ios” width = “114” height = “114” /> <icon src = “res/icon/ios/icon-72-2x.png” gap:platform = “ios” width = “144” height = “144” /> </widget>
All configuration contents are wrapped in <widget> tag. Brief description of these is as follows −
<widget id = ”app_id”>
id is your reserved app-id on various app stores. It is in reverse-domain name style i.e. com.tutorialspoint.onlineviewer etc.
<widget version = “x.y.z”>
This is version number of app in x.y.z format where (x,y,z) are positive integers i.e. 1.0.0, it represents major.minor.patch version system.
<name> App Name</name>
This is the name of the app, which will be displayed below the app icon on the mobile screen. Your app can be searched using this name.
<description> My First Web App </description>
This is a brief description of what the app is about, and what it is.
<author> Author_Name </author>
This field contains name of the creator or programmer, generally set to the name of organization which is launching this app.
<preferences name = “permissions” value = “none”>
The preferences tag is used to set various options like FullScreen, BackgroundColor and Orientation for app. These options are in name and value pair. For example: name = “FullScreen” value = “true” etc. Because we do not require any of these advance settings, we just put permissions to none.
<icon>
Allows us to add icons to our apps. It can be coded in various ways, but since we are learning short-cut of everything, so here it is. The .src determines the path of icon image. The gap:platform determines for which OS platform this icon is to be used. The gap:qualifier is density that is used by android devices. The iOS devices use width & height parameters.
Icons
There are devices of various sizes having same mobile operating system, so to target an audience of one platform you need to furnish icons of all the mobiles types too. It is important that we prepare icons of exact shapes and sizes as required by particular mobile operating system.
Here we are using the folders res/icon/ios and res/icon/android/drawable-xxxx..
To get this work done fast, you can create a logo of size 1024×1024 and log on to makeappicon.com. This website will help you instantly create logos of all sizes for both android and iOS platform.
Offline websites are copied to local hard drive and accessed whenever the user needs to without any internet connection. Likewise, this offline web app will let you create a web application that is downloaded to its entirety to the mobile devices of a user who can access that offline.
An application for this type of app may include app having collection of stories, short tutorials or any other offline content of users’ interest, which he/she can read offline even when internet is not available.
Offline App
The following image represents the folder structure for offline app. At root directory it requires only two files, config.xml and index.xml.
The config.xml contains app configuration settings which we learnt in previous section. The index.html file contains homepage of web contents.
One important thing to learn here is that all links inside all html files should contain relative path only. That is, no absolute path or base href tag should be there.
Online App
The following image shows folder structure for our app to be in online mode. In online mode, entire web content is loaded from internet website.
You may notice that data folder is missing in online mode app, because all the files reside on the actual server and are accessible via internet. The index.html file contains actual links as it contains at the web server and all its links are either absolute or used with base href tag.
After you have decided the mode of your app and organized its files in the file structure mentioned above, you need to zip your file with any standard zip tool and save it. We shall use this file in the next section.
Sign Your App
It is essential for any app to be signed by its developers or developing organization to keep things in order. For this reason, you need to sign your app. You may need keytool which is a part of standard java distribution.
Execute the following command in %JAVA_HOME% in your Windows command prompt or Linux Shell −
keytool -genkey -v -keystore my_keystore.keystore -alias TutorialsPoint -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 10000
This should generate my_keystore.keystore file, which we shall need in the next section.
PhoneGap is a ‘dream come true’ framework for businesses and developers. It lets you build applications for different platforms. Initially, developers had to build different applications based on the platform it was deployed in, and this was a waste of time and resources as they needed to use different frameworks and languages for each of the platform.
With the mobile application development framework, known as PhoneGap, you can write an app once using languages like CSS, Javascript and HTML, and then deploy it across various mobile devices. This would work almost like a native app with native features.
When a developer develops apps using this language, he need not have any programming language knowledge, but just knowledge in web development languages.
Now, while looking at the advantages of this framework, let’s look at how it can help the business owner and the developer.
Step 1: Install PhoneGap
The PhoneGap Desktop application provides a drag and drop interface for creating PhoneGap applications. It’s an alternative to using the PhoneGap CLI built for those who prefer a visual user interface over a command line interface approach.
Select your operating system to continue:
- Mac OS X
- Windows
Mac OS X Installation
- Download the latest Mac OS X Installer.
- Double-click the downloaded file to run the installer. You will initially be prompted with a license agreement to accept:

- Drag and drop the application into the Applications folder on your Mac as prompted:

- Next simply open the application and proceed to Step 2 where you will install the PhoneGap Developer App to your mobile device for previewing the apps you build.

