Overview
SQL Server 2014 Standard edition delivers basic data management and business intelligence database for departments and small organizations to run their applications and supports common development tools for on-premise and cloud — enabling effective database management with minimal IT resources.
Description
Improvements over Microsoft SQL 2014 include:
Database backups with built-in encryption (Standard Only)
Improved performance
Enhanced security
Additional Features Include:
Rich data integration: Integrate data from disparate sources with SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), which includes support for the deployment and administration of ETL tasks such as better tracking of SSIS packet status and the ability to run administration as a separate SQL Server instance.
Improved manageability: SQL Server Management Studio and updated management packs for System Center help you centrally manage your infrastructure. Added support for Windows PowerShell 2.0 automates management tasks, and enhancements to Sys Prep help you more efficiently create virtual machines.
Robust development tools. With SQL Server Data Tools, database development is integrated into Visual Studio and/or available for download to support building next-generation web, enterprise, business intelligence and data-aware mobile applications across on-premises and public cloud.
Rich support for content management. FileTable in SQL Server makes it easier to manage content into FILESTREAM blob storage. Improvements to full-text indexing yield better performance and search functionality. Statistical semantic search technology supports automatic concept extraction and innovative key phrase search options.
Extend any data, anywhere. SQL Server supports relational and non-relational data, including Big Data sources like Hadoop. Customers can extend heterogeneous environments using industry standard APIs (ADO.NET, ODBC, JDBC, PDO, and ADO) across varied platforms including .NET, C/C++, Java, Linux, and PHP.
Highlights
Basic availability and disaster recovery: Standard Edition includes two-node failover clustering and log shipping, plus database mirroring
Support for compliance: easily manage permissions around data access including user-defined server roles to support separation of duties and contained database authentication.
Reporting and analytics: support for multi-dimensional models allows IT to build business logic with Reporting Services. Report Builder 3.0 provides an intuitive report authoring environment. Take advantage of SQL Server predictive analytics.
MS SQL Server is a client-server architecture. MS SQL Server process starts with the client application sending a request. The SQL Server accepts, processes and replies to the request with processed data. Let’s discuss in detail the entire architecture shown below:
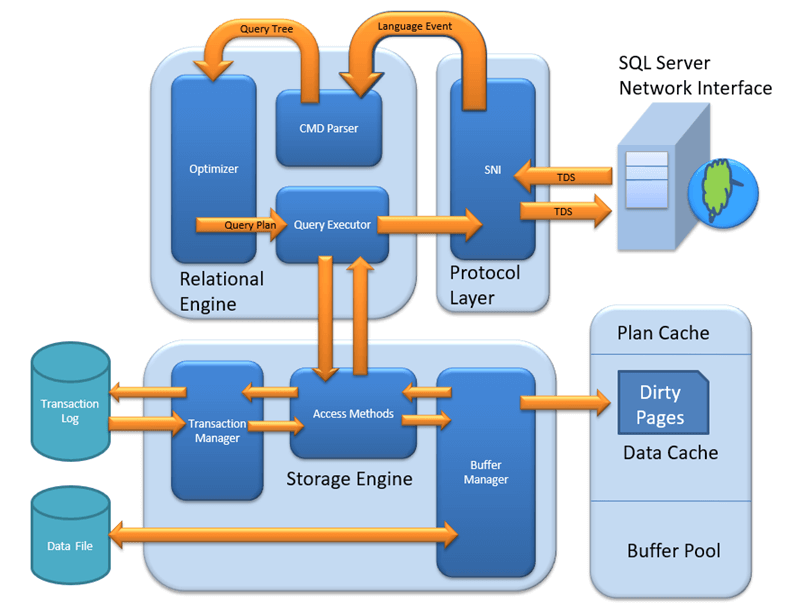
As the below Diagram depicts there are three major components in SQL Server Architecture:
Protocol Layer
Relational Engine
Storage Engine
Protocol Layer – SNI
MS SQL SERVER PROTOCOL LAYER supports 3 Type of Client Server Architecture. We will start with “Three Type of Client Server Architecture” which MS SQL Server supports.
Shared Memory
Let’s reconsider an early morning Conversation scenario.

