1-click AWS Deployment 1-click Azure Deployment 1-click Google Deployment
Overview
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server is a contemporary, modular operating system for both multimodal and traditional IT. This document provides a high-level overview of features, skills, and restrictions of SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP2 and highpoints significant product updates.
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP2 is a multimodal operating system that overlays the way for IT transformation in the software-defined epoch. The modern and modular OS helps streamline multimodal IT, makes traditional IT infrastructure efficient and provides an engaging platform for developers. And we can effortlessly deploy and transition business-critical workloads across on-premise and public cloud environments.
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 is a multimodal operating system that covers the way for IT transformation in the software-defined epoch. The modern and modular OS helps simplify multimodal IT, makes traditional IT infrastructure efficient and provides an engaging platform for developers. Also you can effortlessly deploy and change business-critical capabilities across on-premise and public cloud environments. SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1, with its multimodal design, helps organizations transform their IT site by connecting traditional and software-defined infrastructure.
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP2, with its multimodal design, helps organizations transform their IT landscape by bridging traditional and software-defined infrastructure
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 presents many groundbreaking changes compared to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12. The most important changes are listed below.
Migration from openSUSE Leap to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
Starting with SLE 15, we support migrating from openSUSE Leap 15 to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15. Even if you decide to start out with the free community distribution you can later easily upgrade to a distribution with enterprise-class support.
Extended Package Search
Use the new Zypper command zypper search-packages to search across all SUSE repositories available for your product even if they are not yet enabled. This functionality makes it easier for administrators and system architects to find the software packages needed. To do so, it leverages the SUSE Customer Center.
Software Development Kit
With SLE 15, the Software Development Kit is now integrated into the products. Development packages are packaged alongside regular packages. In addition, the Development Tools module contains tools for development.
RMT Replaces SMT
SMT (Subscription Management Tool) has been removed. Instead, RMT (Repository Mirroring Tool) now allows mirroring SUSE repositories and custom repositories. You can then register systems directly with RMT. In environments with tightened security, RMT can also proxy other RMT servers.
MAJOR UPDATES TO THE SOFTWARE SELECTION
Salt
SLE 15 SP2 can be managed via Salt, making integrate better with modern management solutions, such as SUSE Manager.
Python 3
As the first enterprise distribution, SLE 15 offers full support for Python 3 development in addition to Python 2.
Directory Server
389 Directory Server replaces OpenLDAP to provide a sustainable directory service.
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP2 introduces changes compared to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server SP1. The most important changes are listed below.
Media Changes
The Unified Installer and Packages DVDs known from SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 are deprecated and have been replaced by the following media:
- Online Installation Media:All SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 products can be installed with this stand-alone media, after entering a registration key. The necessary packages are fetched from online repositories only.
- Full Installation Media:All SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 products can be installed without network connection with this media, for offline installation scenarios. The media contains all necessary packages. It consists of directories with module repositories which need to be added manually as needed. RMT (Repository Mirroring Tool) and SUSE Manager provide additional options for disconnected or managed installation.
Kernel SLE 15 SP2 includes the Linux 5.3 kernel. This new kernel release includes upstream features such as 16 million additionally usable IPv4 addresses, utilization clamping support in the task scheduler, power-efficient userspace waiting with the umwait x86 instructions and many more.
Vagrant Boxes
SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 SP2 will be available as a Vagrant Box for the Enterprise Server and the Enterprise Desktop releases. Users can obtain boxes for the following architectures and providers:
- Enterprise Server:
- x86_64: libvirt and VirtualBox
- ARM: libvirt
Support and Life Cycle
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server is backed by award-winning support from SUSE, an recognized technology leader with an established history of delivering enterprise-quality support services. USE Linux Enterprise Server 15 has a 13-year life cycle, with 10 years of General Support and 3 years of Extended Support. The present version (SP2) will be fully maintained and supported until 6 months after the release of SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP3.If you need additional time to design, validate and test your upgrade plans, Long Term Service Pack Support can extend the support duration. You can buy an additional 12 to 36 months in twelve-month increments. This means, you receive a total of 3 to 5 years of support per Service Pack.
Technology Previews
Technology previews are packages, stacks, or features delivered by SUSE to provide sights into upcoming novelties. Technology previews are comprised for your expediency to give you a chance to test new technologies within your environment.
Technology previews come with the following limitations:
- Technology previews are still in development. Therefore, they may be functionally incomplete, unstable, or in other ways not suitable for production use.
- Technology previews are not
- Technology previews may only be available for specific hardware architectures. Details and functionality of technology previews are subject to change. As a result, upgrading to subsequent releases of a technology preview may be impossible and require a fresh installation.
- Technology previews can be removed from a product at any time. This may be the case, for example, if SUSE discovers that a preview does not meet the customer or market needs, or does not comply with enterprise standards.
—
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server is a Linux-based operating system developed by SUSE. It is designed for servers, mainframes, and workstations but can be installed on desktop computers for testing as well.
At the same time, high-transaction applications like databases, event processing, and virtual machines need improved input-output (IO) rates and lower latencies. New hardware technologies like non-volatile memory address these concerns
Cognosys Provides Hardened images of SUSE Linux Enterprise Server on the cloud ( AWS marketplace, Azure and Google Cloud Platform).
Deploy SUSE Linux Enterprise Server securely on cloud i.e. AWS marketplace, Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Features
SLES(Suse Linux Enterprise Server) comprises of following new features:
- Easy transition from community Linux to enterprise Linux:It now takes just a few clicks for developers and operations to move an openSUSE Leap system to SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. Organizations can also install applications from the SUSE Package Hub.
- Enhanced support for edge workloads:SLES 15 SP1 for Arm 15 supports twice the number of system-on-a-chip (SoC) processor options. This broadens support for storage and industrial automation applications on 64-bit Arm server and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. For 64-bit Raspberry Pi devices, it now supports full HDMI audio and video and provides an ISO image for faster installation.
