1-click AWS Deployment 1-click Azure Deployment 1-click Google Deployment
Overview
SQL Server 2017 represents a major step towards making SQL Server a platform that gives you choices of development languages, data types, on-premises or cloud, and operating systems by bringing the power of SQL Server to Linux.
SQL Server 2017 includes many new Database Engine features, enhancements, and performance improvements.
New in Integration Services in SQL Server 2017.
- ScaleOut Master now supports high availability.
- The failover handling of the execution logs from ScaleOut Workers is improved.
- The parameter run in cluster of the stored procedure [catalog].[create_execution] is renamed to runinscaleout for consistency and readability.
- The SSIS Catalog has a new global property to specify the default mode for executing SSIS packages.
Cognosys Provides SQL Server 2017 on Linux on AWS marketplace and Google Cloud Platform marketplace
Features
Major Features of SQL Server :
- New storage features—Column-store indexes, File-table storage.
- New Transact-SQL (T-SQL) constructs—Sequence objects, THROW statement, new conversion, logical, string, and date and time functions, and adhoc query paging.
- New scalability and performance features—Indirect checkpoints, FORCESCAN table hint, number of table partitions increased to 15,000.
- New security features—Database Audit, user-defined server roles, contained databases.
- New availability features—A number of high-availability enhancements known as AlwaysOn, which include AlwaysOn Availability Groups and AlwaysOn Failover Cluster Instances.