MOM and TOM – Here Tom and his Mom, were at the same logical place, i.e. at their home. Tom was able to ask for Coffee and Mom was able it serve it hot.
MS SQL SERVER – Here MS SQL server provides SHARED MEMORY PROTOCOL. Here CLIENT and MS SQL server run on the same machine. Both can communicate via Shared Memory protocol.
Analogy: Lets map entities in the above two scenarios. We can easily map Tom to Client, Mom to SQL server, Home to Machine, and Verbal Communication to Shared Memory Protocol.
From the desk of configuration and installation:
For Connection to Local DB – In SQL Management Studio, “Server Name” Option could be
“.”
“localhost”
“127.0.0.1”
“Machine\Instance”

TCP/IP
Now consider in the evening, Tom is in the party mood. He wants a Coffee ordered from a well-known Coffee Shop. The Coffee shop is located 10 km away from his home

Here Tom and Starbuck are in different physical location. Tom at home and Starbucks at the busy marketplace. They’re communicating via Cellular network. Similarly, MS SQL SERVER provides the capability to interact via TCP/IP protocol, where CLIENT and MS SQL Server are remote to each other and installed on a separate machine.
Analogy: Lets map entities in the above two scenarios. We can easily map Tom to Client, Starbuck to SQL server, the Home/Market place to Remote location and finally Cellular network to TCP/IP protocol.
Notes from the desk of Configuration/installation:
In SQL Management Studio – For Connection via TCP\IP, “Server Name” Option has to be “Machine\Instance of the server.”

Now finally at night, Tom wanted to have a light green tea which her neighbor, Sierra prepare very well.

Here Tom and his Neighbor, Sierra, are in same physical location, being each other’s neighbor. They’re communicating via Intra network. Similarly, MS SQL SERVER provides the capability to interact via the Named Pipe protocol. Here the CLIENT and MS SQL SERVER are in connection via LAN.
Analogy: Lets map entities in the above two scenarios. We can easily map Tom to Client, Sierra to SQL server, Neighbor to LAN and finally Intra network to Named Pipe Protocol.
Notes from the desk of Configuration/installation:
For Connection via Named Pipe. This option is disabled by default and needs to be enabled by the SQL Configuration Manager.
What is TDS?
Now that we know that there are three types of Client-Server Architecture, lets us have a glance at TDS:
TDS stands for Tabular Data Stream.
All 3 protocols use TDS packets. TDS is encapsulated in Network packets. This enables data transfer from the client machine to the server machine.
TDS was first developed by Sybase and is now Owned by Microsoft
Relational Engine
The Relational Engine is also known as the Query Processor. It has the SQL Server components that determine what exactly a query needs to do and how it can be done best. It is responsible for the execution of user queries by requesting data from the storage engine and processing the results that are returned.
CMD Parser
Data once received from Protocol Layer is then passed to Relational Engine. “CMD Parser” is the first component of Relational Engine to receive the Query data. The principal job of CMD Parser is to check the query for Syntactic and Semantic error. Finally, it generates a Query Tree.

Optimizer
The work of the optimizer is to create an execution plan for the user’s query. This is the plan that will determine how the user query will be executed.
Note that not all queries are optimized. Optimization is done for DML (Data Modification Language) commands like SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE. Such queries are first marked then send to the optimizer. DDL commands like CREATE and ALTER are not optimized, but they are instead compiled into an internal form. The query cost is calculated based on factors like CPU usage, Memory usage, and Input/ Output needs.Optimizer’s role is to find the cheapest, not the best, cost-effective execution plan.

Query Executor Query executer calls Access Method. It provides an execution plan for data fetching logic required for execution. Once data is received from Storage Engine, the result gets published to the Protocol layer. Finally, data is sent to the end user.

Storage Engine
The work of the Storage Engine is to store data in a storage system like Disk or SAN and retrieve the data when needed. Before we deep dive into Storage engine, let’s have a look at how data is stored in Database and type of files available.