- Optimize workloads and minimize data latency:With Intel Optane DC persistent memory and second-generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors, SLES can be used to address the challenges of massive data increases with greater speed and agility while incurring lower infrastructure and management costs.
- Improved hardware-based data security:Service Pack 1 features full support for AMD’s Secure Encrypted Virtualization (SEV) SEV enables guest virtual machine (VM)s to run in encrypted memory. This helps protect them from memory scrape attacks from the hypervisor. SP1 also supports AMD Secure Memory Encryption (SME) which uses a single key to encrypt system memory.
- Reduced downtime for updates:Kubic transactional updates can now be used for atomic updates which replaces traditional updates. This decreases maintenance updates time, thus increasing production uptime.
- Simplified installation with enhanced Modular+:The Unified Installer can install more portfolio products, including SUSE Manager, SUSE Linux Enterprise Real Time, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Point of Service.
Diving deeper into the details, SLES 15 SP1 also supports:
- Installation without network using Packages media:To install without network connection, all necessary packages are available on the Packages medium. This medium consists of directories with module repositories which can be added manually as needed. SUSE Manager provide additional options for disconnected or managed installation.
- Extended package search: Use the new Zypper command zypper search-packages to search across all SUSE repositories available for your product even if they are not yet enabled. This functionality makes it easier for administrators and system architects to find the needed software packages.
- RMT replaces SMT: Subscription Management Tool (SMT) has been removed. Instead, Repository Mirroring Tool (RMT)now allows mirroring SUSE repositories and custom repositories. You can then register systems directly with RMT. In environments with tightened security, RMT can also proxy other RMT servers.
- Software updates: SLES 15 SP1 also can be managed with Salt DevOps The new Linux also supports Python 3 and the older Python 2. Finally, OpenLDAP has been replaced by 389 Directory Server.
SLES 15 has a 13-year life cycle, with 10 years of General Support and three years of Extended Support. The current version (SP1) will be fully maintained and supported until six months after the release of SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP2.
- Linux on Windows (without a virtual machine)
- True RPM package management using SUSE’s package repositories.
- System updates with zypper RPM package management.
- rsync, tar, vim, grep, sed, awk, and other UNIX tools without having to install or update CygWin.
- Linux has access to the Windows filesystem (Windows drives are automatically mounted in /mnt/ directory).
- Native “Linux style” connectivity using tools such as SSH, curl, wget, and more.
- SLES offers about every programming language a developer can choose. Go, Rust, Haskell, C++, Ruby on Rails, Java, Python, Perl and more
- SLES has multiple libraries for developers’ needs like libzypp, libvirt, glib, libstorage-ng and more.
- Build shared libraries with libvirt, use the set of shell scripts in libtool-testsuite.
- Use glib as a catch-all utility library for data types, macros, type conversions, string & file utilities, and more.
- Native “UNIX style” DNS capabilities (installed via zypper), such as BIND, pdns, dnsmasq, etc.
- GNU Compiler Collection 8 is available in addition to GCC 7.
openSUSE 15.0 – Leap
Following are the new in open SUSE release:
Base operating system
Linux kernel
Leap 15 ships with Linux 4.12. A prominent feature list and intricate details can be found on kernelnewbies.org.
Networking
Sysadmins can take full advantage of the network management protocol Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), allocate resources of the Domain Name System (DNS) or offer client computers access files over a Network File System (NFS). System Administrators and small businesses can use Leap for hosting web and mail servers or for network management with DHCP, DNS, NTP, Samba, NFS, LDAP, and hundreds of other services.
Security
Leap 15 has received all necessary backports and uses the same Enterprise Linux Kernel that SUSE uses.
OpenSSL
- Support for ChaCha20 and Poly1305
- Support for extended master secret
- CCM ciphersuites
- SSLv2 support removed
- Kerberos ciphersuite support removed
- RC4 removed from DEFAULT ciphersuites in libssl
- 40 and 56 bit cipher support removed from libssl
- Support for OCB mode added to libcrypto
- Support for RFC6698/RFC7671 DANE TLSA peer authentication
- New security levels
- Support for scrypt algorithm
- Support for X25519
- KDF algorithm support. Implement TLS PRF as a KDF.
- Support for Certificate Transparency
- HKDF support.
Hardware Support
Leap works with X86_64 and deployment scenarios can be run for physical, virtual, host and guest, and cloud. Ports to other architectures like ARM64 and POWER are in the works by the community.
More
systemd
Leap 15 has systemd version 234.
Support for dynamically creating users for the lifetime of a service has been added. If DynamicUser=yes is specified, user and group IDs will be allocated from the range 61184..65519 for the lifetime of the service. They can be resolved using the new nss-systemd.so NSS module. The module must be enabled in /etc/nsswitch.conf. Services started in this way have PrivateTmp= and RemoveIPC= enabled, so that any resources allocated by the service will be cleaned up when the service exits. They also have ProtectHome=read-only and ProtectSystem=strict enabled, so they are not able to make any permanent modifications to the system.
MemoryLimit= and related unit settings now optionally take percentage specifications. The percentage is taken relative to the amount of physical memory in the system (or in case of containers, the assigned amount of memory). This allows scaling service resources neatly with the amount of RAM available on the system. Similarly, systemd-logind’s RuntimeDirectorySize= option now also optionally takes percentage values.
In similar fashion TasksMax= takes percentage values now, too. The value is taken relative to the configured maximum number of processes on the system. The per-service task maximum has been changed to 15% using this functionality. (Effectively this is an increase of 512 → 4915 for service units, given the kernel’s default pid_max setting.)
The SystemCallFilter= unit file setting gained support for pre-defined, named system call filter sets. For example SystemCallFilter=@clock is now an effective way to make all clock changing-related system calls unavailable to a service. A number of similar pre-defined groups are defined. Writing system call filters for system services is simplified substantially with this new concept. Accordingly, all of systemd’s own, long-running services now enable system call filtering based on this, by default.
A new service setting MemoryDenyWriteExecute= has been added, taking a boolean value. If turned on, a service may no longer create memory mappings that are writable and executable at the same time. This enhances security for services where this is enabled as it becomes harder to dynamically write and then execute memory in exploited service processes. This option has been enabled for all of systemd’s own long-running services.
