Overview
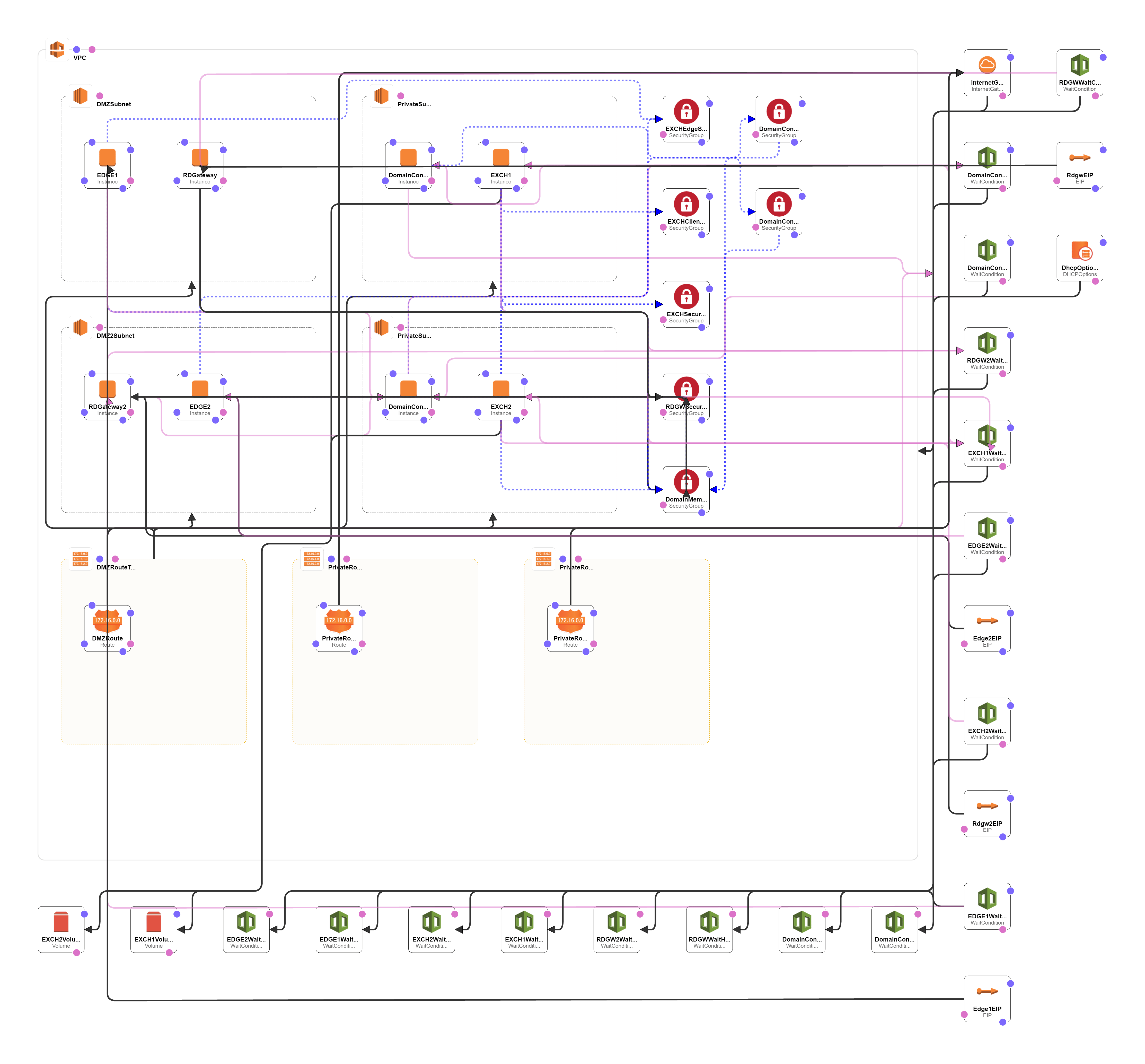
The new Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Building Block Architecture. The Exchange Server 2016 mailbox servers on the Internal network are the points of communication for all clients, Active Directory and all other services that communicate with Exchange server. Internet client communication is also routed to the Exchange mailbox server. It is not recommended you expose the Exchange Client Access server directly on the Internet. Traffic should be routed via a LoadMaster appliance acting as a reverse proxy. The Edge Transport server should also be positioned in the perimeter network where it can help protect the internal mailbox servers. DNS MX records should be configured to use the Edge Transport server, or to any hosted solution like Microsoft Online protection which can then forward mail to the Edge Transport server.