Windows Installation
- Download the latest Windows Installer.
- Double click the downloaded file to run the installer. You will be prompted with the PhoneGap Desktop Setup Wizard:

- Accept the license agreement:

- Select the desired destination for the application and click Next:

- Select the desired location for the shortcut and click Next:

- Click Install to begin the installation:

- Click Finish to close the Setup Wizard:

- Next simply open the application and proceed to next step below where you will install the PhoneGap Developer App to your mobile device for previewing the apps you build.

The PhoneGap CLI provides a command line interface for creating PhoneGap apps as an alternative to using the PhoneGap Desktop App for those who prefer working at the command line. The PhoneGap CLI currently has some additional features over the PhoneGap Desktop for building, running and packaging your PhoneGap applications on multiple platforms. If you’re comfortable using a CLI this option may be best going forward.
Requirements
There are a few simple requirements you’ll need prior to installing the PhoneGap CLI:
- node.js – a JavaScript runtime to build your JavaScript code
- git – used in the background by the CLI to download assets. It comes pre-installed on some operating systems.
To see if you already have it installed, type git from the command line.
Install Steps
- Install the PhoneGap CLI via
npmwith the following command from the Terminal app (Mac) or Command Prompt (Win).$ npm install -g phonegap@latest**TIPS:** 1) The `$` symbol is used throughout this guide to indicate the command prompt, it should not be typed. 2) `npm` is the node package manager and installed with node.js. The `npm` command fetches the necessary dependencies for the PhoneGap CLI to run on your local machine. It creates a *node_modules* folder with the necessary code needed to run the CLI. The `-g` flag specifies that folder to be installed at the global location so it can be accessed from anywhere on your machine (defaults to */usr/local/lib/node_modules/phonegap* on Mac).**OS X Users:** You may need to prefix this command with `sudo` to allow installation to restricted directories and type the following instead: `$ sudo npm install -g phonegap@latest`
**Windows 8 Users:** If you just installed Node.js, be sure to start the *Node.js Command Prompt* application specifically.
- Test to ensure the PhoneGap CLI is properly installed by typing
phonegapon the command line. You should see the followinghelptext output displayed:$ phonegap Usage: phonegap [options] [commands] Description: PhoneGap command-line tool. Commands: help [command] output usage information create <path> create a phonegap project ...**TIP:** You can access the PhoneGap CLI usage text at any time by adding the keyword `help`, or the `-h` or `–h` attribute with any phonegap command i.e.: `$ phonegap create help`, `$ phonegap serve -h`.
Step 2: Install Mobile App
The PhoneGap Developer App is a mobile app that runs on devices and allows you to preview and test the PhoneGap mobile apps you build across platforms without additional platform SDK setup. It automatically provides access to the PhoneGap core APIs providing instant access to the native device features without having to install any plugins or compile anything locally. It’s meant to provide an easy way for developers to get started creating and testing their PhoneGap applications quickly with minimal setup.
Install PhoneGap Developer
- Locate the free PhoneGap Developer app from one of the following supported app marketplaces and install it to your mobile device:
- Google Play
- Windows Phone Store
- ~iTunes~ Currently not available but you can still build it yourself!
- Once installed, tap the PhoneGap Developer app icon from your home screen to open it:

- Once installed, move on to the next step where you will create your first PhoneGap app using the tool you selected in step 1.
**NOTE:** The platform SDKs mentioned above refer to the software development kits Apple, Google and Microsoft provide to build applications for their platforms (iOS, Android and Windows respectively). When you’re ready to take your mobile application development further or decide you want to build for each platform locally yourself, you can find the specific instructions for each platform in the PhoneGap Platform Installation Guides.
The positive sides
1.Two benefits in one go
Obviously, PhoneGap is well known for cross platform capabilities, so you can develop a single app, and deploy it across all mobile platforms. This is a huge win for both the developer and the business, because within the shortest possible Time To Market, their product is on the roll. Less effort, less time and less money!
2. Release uniform products across all platforms
Uniformity was a prime issue that businesses faced in the initial stages of product development as they were unable to release uniform functionalities across all the mobile platforms. An app developed for iPhone may look different in Android and vice versa. The framework makes it possible to have uniformity through the system of cross-platform app development.
3. No need to hire expert developers
Native app development required experts who would probably work only to develop products for a particular platform. But PG makes it lucky for businesses because just working knowledge of Javascript, CSS3 and HTML5 would be perfect to create cross-platform apps. And this you can get in-house as well. It’s good news for the developers too because they don’t have to learn a new language to use this framework.
4. Each app can behave like native apps
An app behaves like native application when it taps into the smartphone’s hardware and make use of attributes like geolocation, camera, accelerometer and so on. This framework taps into these hardware capabilities and provides excellent UX in the process. In fact, the user would hardly know that it is a cross-platform one.
5. Robust Backend
The highly robust backend system helps in rapid product development and this reduces development efforts. However, if you are a beginner in the field of development, you can refer to PhoneGap’s beginner’s guide to know how to speed up development process. A robust backend is like having strong roots because it really affects the performance of your app.
6. Open Source
With its open source license, the framework is essentially free. And there is a huge and growing community of developers that uploads details of new codes and modules, making to easier for newcomers.
7. Backed by Apache, Powered by Apache Cordova
Being a distribution of Apache Cordova, PhoneGap is powered by it, and contains several additional tools that tie into other services of Adobe. Therefore, you can also say that Adobe backs the technology. In turn, PhoneGap powers AEM mobile (Adobe Experience Manager), through which developers target multiple platforms. Through AEM Mobile, enterprises can manage all the activities of their mobile apps from a single place. With the help of PhoneGap plugin ContentSync, you can fetch and cache your app’s content. AEM Mobile Verify is also powered by this technology and this helps you to test and preview the changes you make on an app. The tests can be performed on both iOS and Android devices.
8. Easy to work plugins
The PhoneGap native-app container, PhoneGap Build supports several PhoneGap or Cordova plugins, aiding in extending the native functionalities while developing apps. You can get the plugins from the Adobe repository, public git repository and npm. Some of the well known recent plugins in the repositories are StatusBar, PushPlugin, Barcode Scanner, Social Sharing, GAPlugin, Facebook Connect and Pushwoosh.
Potential drawbacks
1. Doesn’t support Plugins with hooks
PhoneGap Builds do not support plugins with hooks, so at certain times that can hinder with the functionality. For example, there are hooks in WordPress that helps the developer to tie their code with the core code base, plugins and themes in WP. Similarly, PGBuilds doesn’t support Cordova hooks.
2. Not suitable for hardware intensive apps
PG, with all its complexity of plugins and APIs may fail to deliver while developing a gaming app. The gaming developers are likely to experience ‘freeze’ and ‘drop’ issues after push notification from their apps.
3. Need a Mac for developing iOS apps
PhoneGap app developers cannot develop an iOS program without downloading iOS SDKs, and this is not possible without a Mac. However, you can counter with limitation with the help of PG Builds as it can compile your build and return the final file.
4. Plugins could be outdated
Sometimes, the plugins in PG could be outdated, and this could hinder with app functionality. And for some features, you don’t have a related plugin. For example, geolocation in your app may not function optimally, or the camera may not work well. You may realise this only half-way through the project, and that is not an option for many enterprises.