The unified cgroup hierarchy added in Linux 4.5 is now supported. Use systemd.unified_cgroup_hierarchy=1 on the kernel command line to enable. Also, support for the “io” cgroup controller in the unified hierarchy has been added, so that the “memory”, “pids” and “io” are now the controllers that are supported on the unified hierarchy.
A new command “systemctl revert” has been added that may be used to revert to the vendor version of a unit file, in case local changes have been made by adding drop-ins or overriding the unit file.
PHP 7
PHP7 is a server-side HTML embedded scripting language designed primarily for web development but also used as a general-purpose programming language. This package contains the standard implementation of PHP, namely Zend PHP. Included are the PHP command-line binary and the configuration file (php.ini). This package must be installed in order to use PHP. Additionally, extension modules and server modules (e.g. for Apache) may be installed. Additional documentation is available in package php-doc.
Printing System
Office and Groupware
Libreoffice
LibreOffice is a free and open source office suite, a project of The Document Foundation. LibreOffice is a comprehensive office package featuring a word processor, a spreadsheet, a presentation program, and much more. This package provides only the basic framework. You have to install the additional modules to get the required functionality, see packages: – libreoffice-base – libreoffice-calc – libreoffice-draw – libreoffice-impress – libreoffice-math – libreoffice-writer Some optional features are provided by extra packages, for example: – libreoffice-mailmerge – libreoffice-filters – libreoffice-kde4 – libreoffice-gnome Non-English localizations are provided by extra packages as well, for example: – libreoffice-l10n-de – libreoffice-l10n-fr – libreoffice-l10n-it
Writer
Various
- Direct cursor: Add option to insert only spaces tdf#108427 (Samuel Mehrbrodt, CIB)
- Find toolbar: Add drop down list to change search type tdf#79167 (Jim Raykowski)
- The main menu (top level) now has an entry “Form” tdf#91781 (Yousuf Philips)
- Page dialog: page orientation automatically adjusts based on manual input tdf#106890 (Heiko Tietze)
- Default column spacing (aka gutter) changed to 0.5cm tdf#67670 (Heiko Tietze)
- Support for split sections inside tables blog entry (Miklós Vajna, Collabora)
- New set of default numbering list styles tdf#106988 (Yousuf Philips)
Input fields
- Improved input field behavior tdf#79877 (Bernhard Widl, CIB)
- double click on input field brings up old input fields dialog
- that dialog now starts at current field and has previous/next navigation
Images rotation
- Implement rotation of images in Writer to any angle tdf#73797 (Armin Le Grand, CIB)
- This long requested feature (there are 20 year old reports) could now be implemented. It supports rotating Writer FlyFrames (e.g. inserted Graphics) freely around their center. UI elements to support this were added in various places (Dialog, Sidebar). Direct setting of rotation is extended to allow simple reset (‘Reset Rotation’). A ‘rotate’ interactive mode was added to allow the same interactions as when Draw-Objects are selected. The interactive Cropping was adapted to work with rotated graphics (WYSIWIG). When a frame is used, it gets ‘expanded’ to the bounding rectangle of the rotated graphic (a feature to allow rotating with the Object is planned for the future). The text can wrap around a rotated Image using the existing ‘Contour’ feature (‘Edit Contour’) adding a whole rectangle covering the Image using the Contour-Editor (a single action, e.g. a Button, to do this in one step may be implemented to make this more accessible to the user). The following picture shows examples of this feature in action.
Mail Merge
- Writer document as mail merge data source (Miklós Vajna, Collabora)
- Mail Merge now can use XLSX files as data source tdf#98168 (Miklós Vajna, Collabora)
- Temporary connections created during mail merge are no longer stored tdf#108572 (Szymon Kłos, Collabora)
Tables
- New default table style tdf#107554 (Yousuf Philips)
- Default table style applied to inserted tables tdf#107555 (Jim Raykowski)
- Default table border width changed to 0.5pt tdf#99027 (Yousuf Philips)
- Old collection of autoformat table styles were replaced with a new collection of table styles: Default, Academic, Box List Blue, Box List Green, Box List Red, Box List Yellow, Elegant, Financial, Simple Grid Columns, Simple Grid Rows, Simple List Shaded tdf#101349 (Andreas Kainz, Eike Rathke, Heiko Tietze, Yousuf Philips)
“Grammar By” spell checking
This is a general spell checking improvement of LibreOffice, but it can speed up especially the work of Writer users. Instead of manual handling of hundreds of correct word forms of a new word in a language with rich morphology or compounding, Hunspell spell checker will recognize the new user dictionary word with affixes or in compounds, too, based on a “Grammar By” model word. Screencasts about the usage: English, German.
Calc
Various
- Pivot table interop fixes (
- Default 2-entry color scale conditional formatting colors changed to Yellow and Green. tdf#86508 (Yousuf Philips)
- Enhanced “Links” dialog tdf#113807 (Serge Krot, CIB)
- Number format: accept English syntax keywords; some languages use localized keywords (AAAA for YYYY in French for instance). Now these languages can use English keywords to get valid format in any UI language tdf#33689 (Laurent Balland-Poirier)
- The main menu (top level) now has an entry “Styles” tdf#91820 (Yousuf Philips)
Exporting images
- A cell range selection or a selected group of shapes (images) can be exported to PNG or JPG graphics format with File ▸ Export… if the Selection checkbox is marked in the file dialog. tdf#108317 (Eike Rathke (Red Hat, Inc.))
Pasting: unformatted text
- The text/plain Unformatted text format results in unquoted/unescaped content as expected for external pastes. For single cell copy&paste embedded line breaks and tabs are preserved, for multiple cells they are replaced with spaces, effectively being a tab-separated-values (TSV) format. For intra-Calc on-cell pastes using the paste special toolbar button the Unformatted text [TSV-Calc] format can be used, which preserves embedded line breaks and tabs across multiple cells. tdf#113571 tdf#32213 (Eike Rathke (Red Hat, Inc.))