 What is Exchange Server?
What is Exchange Server?
Exchange server, being a product of Microsoft, is a mail server and calendar server, that helps small and medium scale companies to achieve better reliability and improved performance.It runs only on Windows Server Operating systems. It can also be called as a server-side application which provides data to the client-side collaborative application platform. This messaging platform or exchange mail server provides flexibility for sending emails, calendaring, voicemail transcriptions, scheduling, and tools to customize collaboration and messaging service applications.There are various other email protocols apart from an exchange server, like POP3, IMAP, MAPI, and Exchange ActiveSync.
Benefits of Exchange Server
Microsoft Exchange server plays a vital role in your day to day life. Be it official documents, security or mobility, Exchange server’s capabilities could not be paralleled so far.
The top 10 benefits of an exchange server are:
- Official appointments: The mail exchange server won’t let you miss an appointment again. It will inform your customers in case you are out of office, as they get an auto-generated reply right away.
- Confidentiality of emails: When you are out of your office, it gives you the flexibility of allowing your trustworthy colleagues to check that nothing important gets unnoticed. Thus, it keeps the business moving forward by enabling others to check your availability for a crucial meeting and book appointments.
- Address book feature: Now, you need not worry about the email address of different employees. All the addresses will be automatically updated in the address book and will come in handy during an urgent requirement like bulk messaging or other urgent confidential messaging ensuring security.
- Enhanced team productivity: It helps in maintaining proper communication between employees by providing them access from home, office, away from the office or abroad. Thus, it simplifies the means of communication very effectively and helps in rapid growth and productivity.
- Cost effective: In comparison to other email protocols, Exchange mail server reduces the cost of communication because it is quick and consumes less budget as compared to a phone call, fax, and type and send hard copies of letters.
- Customer satisfaction: Microsoft exchange server enables companies to be extremely responsive to customers’ queries and resolve issues at the earliest possible leading to the greater satisfaction of customers in no time.
- Security: It offers better security options than fax and emails. The companies need not worry about leakage of confidential data as it has features like leakage protection, archiving and retention of sensitive information, without compromising on the maintenance of compliance with the government’s and industry’s regulations.
- Mobility and portability: Exchange server enables a company’s employees /users to securely access email messages, instant messaging, voice mails, video calls and SMS texts from anywhere in the world. All they need is a computing device of their choice (a laptop, desktop, tablet or mobile phones) and an internet connection.
- Cloud Computing benefits: Exchange allows the users to move to the cloud on their terms – be it immediate on-boarding to the cloud or managing a hybrid deployment with on-premises and online mailboxes to meet their business needs.
It provides the end users a seamless experience that includes sharing multiple calendars and scheduling meetings between on-premises and online users.
- Agility: Exchange server helps in decreasing the amount of time spent in managing the messaging systems providing very flexible control, and thus, enhancing the speed of the processes.It also manages most of the powerful capabilities that include Apps for Outlook, DLP, and site mailboxes from the Exchange Administration Centre – a single, handy, web-based administration interface.
How do Emails work?
Before we understand how exchange server works, let us discuss how email works.At first, the user creates and sends a message to an email client that uses the Microsoft Exchange Server. In the beginning, they need to connect or link the account to the server. This happens automatically upon signing in.Once the message is sent, it goes to the server and will be stored in certain server’s database location.
The moment an email message is stored in the database of the exchange server, they are routed to the appropriate client by sending a notification to their account.As soon as the receiver’s account gets the notification that there is an incoming message from the server (this requires an internet connection in the client’s system), the server transfers the message to the recipient’s inbox. Soon after that, the recipient can open the message.


(This is how email practically works.)
Now let us discuss How Exchange Server works
Exchange server has four primary components which work hand-in-hand to run the process smoothly.