- Statistical Semantic Search—Statistical Semantic Search builds upon the existing full-text search feature in SQL Server by querying the contextual meaning of terms within a document repository.
- Data Quality Services—This new feature allows you to build a knowledge base of data rules and use those to perform a variety of critical data quality tasks, including correction, enrichment, standardization, and de-duplication of your data.
AWS
Installation Instructions For Ubuntu
Step 1) Deploy the instance from the Marketplace
Please note about the size of instance:
For SQL server CPU > 2 cores and RAM > 4 GB is recommended
SQL server requires instance size with minimum 3250 megabytes of memory to start.
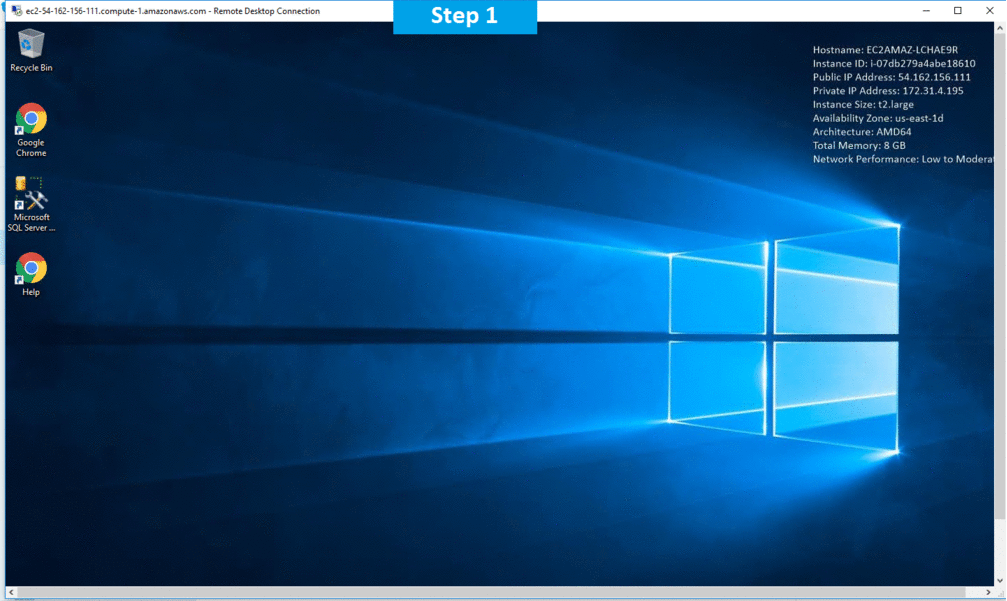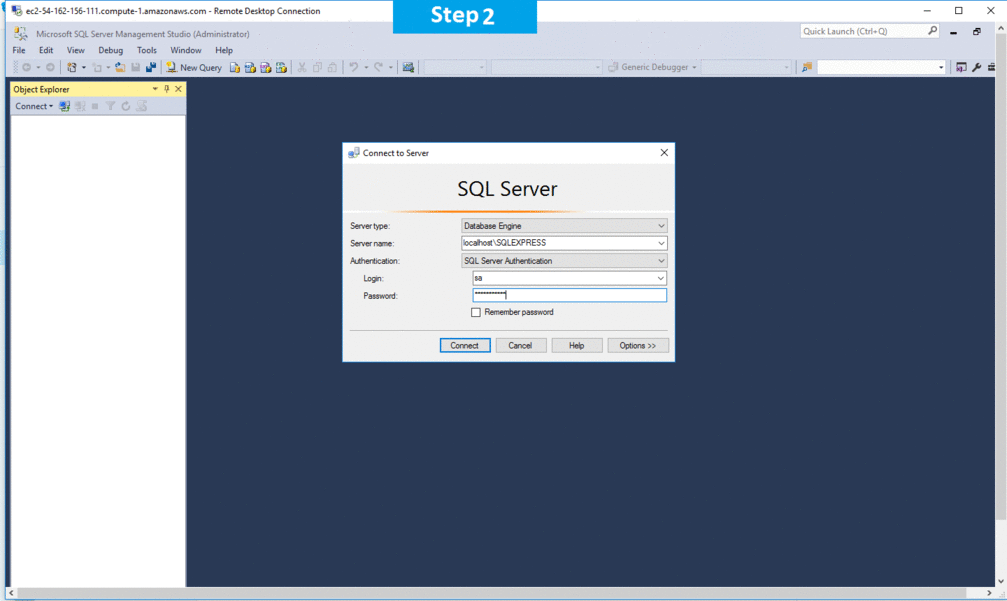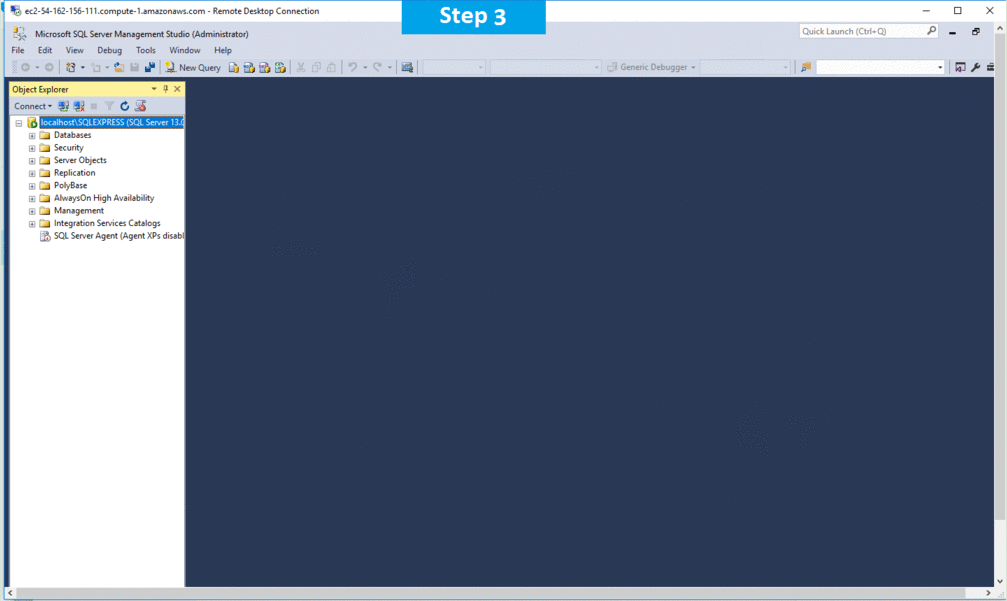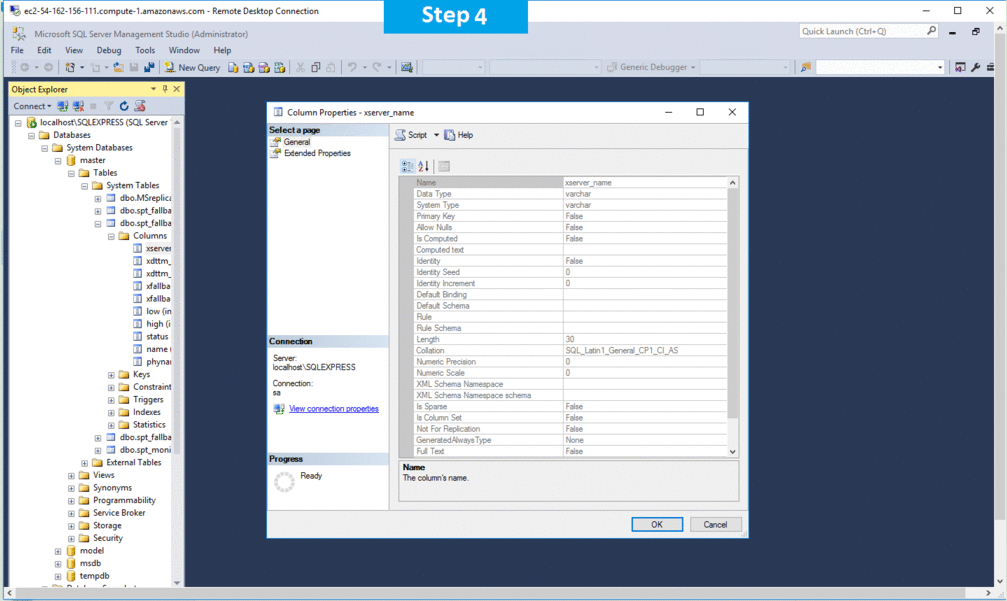
Step 2) SSH Connection: Please connect to the deployed instance after about 2 minutes of booting.
To connect to the deployed instance, please follow Instructions to Connect to instance on AWS Cloud
Note: For RHEL, the user name is ec2-user. For Ubuntu, the user name is ubuntu . For Centos, the user name is centos. For Fedora, the user name is ec2-user. For SUSE, the user name is ec2-user.
Step 3) Database Credentials:
You can Login by below SQL Database credentials
SQL UserName : sa
SQL Password : Your Instance ID
You can find the instance ID from Ec2 console
Step 4) SQL Connection: To Connect Microsoft SQL Server on Linux:
1) You can use command line after connecting with SSH and using the below command
sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -P ‘InstanceID’
2) You can allow port 1433 with proper ACL and connect with Management Studio from windows server by giving proper IP address as hostname.
sudo systemctl status mssql-server
Step 5 ) Other Information:
1.Default ports:
- Linux Machines: SSH Port – 22
- SQL server port:1433: By default, this is blocked on the Public interface for security reasons.
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link
Azure
Installation Instructions For Ubuntu
Installation Instructions for Ubuntu
1.Default installation path: will be on your root folder “/opt/mssql-tools/bin”
2.Default ports:
- Linux Machines: SSH Port – 22
3.SQL Connection: To Connect Microsoft SQL Server on Linux:
1) You can use command line after connecting with SSH and using the below command
sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -P ‘InstanceID’
2) You can allow port 1433 with proper ACL and connect with Management Studio from windows server by giving proper IP address as hostname.
sudo systemctl status mssql-server
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link
Installation Instructions For Windows
Installation Instructions
Step 1) VM Creation:
- Click the Launch on Compute Engine button on the solution
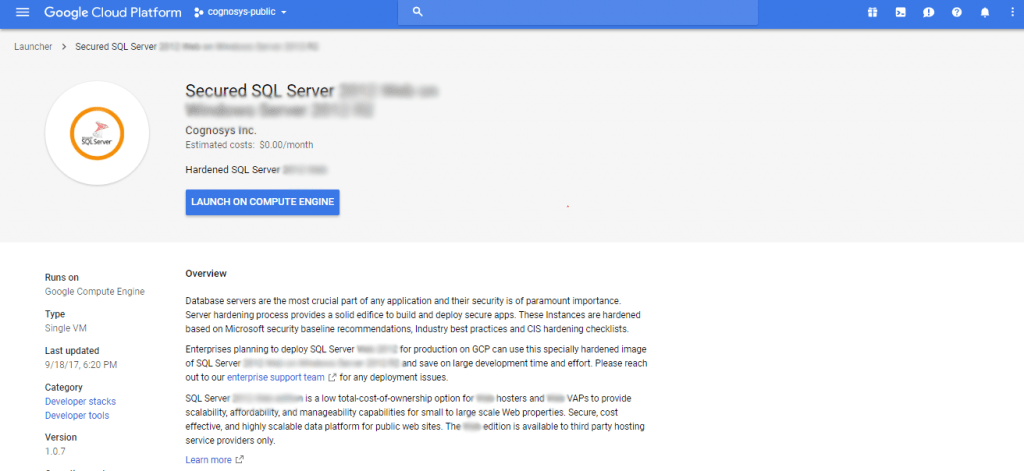 2. At this page, you can see an overview of Cognosys Image as well as the estimated cost of running the instance.