- Added “Paste unformatted text” command with its hot key Ctrl+⇧ Shift+Alt+V tdf#50746 (Serge Krot, CIB)
Protection, cells, sheets
- Added new command to select unprotected cells on protected or unprotected sheet. Located Edit ▸ Select ▸ Select Unprotected Cells. tdf#95883 (Gülşah Köse, Eike Rathke)
- If a tab is protected, the lock symbol (?︎) appears at the beginning of the tab name. tdf#95880 (Gülşah Köse, Eike Rathke)
New spreadsheet functions
- New ODFF1.2 compliant functions SEARCHB, FINDB and REPLACEB added (commit1, commit2, commit3). (Winfried Donkers)
- FINDB returns the starting position of a given text, using byte positions. FINDB is case sensitive.
- SEARCHB returns the starting position of a given text, using byte positions.
- REPLACEB returns text where an old text is replaced with a new text, using byte positions.
Impress and Draw
Various
- Addition of 10 new Impress templates and improvement of two existing templates tdf#103317 (Ashisuto, Yousuf Philips, Heiko Tietze, Laurent BP)
- Removal of confirmation dialog when setting image as slide or page background (preferably make use of Slide masters to set for more/all slides) tdf#112650 (Heiko Tietze, Samuel Mehrbrodt)
- Set default slide format 16:9 tdf#93244 (Heiko Tietze)
- Duplicate dialog ⇧ Shift+F3:
- Offer more possibilities for placement and enlargement tdf#61561 (Laurent BP)
- Enable negative angle commit (Laurent BP)
Layers in Draw Better UI for handling layer attributes tdf#89130 (Ulrich Gemkow):
- ⇧ Shift+click: toggle visible/hidden layer, with name in blue (like in previous versions)
- Ctrl+click: lock/unlock layer with italic name
- Ctrl+⇧ Shift+click: printable/not printable layer with underline name
New UI behavior for tabs attributes in Draw
ThunderBird
Mozilla Thunderbird is a redesign of the Mozilla Mail component. It is written using the XUL user interface language and designed to be cross-platform. It is a stand-alone application instead of part of the Mozilla application suite.
Browsers and Web Search
Chromium
Chromium is the open-source project behind Google Chrome. Chromium is an open-source browser project that aims to build a safer, faster, and more stable way for all users to experience the web.
Firefox
Firefox is created by Mozilla, a global non-profit organization dedicated to putting individuals in control online. Leap 15 ships version 60 which comes with the new Servo engine, a refreshed UI and WebExtensions.
Surfraw
Surfraw allows the user to launch Web search directly in terminal emulators with several different Web engines (called elvis in surfraw). For instance: surfraw duckduckgo opensuse will open a duckduckgo search page for the “opensuse” key word in the default web browser (defined in $BROWSER env var).
Desktop Environments
Enlightenment
Enlightenment window manager and desktop environment is really fast, configurable and beautiful. This package will provide the latest released version of enlightenment, as opposed to e16 or e17.
Changes
Enlightenment 0.22.3 is a bugfix and stability release for the Enlightenment 22 Release series.
Carsten Haitzler (5):
- fix autofoo build to match e auth patch backport
- desklock – make it fail to lock on non-bsd platforms if no pam support
- e desklock pam error – go back to previous text
- move from data_home/apps/defaults.list to config_home/mimeapps.list
- build – make pam a requirement on non-bsd unless disabled
Derek Foreman (1):
- Revert no-longer required pulseaudio hack for wayland
GNOME
The GNOME Desktop Environment in Leap 15.0 pulls in innumerous features and bug fixes from three major GNOME releases since version 3.20.x (which came out with Leap 42.3), GNOME 3.22, “Karlsruhe“, GNOME 3.24, “Portland” and GNOME 3.26, “Manchester“. Now bringing Wayland — the next generation technology for display and input on GNU/Linux, as its default desktop session. It eliminates graphics glitches, addresses long-standing bugs, and lays the foundation for more secure applications. Wayland also brings new functionality, such as multitouch touchpad gestures.
There have been a number of highly visible visual refinements for GNOME 3.26. These include:
- Windows now smoothly transition when they are maximized, unmaximized or snapped to one half of the screen. As well as looking good, this makes it easier to track what’s happening on screen.
- The size of window thumbnails has been increased in the Activities Overview, making it easier to pick the window you want.
- The top bar now becomes transparent when there aren’t any maximized windows. This is more attractive and gives a better sense of space.
- The dialogs which inform you when an application isn’t responding have a new style, making them look more integrated and refined.
GNOME 3.26 no longer shows status icons in the bottom-left of the screen. This prevents the status icon tray from getting in the way and is expected to provide a better overall experience. The lack of status icons is not expected to cause serious issues for users. However, if you do find that you need to access them, they can be restored using the TopIcons extension.
The visual style of many of the device, file type and application icons has also been improved, with a new more streamlined look. Extraneous bevels and shading have been removed and the overall brightness has been increased, resulting in a more engaging appearance. All the document and folder icons have been updated along with many application icons.
Support for machines that have two graphics cards is being provided now. If you have this hardware and switcheroo-control installed, you can select which GPU to use when launching an application. Settings will also give information on both graphics cards.
Flatpak is the next generation application distribution framework for Linux. This technology aims to make it easier to distribute applications for Linux, and thereby increase the number of applications that are available. Flatpak applications have other advantages, too: they are more secure, and can be safely updated without having to reboot.
GNOME now comes with comprehensive Flatpak support. The Software application is now able to install Flatpak repository files, which means that it is possible to install Flatpak repositories and applications without ever having to use the command line. Numerous other smaller changes makes it easy to install and update Flatpak applications, such as the display of source information for each application, as well as details about whether applications are sandboxed.
dconf Editor, the application for browsing and changing settings, has had a design refresh. The new version has a simplified interface, based around a path bar. A new “delay mode” allows multiple changes to be made at once. Additionally, several reset options allow either resetting visible settings, or recursively resetting them (for the current folder and any subfolders).