The components of the mail exchange server are:
1.) Information Store: This is the place where email messages are stored, located and organized.
2.)System Attendant: It makes these messages relevant to the client sending and receiving the
message. In other words, it creates and manages email addresses.
3.) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP): This is the component that plays the vital role. It allows inter-server message transmission. Often messages are supposed to be relayed from one server to another, especially in the case where the location of the recipient client is quite far, and/or is using a non-Microsoft email provider.
4.) Active Directory: Its job is to update the system attendant with new mailbox information. It also manages user accounts and distribution lists by itself.With the functionalities of the individual components, their roles are clear. Hence, Microsoft Exchange Server requires all of the components mentioned above to deliver flawless service to the user.
The user can thus create new email accounts, manage various forms of data, such as calendars, address books and emails. Rest assured, the sent emails are delivered to the inbox where it is supposed to be so that the communication between the users is quick and efficient.
Exchange Server Version List
Apart from Exchange Server, Microsoft has sold many simpler email products, but this is entirely new and a remarkable one. It is X.400 based client-server mail system that comes with a single database store supported by X.500 directory services.
Exchange Server’s directory eventually became Microsoft’s Active Directory service( a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol(LDAP)-compliant directory service. Later, it was integrated into Windows 2000 as the foundation of Windows Server domains.
Exchange server 4.0 was released in March 1996 and it tops in the exchange server version list. There were five service packs (SP) released over a couple of years.The latest release, exchange server -2016 came up with a few spectacular features and multi-compatibility solutions:
- Combine roles: The number of available roles came down to two – Mail Box Server and Edge Transport.
- Office 365 hybrid: The Hybrid Configuration Wizard (HCW), formerly included with Exchange 2013 is going to change into a cloud-based application. When the user chooses to a hybrid deployment in the current version, he must download and install the wizard as a small app.
- Outlook on the web: It was formerly known as an Outlook Web App and the latest release has a few changes in the UI.
Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Architecture
With the release of Exchange Server 2016 Microsoft took the opportunity to simplify some of the architecture complexity that was present in previous versions. It also includes new features which make communication and collaboration easier. Microsoft has changed the way Exchange deployment has been done for the last few releases. Implementation is now easier, the configuration is simpler, and upgrading has fewer steps. The number of servers required have been reduced, as have licensing costs and infrastructure requirements. Hybrid deployments are also much easier using on premise and Exchange Online or Office 365, which can further reduce the required on premise infrastructure.
Microsoft simplified the architecture by removing the Exchange 2013 Client Access Server role and added it as a service on the Exchange 2016 Mailbox Server Role. Now there is just one Exchange 2016 Mailbox Server role with Client Access and Transport services included on it. The Edge Transport Server is retained from the previous versions of Exchange and provides inbound and outbound mail routing as well as anti-spam, antivirus, and content connection filtering via address rewriting to protect internal servers.

The Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Client Access Service (CAS) running on the mailbox servers can communicate with legacy Exchange servers using the same protocols as Exchange Server 2013 and 2010. This includes protocols like EWS, MRS Proxy, and SMTP Transport. If Exchange 2016 sends an email to a Exchange 2013 user, then the Exchange 2016 transport service forwards the email to an Exchange 2013 server and then the mail is delivered to the user’s mailbox. This feature helps Exchange Server 2016 to co-exist with legacy Exchange servers without having to implement a completely new Exchange Server 2016 deployment. Currently Exchange Server 2016 can co-exist only with Exchange Server 2010 SP3 RU11 and Exchange Server 2013 CU11. It cannot co-exist with Exchange 2007 or earlier versions.

Figure 2: Exchange 2016 Server Communication with other Exchange versions
In Exchange Server 2016 clients connect to a mailbox server, but the interactions are with the Client Access Service that is running there. The target mailbox that a client is using could be on the same server or a different mailbox server. In the latter case the Client Access Service proxies the client connection to the correct backend server connected to the active Exchange database.

Figure 3. Clients Communication with Exchange 2016 Mailbox Server
Below are some noteworthy new features and improvements in Exchange Server 2016.