Data File, physically stores data in the form of data pages, with each data page having a size of 8KB, forming the smallest storage unit in SQL Server. These data pages are logically grouped to form extents. No object is assigned a page in SQL Server.
The maintenance of the object is done via extents. The page has a section called the Page Header with a size of 96 bytes, carrying the metadata information about the page like the Page Type, Page Number, Size of Used Space, Size of Free Space, and Pointer to the next page and previous page, etc.
File types

Primary file
Every database contains one Primary file.
This store all important data related to tables, views, Triggers, etc.
Extension is .mdf usually but can be of any extension.
Secondary file
Database may or may not contains multiple Secondary files.
This is optional and contain user-specific data.
Extension is .ndf usually but can be of any extension.
Log file
Also known as Write ahead logs.
Extension is .ldf
Used for Transaction Management.
This is used to recover from any unwanted instances. Perform important task of Rollback to uncommitted transactions.
Storage Engine has 3 components; let’s look into them in detail.
Access Method
It acts as an interface between query executor and Buffer Manager/Transaction Logs.
Access Method itself does not do any execution.
The first action is to determine whether the query is:
Select Statement (DDL)
Non- Select Statement (DDL & DML)
Depending upon the result, the Access Method takes the following steps:
If the query is DDL, SELECT statement, the query is pass to the Buffer Manager for further processing.
And if query if DDL, NON-SELECT statement, the query is pass to Transaction Manager. This mostly includes the UPDATE statement.

Buffer Manager
Buffer manager manages core functions for modules below:
Plan Cache
Data Parsing: Buffer cache & Data storage
Dirty Page

Plan Cache
Existing Query plan: The buffer manager checks if the execution plan is there in the stored Plan Cache. If Yes, then query plan cache and its associated data cache is used.
First time Cache plan: Where does existing Plan cache come from?
If the first-time query execution plan is being run and is complex, it makes sense to store it in in the Plane cache. This will ensure faster availability when the next time SQL server gets the same query. So, it’s nothing else but the query itself which Plan execution is being stored if it is being run for the first time.
Data Parsing: Buffer cache & Data Storage
Buffer manager provides access to the data required. Below two approaches are possible depending upon whether data exist in the data cache or not:
Buffer Cache – Soft Parsing:
Buffer Manager looks for Data in Buffer in Data cache. If present, then this Data is used by Query Executor. This improves the performance as the number of I/O operation is reduced when fetching data from the cache as compared to fetching data from Data storage.
Data Storage – Hard Parsing:If data is not present in Buffer Manager than required Data is searched in Data Storage. If also stores data in the data cache for future use.

Dirty Page It is stored as a processing logic of Transaction Manager.
Transaction Manager Transaction Manager is invoked when access method determines that Query is a Non-Select statement.

Log Manager
Log Manager keeps a track of all updates done in the system via logs in Transaction Logs.
Logs have Logs Sequence Number with the Transaction ID and Data Modification Record.
This is used for keeping track of Transaction Committed and Transaction Rollback.
Lock Manager
During Transaction, the associated data in Data Storage is in the Lock state. This process is handled by Lock Manager.
This process ensures data consistency and isolation. Also known as ACID properties.
Execution Process
Log Manager start logging and Lock Manager locks the associated data.
Data’s copy is maintained in the Buffer cache.
Copy of data supposed to be updated is maintained in Log buffer and all the events updates data in Data buffer.
Pages which store the data is also known as Dirty Pages.
Checkpoint and Write-Ahead Logging: This process run and mark all the page from Dirty Pages to Disk, but the page remains in the cache. Frequency is approximately 1 run per minute.But the page is first pushed to Data page of the log file from Buffer log. This is known as Write Ahead Logging.
Lazy Writer: The Dirty page can remain in memory. When SQL server observes a huge load and Buffer memory is needed for a new transaction, it frees up Dirty Pages from the cache. It operates on LRU – Least recently used Algorithm for cleaning page from buffer pool to disk.
HOW TO INSTALL SQL SERVER 2014 STANDARD EDITION
Follow below steps to install SQL Server 2014 Standard Edition
1.Environmental Prerequisites for SQL Server 2014
2.SQL Server 2014 Prerequisites
3.Install SQL Server 2014
Environmental Prerequisites for SQL Server 2014
1.Active Directory Directory Services
2.DNS
SQL Server 2014 Prerequisites
Install .netFramework3.5 ” Server Manager> click Add roles and features>Add .NET Framework 3.5. >Click Install”
Install SQL Server 2014
1.Once you launch the installer, Click installation from the left pane and select -New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation

2.On Product Key Screen, Click Next

3.Accept the license terms then click Next

4.On Microsoft Update page, Click Next.