Closing Thoughts
It is believed that Adobe PhoneGap acts as an alternative to Xamarin, and it shares a lot of features with hybrid app development framework. PG does play an important role in the thriving hybrid app development ecosystem. With a toolkit consisting of JavaScript, HTML5, and CSS3, you can easily develop quality apps and market them in a reasonable amount of time.
Cognosys provides hardened images of Phonegap on all public cloud i.e. AWS marketplace and Azure.
Phonegap on cloud for AWS
Features
Major Features Of Phonegap
1. STRONG AND ROBUST BACKED-
PhoneGap has a robust backend system that tremendously speeds up the development process and reduces developer’s efforts. The beginner’s guide also helps in speeding the process further.
2. OPEN SOURCE-
With the PhoneGap framework, you get the best for free. The PhoneGap community compiles new codes and modules which are available for free because of its Open Source License.
3. FLEXIBILITY-
It offers great flexibility to the developers as they can develop any type of mobile app without any serious efforts. Developers familiar with basic knowledge of HTML5, CSS3 and JavaScript can get started with PhoneGap. No need for developers to learn additional languages.
With all these super features, PhoneGap has emerged as a great framework for mobile app development. We will now check some of its advantages –
1. COMPATIBLE ON ALL THE PLATFORMS-
A high level of uniformity can be maintained when the apps are developed for multiple platforms. PhoneGap abolishes the differences in the app’s look and feel when viewed on different platforms.
2. EASE OF DEVELOPMENT-
PhoneGap works on HTML5, CSS3 and JavaScript, the most common browser based skills which do not require any additional inputs. Hence the business owners can utilize their own tech team and get it developed smartly.
3. TWO FOLD BENEFITS-
It’s a win win for all the stakeholders. The developers gain as they have to spend less effort and get develop an app which will work across all mobile platforms. The businesses gain as the app is prepared and ready to hit the market in minimalistic time.
4. TAPPING INTO THE DEVICE’S HARDWARE-
One of the most amazing things about this framework is that it taps into the device’s hardware such as the camera, geo location, accelerometer and few others. With this, the apps developed on PhoneGap can easily make use of the properties of the native resources of the device, without compromising on the User Experience.
Like everything else, PhoneGap too has some areas of improvement. Now that we have looked at its advantages, we can move ahead to look at its disadvantages.
- It does not support all the functionalities.
- PhoneGap can be inefficient sometimes, while working with native apps.
- The performance of cross platform apps is a little subdued when compared to apps developed for individual platforms
4. PhoneGap framework lets the developers to develop the apps only for once. Thereafter it charges some monthly fees
-
- Connectors- Connect to enterprise data Using a wide range of connectors such as SQL or Web Services or create API from Mainframe or HTML applications.
-
- Cross Platform- Create Desktop web and Mobile apps once and run on multiple devices (iOS, Android, Windows phone).
- Server Side Business Logic- Build, Enrich, Optimize, Share and Expose new or existing processes and logics.
AWS
Installation Instructions for Windows
Note: How to find PublicDNS in AWS
Step 1) RDP Connection: To connect to the deployed instance, Please follow Instructions to Connect to Windows instance on AWS Cloud
1) Connect to the virtual machine using following RDP credentials:
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 3389
Username: To connect to the operating system, use RDP and the username is Administrator.
Password: Please Click here to know how to get password .
Step 2) Choose Start, expand All Programs, and then select PHP
Step 3) Other Information:
1.Default installation path: will be in your root folder “C:\inetpub\wwwroot”
2.Default ports:
- Windows Machines: RDP Port – 3389
- Http: 80
- Https: 443
Internal Endpoints: Internal Services are normally running on below ports and Shall be NAT-ted with the Public Endpoint as required. Although we do not recommend
Any RDBMS or Nosql admin ports to be opened to Public endpoints and these are all not exposed by default externally
External Endpoints: For Public Endpoints, Normally only below port are Opened, although this can change from stack to stack. We recommend changing RDP port to Non Standard ports and Putting ACL to your IP.
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link .
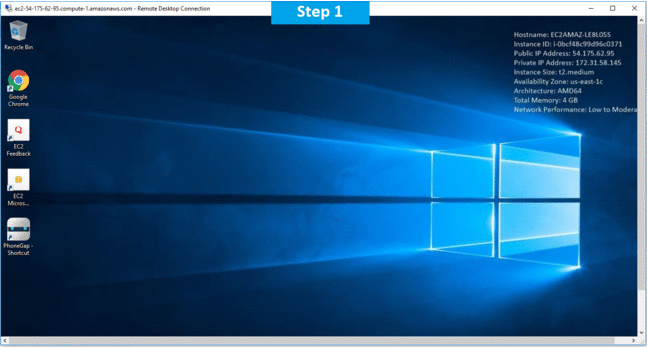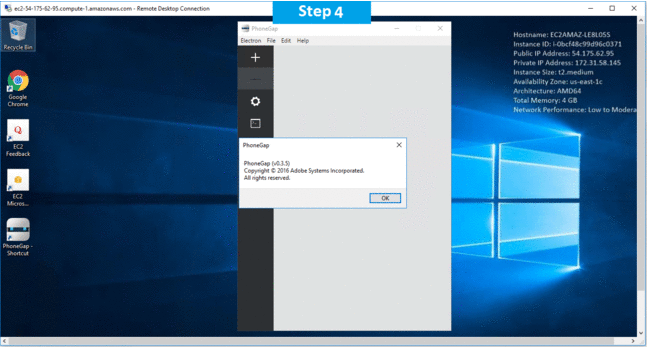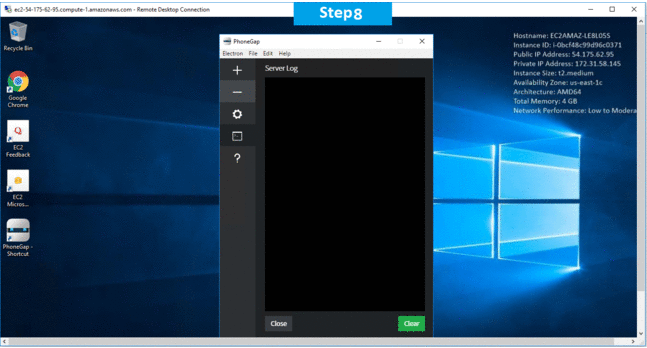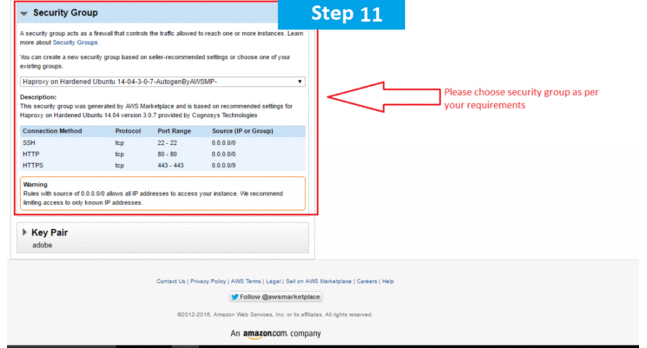
AWS Step by Step Screenshots
Videos
PhoneGap Tutorial