GNOME Applications
For Users
GNOME 3.26 got a new look for the Settings application, which has a new navigation sidebar and improved network and display settings, and browser synchronization thanks to the Firefox Sync service. Color emoji are now supported throughout GNOME and will be visible wherever they appear. It also includes ways to insert emoji into chats, messages and documents.
GNOME’s file manager, Files gained a much-demanded feature of batch-renaming files. Just select multiple files and hit Alt+F2 (or right click and select Rename) to sort out all your file renaming problems! Files also makes it easier and safer to work with restricted files and folders: if you try to do something that requires additional permissions, you will be automatically asked to enter a password.
System Search has a fresh layout that makes it easier to read the results as well as fits more results in the screen space. It also shows session actions such as power off, suspend, lock screen and others right in the search results.
Night Light support is now integrated into GNOME (since v3.24), subtly transforming screen colors toward the warmer to reduce interference with sleep patterns should you be using your device late at night.
Numerous improvements to the notifications area occurred throughout the 3.22–3.26 cycle, with a much cleaner, simpler interface the final result, not to mention the integration of weather reports in the notification area.
GNOME HiRes icons now look even better on HiDPI displays, having doubled in size from 256×256 to 512×512.
Photos gained a whole new photo-sharing feature that blends in with GNOME’s online accounts. Simply set up your Google account from Settings and start sharing your pics from Photos via google drive. It also looks gorgeous with improvements to the grid view showing high quality thumbnails of your photo collection.
Polari, the default IRC client in GNOME, has a brand new guided setup to get you up and running if you are using it for the first time. It also remembers your password and reuses it automatically when required. Polari has also gained the ability to run in the background, sending you notifications and letting you reply right from the notification area. Just select the “Run in background” option from the application menu. Finally, like other apps, you can now insert colorful emojis in your IRC messages too!
GNOME’s other browser Web — openSUSE ships Firefox as the default browser irrespective of the DE — has several new features of its own: you can now synchronize your bookmarks, passwords and browser history, using the Firefox Sync service; a brand new address bar; overhauled bookmarks, with a new, simple, one-click interface for bookmarking pages, a bookmarks popover for quickly accessing your bookmarks, and a new interface to easily organize them; and a host of privacy related improvements. Just install Web from GNOME’s Software store and you are ready to go!
Speaking of GNOME Software, the app store, it has gained several usability and feature improvements of its own. Users will notice a fresh look that minimizes clutter, putting installed and available apps at the front and center of the UI. It also sports an updated view for user ratings and displays disk space usage for each application.
GNOME Calendar has grown up! It now sports a weekly view, drag-and-drop support for events, support for adding and editing recurring events and for doing all that offline (results are synced online when you go online some time thereafter).
For Developers and System Administrators
GTK+ Long Term Support
The 3.22 marked a significant moment in the history of GTK+. While it did not have a .0 version number, 3.22 was the first in a major new stable release series and is the first major GTK+ version since 3.0. Subsequent releases in the 3.22.x series are guaranteed to be API and ABI stable, with new releases being limited to bug and security fixes. These 3.22.x updates will be provided for at least three years (until 2019). Major development work will continue in a separate release series, which will be consumable by application authors who want the latest features and are happy to deal with a moderate amount of instability.
GTK+ 3.22 made all the improvements introduced in the 3.x series, such as CSS styling, GTK+ inspector, animations, new widgets and much more, available in a stable form. This new way of organizing GTK+ releases promises to provide long-term stability for application authors who require it, while not impeding the overall speed of GTK+ development. It was introduced after significant discussion and consultation with GTK+ users
Glib’s structured logging
GLib’s logging API has been reworked to support structured key–value log fields. This makes it easier to add logging and makes it possible to write more powerful logging schemes. It also makes it possible to include more metadata in log messages.
As a part of this work, GLib’s logging infrastructure has been reorganized around a “writer” function, where an application specifies its logging policy. Log handlers are deprecated in favor of this, which reduces ambiguity about how and where logs should be handled, and eliminates conflicts between log handlers.
GLib will now automatically pass logging data to systemd-journald, if it is running. stdio-based output works as previously, but with the addition of color!
Builder
The GNOME integrated development environment (IDE), has made major advances in 3.26, with general improvements as well as new features. One of the most obvious changes in the new version is a redesigned editor interface. This makes it easier to open and switch between files, terminals and documentation, using either the header popover or the project sidebar. There have been a lot of user interface refinements as part of this work, including document headers which blend into the background.
With 3.26 it’s now possible to search for symbols throughout your project. Selecting a search result jumps to that location, so you can quickly navigate using only the keyboard. The presentation of search results has also been improved.
It now includes a debugging feature for the first time in 3.26. This is an initial preview and is expected to mature in subsequent releases. The debugger allows running your project in debug mode and to step through to find the source of issues. It supports debugging Flatpak applications.
Flatpak
It’s the new technology for distributing and installing applications. While it’s independent of the GNOME project, Flatpak is an increasingly important part of GNOME’s developer experience, and is integrated throughout GNOME.
Some of the enhancements that have been introduced include:
- Improved support for the Open Container Initiative (OCI) specification.
- flatpak-builder has been separated into its own module.
- Flatpak applications can now be used through accessibility frameworks.
- It’s now possible to use input methods within Flatpak applications.
- An experimental peer to peer installation method allows using dynamically available software sources, including removable media or resources on the local network.
- Flatpak now supports a default language setting, which is used to ensure that the correct translations are installed for each application.
- Improved progress reporting, particularly for download and installation progress.
- Lots of improvements to the command line interface, including a new flatpak repo command, better presentation of results and smarter handling of .flatpakref files.
flatpak-builder, the tool for generating Flatpak applications, has been split out into its own module and has had a lot of improvements. These include:
- Performance improvements which make building much faster.
- It’s now possible to specify both a tag and commit ID for Git sources.
- Manifests can specify SDK extensions to be installed for the application to build.