2. At this page, you can see an overview of Cognosys Image as well as the estimated cost of running the instance.
3.In the settings page, you can choose the number of CPUs and the size of RAM, the disk size and type etc.
For SQL server CPU > 2 cores and RAM > 4 GB is recommended
SQL server requires instance size with minimum 3250 megabytes of memory to start.
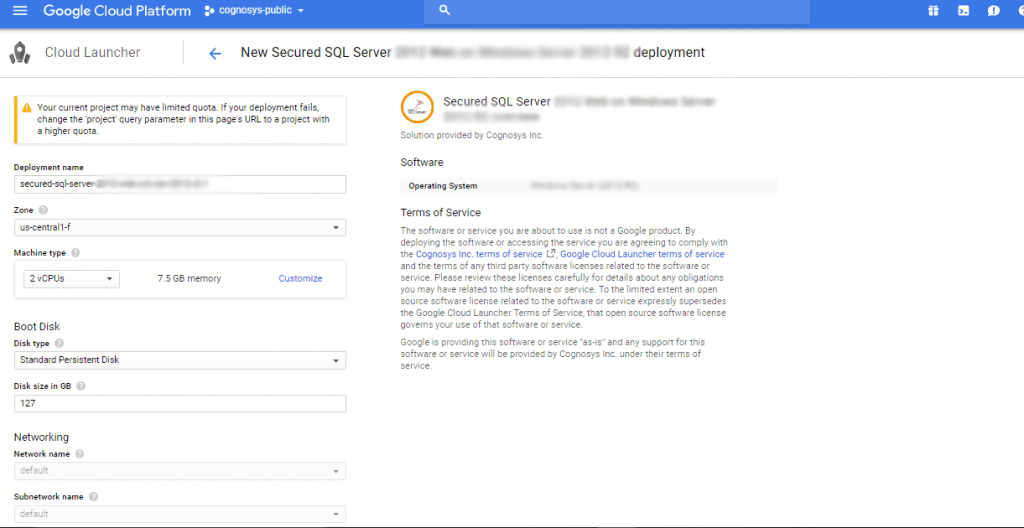
Step 2) SSH Connection: Please connect to the deployed instance after about 2 minutes of booting, Please follow Instructions to Connect to Linux instance on Google Cloud
Step 3) Database Credentials:
You can Login by below SQL Database credentials
SQL UserName : sa
The sa password is generated as a random string during deployment. It can be obtained from the below screen which appears after successful deployment of the image.
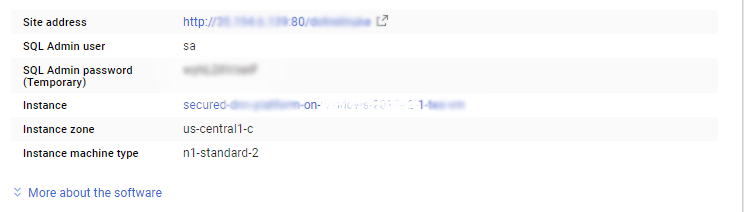
If you have closed the deployment page you can also get the sa password from VM Details “Custom metadata” Section.
Step 4) SQL Connection: To Connect Microsoft SQL Server on Linux:
1) You can use command line after connecting with SSH and using the below command
sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -P ‘PasswordinStep3’
2) You can allow port 1433 with proper ACL and connect with Management Studio from windows server by giving proper IP address as hostname.
You can give SQL server instance hostname as IP address. Username is sa and password is provided in Custom Metadata.
sudo systemctl status mssql-server
If you have closed the deployment page you can also get the sa password from VM Details “Custom metadata” Section.
Step 5 ) Other Information:
1.Default installation path: “/opt/mssql-tools/bin ”
2.Default ports:
- Linux Machines: SSH Port – 22
- SQL server port:1433: By default, this is blocked on the Public interface for security reasons.