5.On Install Rules page, Click Next.

6.On Setup Role Screen, Select “SQL Server Feature Installation” Click Next

7.Select the features to install. Select the Database engine, Full-Text, Management tool, and Reporting Services. Click Next.

8..On Instance Configuration Page, Click Next.

9.On Server Configuration Page, Click Next

10.Enter the domain account and password for the services <FTC\ftcadmin> then click Next.

11.On Report Services Native mode, Select “Install and Configure”, Click Next.

12.Copy the configuration file, click Install.

13.After the successful installation, Click Close.

SQL Server Standard Edition Advantages:
1.The Standard Edition also offers high availability options not found in Express, such as log shipping, backup compression, failover clustering and database mirroring, although support for the last two is not as robust as in the Enterprise Edition. However, the Standard Edition also provides the full complement of replication features, compared with the Express Edition, which can act only as a subscriber.
2.The Standard Edition also includes a number of tools not in Express, such as Distributed Replay, SQL Profiler, SQL Server Agent and Microsoft System Center Operations, all important tools to the daily maintenance and operation of SQL Server. Within the Standard Edition, you’ll also find support for such features as policy automation, multi-instance management, automatic indexed view management, standard performance reports and performance data collection.
3.One area that is important to you in selecting a database system is business intelligence (BI). Although the Express Edition might give you some support for a small-scale BI operation, you’ll need at least the Standard Edition for any serious warehousing; analytics; and data extract, transform and load operations. The Standard Edition comes with SQL Server Data Tools, which let you develop projects related to Integration Services, Reporting Services and Analysis Services, all of which are also included in this edition. You get everything from the Integration Services runtime to multidimensional data models to a variety of reporting options and configurations. Clearly, if you’re thinking BI, the Standard Edition wins hands down over Express.