- A new add-extension property makes it easier to create extension points.
- –from-git=URL allows pulling the JSON manifest and related files directly from a Git repository.
Other Little Improvements
- Simple Scan has had some interface improvements for 3.26. A new start screen provides some useful guidance, editing tools are easier to identify and preferences can be accessed from the header bar.
- Logs now groups similar messages together, which makes the history much shorter, making it easier to find what you’re looking for.
- When you resize a file system in Disks it’s now possible to also resize its partition, which often saves an extra task.
- Maps has a collection of small improvements: there are new keyboard shortcuts, more information is shown about places and the last transportation method is remembered when plotting routes.
- GNOME’s calendaring, contacts, to do and mail applications now perform better offline — many items can now be edited when you don’t have an internet connection, and any changes will be uploaded the next time you are online.
- Photos has new controls for zooming.
- It’s now possible to add and edit reoccurring events in Calendar.
- Terminal now highlights and makes it easy to open hyperlinks.
- In Evolution, the new To Do bar allows you to view a list of upcoming events and tasks. Also, it’s now possible to use Evolution without having a mail account.
- Tweak Tool has been renamed to Tweaks and has gained three new settings: a switch to move window buttons to the left or right, a Disable While Typing option for touchpads and an option to show the battery percentage in the top bar. There has also been a good amount of clean up and refinement.
- GNOME’s use of typography has been improved, by making maximum use of Unicode. Many of these changes are subtle but give a better appearance overall.
- The Calculator has had a number of enhancements, including an improved appearance, a keyboard shortcuts window, new variables and functions popovers, better error highlighting and improved complex number handling.
- Polari is now able to remember and automatically reuse passwords that have been sent to NickServ.
- Maps now uses Mapbox as the supplier of its OpenStreetMap data. This is expected to provide a more reliable service in the future.
- Performance has been dramatically improved in Music. The application now loads faster and the albums grid automatically adjusts to make the best use of the space available.
- Videos now allows playback at different rates. This is useful for various things, such as when listening to talks or taking notes.
- Boxes has gained a clone function. This makes it easy to create copies of your boxes.
KDE
Plasma 5.12 LTS is the second long-term support release from the Plasma 5 team. We have been working hard, focusing on speed and stability for this release. Boot time to desktop has been improved by reviewing the code for anything which blocks execution. The team has been triaging and fixing bugs in every aspect of the codebase, tidying up artwork, removing corner cases, and ensuring cross-desktop integration. For the first time, we offer our Wayland integration on long-term support, so you can be sure we will continue to provide bug fixes and improvements to the Wayland experience.
Smoother and Speedier
Speed and memory improvements are the focus of this long-term release. The new Plasma LTS uses less CPU and less memory than previous versions. The process of starting the Plasma
openSUSE technologies
AutoYaST
Administrators in need of mass deployments e.g. in cloud solutions will find helpful improvements in AutoYaST. Its profiles contain installation and configuration data to simplify unattended installations. The new AutoYaST version benefits from cleaned-up profiles, extended documentation and now supports the new partitioning features of libstorage-ng.
Kubic
This release has a system role selection that offers a classic server role and a Transactional Server role. Contributed by openSUSE’s container platform project Kubic, this role uses transactional updates and a Read-Only Root Filesystem to provide Leap with all the benefits of atomic updates in a multitude of use cases, including container hosts, Internet of Things (IoT), and classic server functions with potential future applications also involving desktops. Transactional Updates provides openSUSE systems with a method of updating the operating system and it’s packages in an entirely ‘atomic’ way. Updates are either applied to the system all together in a single transaction, or not at all. This happens without influencing the running system. If an update fails, or if the successful update is deemed to be incompatible or otherwise incorrect, it can be discarded to immediately return the system to its previous functioning state.
YaST
Leap 15 further improves one of openSUSE’s most powerful tools YaST. For example, the partitioner’s Libstorage-ng subsystem has been reworked, making it more powerful and reliable and taking ease-of-use to a new level. The same applies for the move from SuSEfirewall2 to the widely used firewall management tool Firewalld which provides better integration with dynamic network setups.
Leap 15 also improves experience when using non-major desktops. As opensuse switch from hardcoded list of desktops to update-alternatives approarch, now it is possible to simply pick any desktop and it will be used even when it is exotic desktop.
Another important part of YaST is adapting to changes done in Linux and openSUSE world. So YaST switches from ntp daemon to chrony implementation for ntp protocol. Also xinetd was dropped and everywhere is used systemd sockets. And last but not least ftp-server was simplified to support only single backend vsftpd and drop pureftp. This allows to simplify code and makes switch to systemd sockets easy.
VNC during installation is useful when user has no access physical access to machine. For Leap 15 we switched browser vnc from java applet that is no longer supported in browsers to javascript one.
Multimedia
- openSUSE Leap 15.0 features VLC 3.0, the major upgrade to the immensely popular multimedia player. The update features a slew of improvements, including HiDPI support, Wayland support and lots more.
- Vocal is a beautiful podcast manager and player that makes its openSUSE debut in Leap 15.0. It features podcast browsing and subscription from the iTunes store, automatic download of new episodes for your subscribed shows and much more.
- Audio player Lollypop sees an update to version 0.9.508 featuring a new lyrics widget, improved album art fetching and display, and better queue management.
- Amsynth, an analog modelling synthesizer, is brought up to version 1.8.0 with improved plugin integration and several bug fixes.
Scientific and Educational Apps
- Armadillo the blazingly fast C++ linear algebra library sees a bump to version 8.400.0 (from 7.300.0 in Leap 42.3) featuring improved and faster sparse matrix handling, new statistical functions and numerous bug fixes.
- openSUSE Leap 15.0 releases with version 8.1 of the scientific data visualisation toolkit VTK, a major refresh from the 7.0.x series carried on Leap 42.3 especially focusing on massively parallel processing on GPUs and multi-core processors, amongst other numerous improvements.