4. Carefully examine all the features that the Standard Edition offers, and be sure you’re getting what you need and not paying for what you don’t. The Microsoft Developer Network provides a handy resource that breaks down the features offered in each edition. You get a lot more with Standard than you do Express, but not nearly as much as you get in the Enterprise Edition. For that reason, the next article in this series will focus on what Enterprise has to offer and why you should carefully consider all your options before deciding upon a SQL Server edition.
–SQL Server Standard 2014 is designed for serving as a back end for internal applications, or even powering a dynamic website. It offers basic subset of database, reporting and analytic capabilities.
Standard edition of SQL server 2014 provides basic availability and disaster recovery with up to two node fail-over clustering, log shipping and peer-to-peer replication. As basic availability and disaster recovery with two node failover clustering, log shipping and peer-to-peer replication.
Cognosys Provides Hardened images of SQL Server Standard 2014 on the cloud ( AWS marketplace, Azure and Google Cloud Platform).
Deploy Standard edition of SQL server 2014 securely on cloud i.e. AWS marketplace, Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
We also provide the different edition’s of SQL Server 2014 such as SQL Server 2014 Web Edition, SQL Server 2014 Express and SQL Server Enterprise 2014.
SQL Server Standard 2014 on cloud for AWS
Features
Features of SQL server 2014:
1. In-Memory OLTP Engine
SQL Server 2014 enables memory optimization of selected tables and stored procedures. The In-Memory OLTP engine is designed for high concurrency and uses a new optimistic concurrency control mechanism to eliminate locking delays. Microsoft states that customers can expect performance to be up to 20 times better than with SQL Server 2012 when using this new feature. For more information, check out “Rev Up Application Performance with the In-Memory OLTP Engine.”
2. AlwaysOn Enhancements
Microsoft has enhanced AlwaysOn integration by expanding the maximum number of secondary replicas from four to eight. Readable secondary replicas are now also available for read workloads, even when the primary replica is unavailable. In addition, SQL Server 2014 provides the new Add Azure Replica Wizard, which helps you create asynchronous secondary replicas in Windows Azure.
3. Buffer Pool Extension
SQL Server 2014 provides a new solid state disk (SSD) integration capability that lets you use SSDs to expand the SQL Server 2014 Buffer Pool as nonvolatile RAM (NvRAM). With the new Buffer Pool Extensions feature, you can use SSD drives to expand the buffer pool in systems that have maxed out their memory. Buffer Pool Extensions can provide performance gains for read-heavy OLTP workloads.
4. Updateable Columnstore Indexes
When Microsoft introduced the columnstore index in SQL Server 2012, it provided improved performance for data warehousing queries. For some queries, the columnstore indexes provided a tenfold performance improvement. However, to utilize the columnstore index, the underlying table had to be read-only. SQL Server 2014 eliminates this restriction with the new updateable Columnstore Index. The SQL Server 2014 Columnstore Index must use all the columns in the table and can’t be combined with other indexes.
5. Storage I/O control
The Resource Governor lets you limit the amount of CPU and memory that a given workload can consume. SQL Server 2014 extends the reach of the Resource Governor to manage storage I/O usage as well. The SQL Server 2014 Resource Governor can limit the physical I/Os issued for user threads in a given resource pool.
6. Power View for Multidimensional Models
Power View used to be limited to tabular data. However, with SQL Server 2014, Power View can now be used with multidimensional models (OLAP cubes) and can create a variety of data visualizations including tables, matrices, bubble charts, and geographical maps. Power View multidimensional models also support queries using Data Analysis Expressions (DAX).
7. Power BI for Office 365 Integration
Power BI for Office 365 is a cloud-based business intelligence (BI) solution that provides data navigation and visualization capabilities. Power BI for Office 365 includes Power Query (formerly code-named Data Explorer), Power Map (formerly code-named GeoFlow), Power Pivot, and Power View. You can learn more about Power BI at Microsoft’s Power BI for Office 365 site.
8. SQL Server Data Tools for Business Intelligence
The new SQL Server Data Tools for BI (SSDT-BI) is used to create SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) models, SSRS reports, and SSIS packages. The new SSDT-BI supports SSAS and SSRS for SQL Server 2014 and earlier, but SSIS projects are limited to SQL Server 2014. In the pre-release version of SQL Server 2014, SQL Server Setup doesn’t install SSDT-BI. Instead, you must download SSDT-BI separately from the Microsoft Download Center.
9. Backup Encryption