- Paraview, a large-scale data analysis and visualization application based on VTK, sees an update to the 5.4 series featuring much improved HiDPI support and, for the first time, support for virtual reality visualisations based on OpenVR. Leap 15.0 ships with Paraview 5.4.1, which is a bug-fix update to version 5.4.0.
- Scilab, a powerful open source software for numerical computation has been updated to version 6, bringing forth a new language parser and a refreshed core.
- Maxima, the popular and powerful computer algebra software, got bumped to version 5.41 bringing a much improved differential equation solver, several new functions, speed improvements in existing functions, improved plotting capabilities with gnuplot 5.0 support baked-in, and lots more — and that’s without even mentioning the plentiful bug fixes! The handy GUI app for Maxima, wxMaxima, is now at version 18.02 and features improved HiDPI support, improved notebook structuring, speed improvements and many bug fixes of its own.
- Engauge digitizer is a data picker from plots and charts and it sees an upgrade to version 10.4 bringing support for plots with a scale bar, improvements to its file format and better support for RTL languages.
- Stellarium is updated to version 0.16.1, featuring a new AstroCalc tool, Remote Sync plugin, GPS device support amongst numerous other improvements.
- Veusz is a python-based GUI plotting app, and sees many new features including the addition of color themes in plots, n-dim data support and much more as it sees a bump to version 2.1.1. It is now built against Qt5 rather than Qt4.
- PLplot, a plotting library with bindings in several programming languages, got updated to version 5.13.0, and now comes with python3 and Qt5 support, completely rewritten Fortran binding, and improvements for its wxWidgets device driver.
- Form, a symbolic calculator, has had its first major release in four years, and we have got this update (version 4.2.0) covered with Leap 15.0! It comes with “more than 360 revisions, including more than 50 bugfixes, and the introduction of more than 20 new features.”
Security
dehydrated / letsencrypt
Dehydrated is a client for letsencrypt. The SUSE integration provides templates for Apache, nginx and lighttpd. It also supports DNS-based issuance including support for wildcard certificates.
GNU Compiler Collection
GCC has been bumped to version 7, bringing support for C++17 to Leap.
—
Major Features Of SUSE 15.0
Security and Identity Management:
- Reliability, Availability and Serviceability
- Key Technical Features
- Customized Images
- System Reliability and Security
- Lower Total Cost of Ownership
- Freedom from Vendor Lock–in
- Established Ecosystem
- New in Service Pack 3
- New in Service Pack 2
Azure
Installation Instructions For Suse
Installation Instructions For SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
Note: How to find PublicDNS in Azure
Step 1) SSH Connection: To connect to the deployed instance, Please follow Instructions to Connect to SUSE instance on Azure Cloud
1) Download Putty.
2) Connect to the virtual machine using SSH key Refer this link:
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 22
Step 2) Other Information:
1.Default ports:
- Linux Machines: SSH Port – 22
2. To access Webmin interface for management please follow this link
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link
AWS
Installation Instructions For Suse
Installation Instructions For SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
Note: How to find PublicDNS in AWS
Step 1) SSH Connection: To connect to the deployed instance, Please follow Instructions to Connect to SUSE instance on AWS Cloud
1) Download Putty.
2) Connect to the virtual machine using SSH key Refer this link:
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 22
Step 2) Other Information:
1.Default ports:
- Linux Machines: SSH Port – 22
2. To access Webmin interface for management please follow this link
Configure custom inbound and outbound rules using this link
Installation Instructions For SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
Step 1) VM Creation:
1.Click the Launch on Compute Engine button to choose the hardware and network settings.
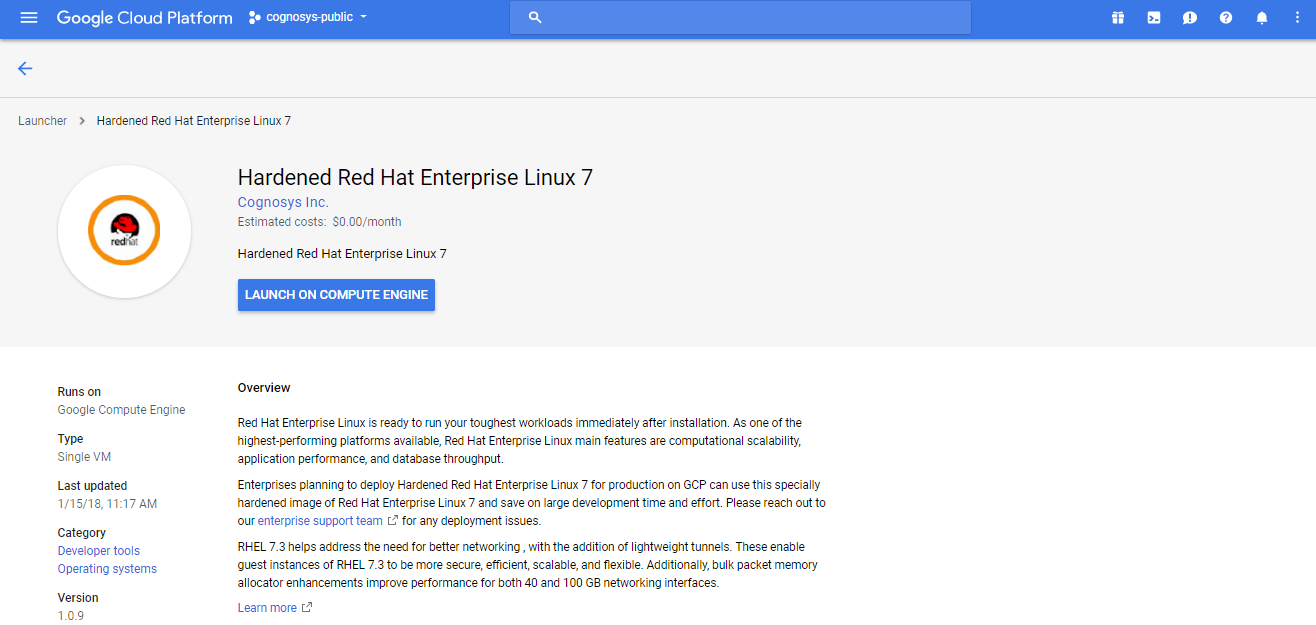
2.You can see at this page, an overview of Cognosys Image as well as some estimated costs of VM.