One welcome addition to SQL Server 2014 is the ability to encrypt database backups for at-rest data protection. SQL Server 2014 supports several encryption algorithms, including Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 128, AES 192, AES 256, and Triple DES. You must use a certificate or an asymmetric key to perform encryption for SQL Server 2014 backups.
10. SQL Server Managed Backup to Windows Azure
SQL Server 2014’s native backup supports Windows Azure integration. Although I’m not entirely convinced that I would want to depend on an Internet connection to restore my backups, on-premises SQL Server 2014 and Windows Azure virtual machine (VM) instances support backing up to Windows Azure storage. The Windows Azure backup integration is also fully built into SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Major Features of SQL Server Standard 2014
1. Cross-Box Scale Limits
2. High Availability
3. Scalability and Performance
4. Security
5. Replication
6. Management Tools
7. RDBMS Manageability
8. Development Tools
9. Programmability
AWS
Installation Instructions For Windows
Installation Instructions For Windows
Step 1) RDP Connection: To connect to the deployed instance, Please follow Instructions to Connect to Windows instance on AWS Cloud
1) Connect to the virtual machine using following RDP credentials:
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 3389
Username: To connect to the operating system, use RDP and the username is Administrator.
Password: Please Click here to know how to get password
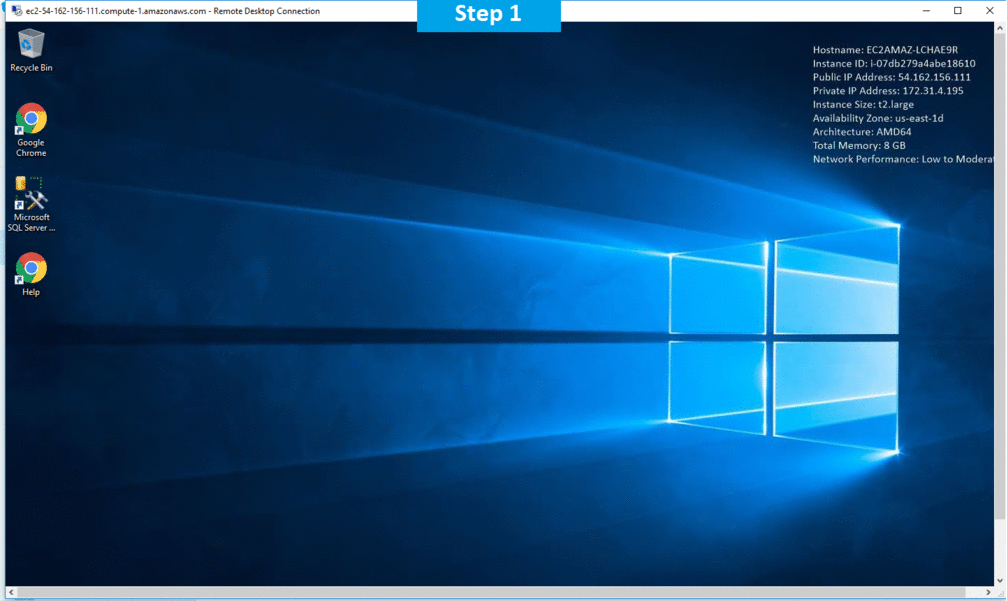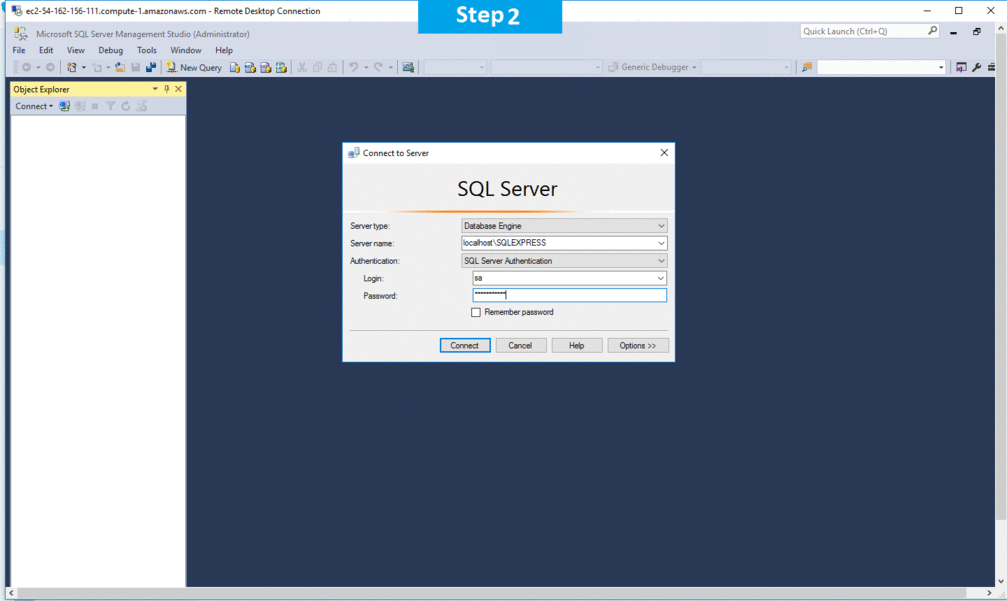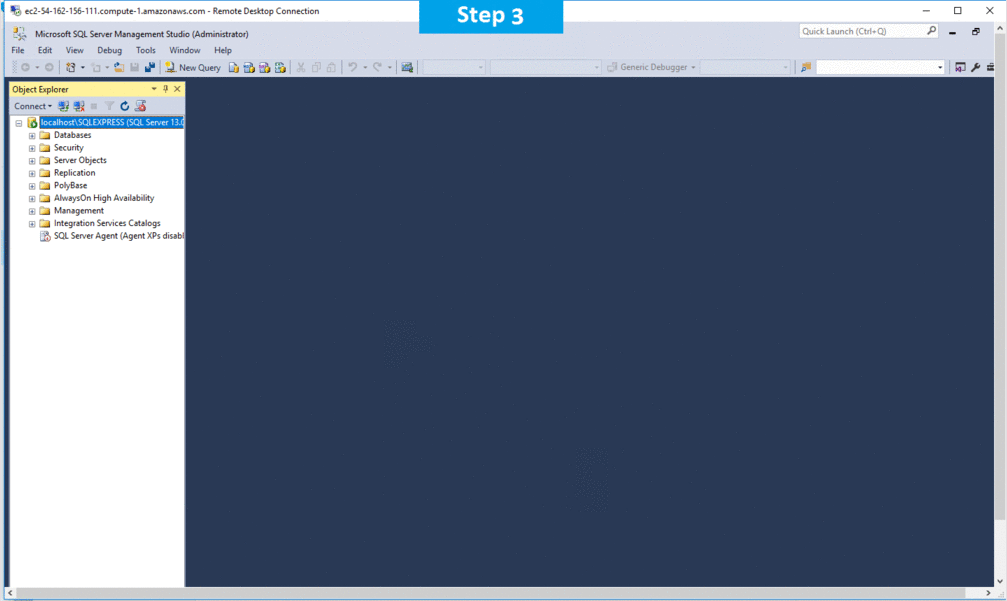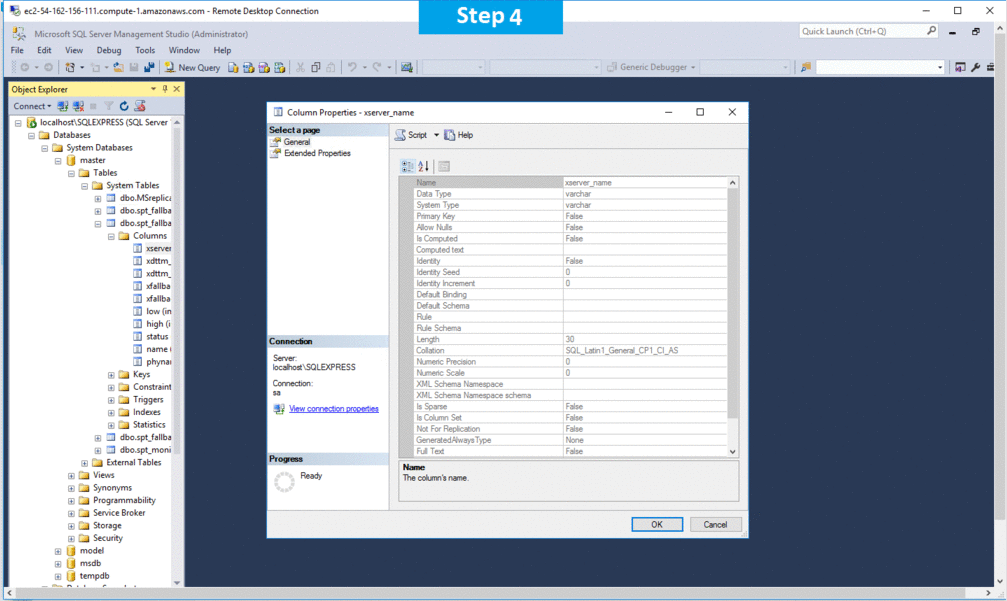
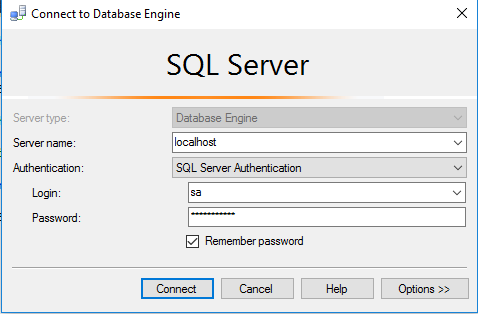
Step 2) SQL Connection: To Connect Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio in Windows server, Please follow Instructions to Connect Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
Step 3) Database Credentials: You can Login by below SQL Database credentials
SQL UserName : sa || Password : Passw@rd123
Note: You can reset ‘sa’ password by using windows authentication to connect to local SQL instance.Please use localhost in the server name when connecting from inside the RDC
Note: Please change the password after the first login.
Step 4) Other Information:
1.Default ports:
- Windows Machines: RDP Port – 3389
- Http: 80
- Https: 443
- SQL Server Port: 1433 this is by default not allowed on the firewall for security.
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link
Installation Step by Step Screenshots