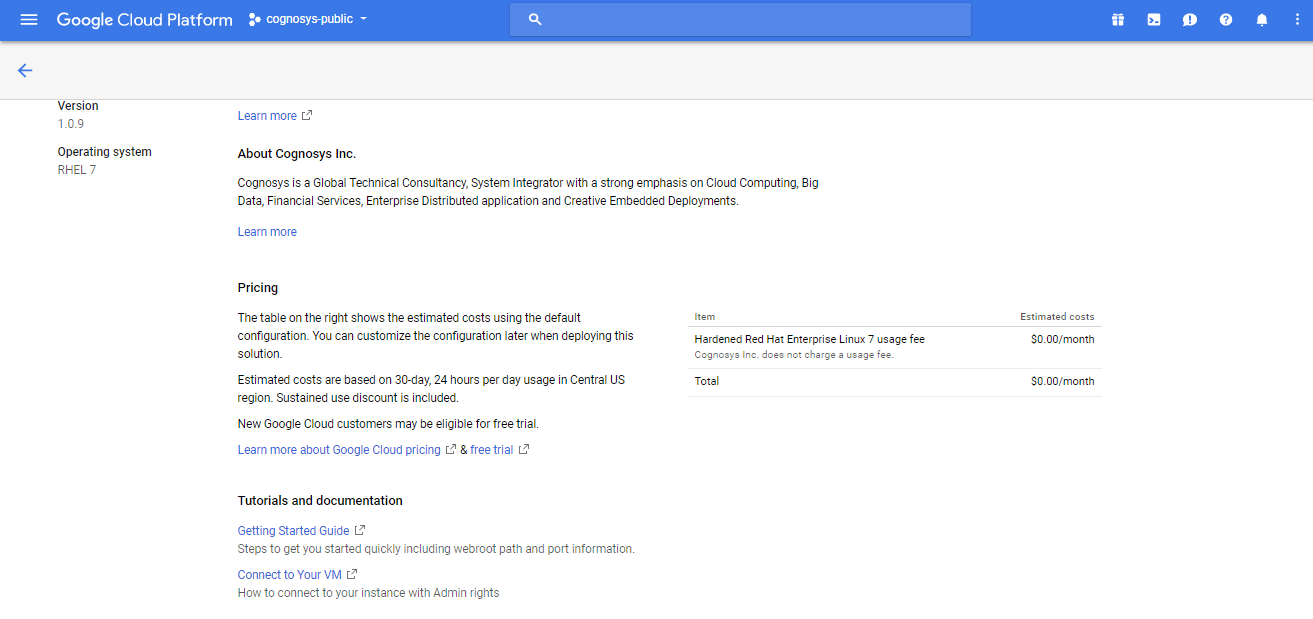
3.In the settings page, you can choose the number of CPUs and amount of RAM, the disk size and type etc.
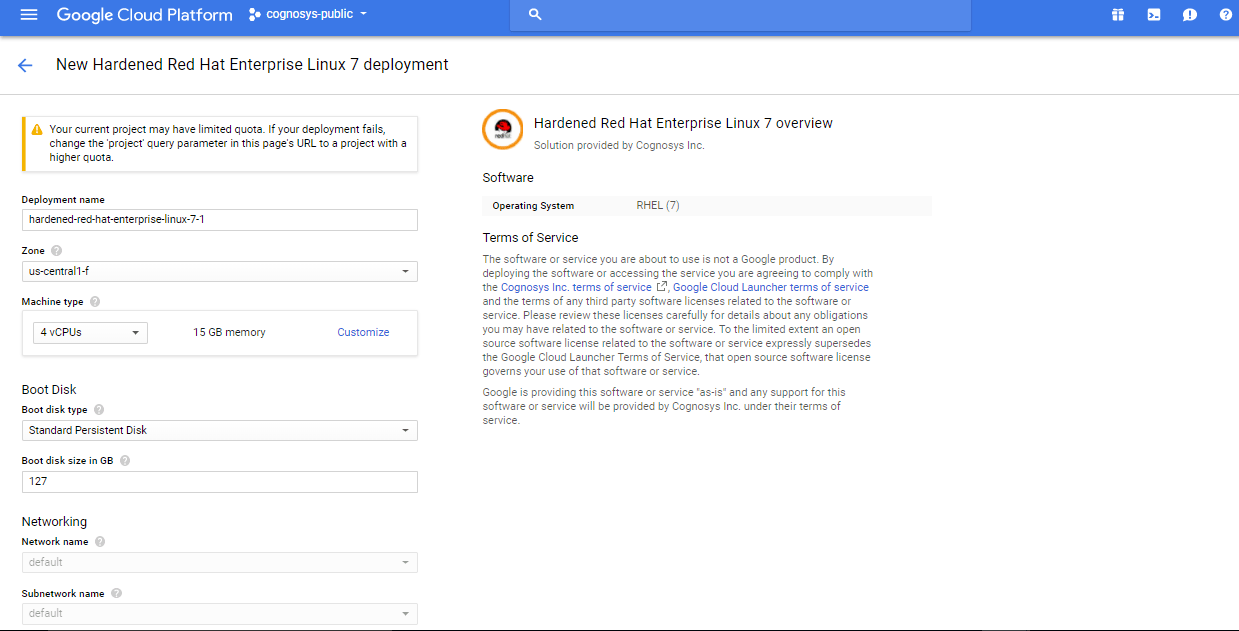
Step 2) SSH Connection: To connect to the deployed instance, Please follow Instructions to Connect to Suse
1) Download Putty.
2) Connect to the virtual machine using SSH key
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 22
Step 3) Other Information:
1.Default ports:
- Linux Machines: SSH Port – 22
2. To access Webmin interface for management please follow this link
Video
Suse Installation