Mailbox Server Enhancement Features
- Database Divergence Detection – Detects database corruption, determines the cause, then fixes the issue and reseeds the failed database to return it to a healthy state.
- Loose Truncation – Introduced initially in Exchange Server 2013 SP1. If a server or database is offline, then the other active and passive copies accumulate all the transaction logs without truncation until the offline server/database comes online. This can lead to the available disk space on these servers filling up and cause them to go offline. Loose Truncation allows each database copy to track its own free disk space and start to truncate transaction log files independently if the available disk space falls below a threshold set by the administrator.
- ReFS Support – Resilient File System (ReFS) is a new file system introduced in Windows Server 2012. Exchange Server 2013 databases could be placed on this file system. In Exchange Server 2016 it is recommended. It provides more robust storage and resilience features to reduce the possibility of database corruption, and hence the number of database reseeds.
- Replay Lag Manager – Introduced as part of the high availability enhancements in Exchange 2013. It is a component of the Microsoft Exchange DAG management service, the process that deals with tasks like checking whether databases have sufficient redundancy.
- DAG deployments are simpler and can be deployed without a cluster administrative access point
- DAG File Share Witness instances can now be placed in Microsoft Azure to provide 3rd party site resilience
- Content or search indexes are built from the local database copy rather than from the active database, which can sometimes cross the network, thus reducing network utilization.
- BitLocker can be used to encrypt Exchange Server 2016 disks to provide additional security.
- OPs use has been reduced by 22% from Exchange 2013 which allows more users per mailbox server.
Hybrid Enhancement Features
- Exchange Server 2016 is Cloud ready and built on hybrid capabilities introduced in Exchange Server 2013 and tested in Exchange Online and Office 365 over the last few years.
- Exchange Server 2016 on premise deployments also make use of some of the Office 365 Cloud features such as archiving, data loss prevention, rights management, advanced thread protection, mobile device management, and SPAM & virus filtering.
Client Enhancement Features
- MAPI over HTTP is now the default protocol for Outlook communications with Exchange Server. MAPI over HTTP is a more robust, stable and reliable client communications protocol.
- Outlook and Outlook Web Access (OWA) can collaborate with SharePoint Server 2016 or OneDrive for Business to share and edit documents with email recipients. Email recipients are automatically provided permissions to edit shared documents.
- Search has been significantly enhanced in Exchange Server 2016. Search speed is also greatly increased, and Calendar items can also be searched via OWA.
- A smarter Inbox in Outlook 2016 helps users to manage email to increase their efficiency and productivity. It also includes a new intelligent recipient and people search, a ‘Tell me what you want to do’ search option, plus the ability to do inline previews of URLs and videos in Outlook 2016.
- Enhancements in OWA include one-click archiving, better spell checking and autocorrect, contacts import from CSV files, better format controls, better attachment views, inline replies, insert images, pin items, undo, and more.
Mobile Enhancement Features
- Mobile Outlook increases productivity by providing a rich user experience on phones and tablets. It now presents two tabs called Focused and Other. Outlook intelligently uses Focused for all important email, and Other contains items like newsletters, system notifications, subscriptions and another general email. Search in Mobile client is improved to provide filtered and accurate search results.
- One of the new interesting features in mobile Outlook is Send Availability. It is used to send available time slots to recipients when planning meetings.
- Mobile Calendar view has been improved. It provides more detailed information of all invitees and other meeting information. It also allows joining a Skype meeting directly from a mobile device.
Security and Compliance Enhancement
- The Data Loss Prevention (DLP) feature has been enhanced by adding new DLP sensitive information types into Exchange.
- Auditing has been enhanced and updated with a new architecture and schema. Built on the Exchange 2013 Audit log model, it follows the Office 365 Audit logging schema. In Exchange Server 2016 audit logs are no longer stored in a user’s mailbox, but rather in a centralized audit report mailbox for the organization. This helps with the long term retention of logs and the generation of reports from the log data.
- eDiscovery search has been improved via the eDiscovery console to provide more reliable results and increased speed. Public Folders can now also be put on hold so that contents cannot be deleted.
Exchange Server 2016 installation step by step
Before you install Microsoft Exchange Server 2016, you need to prepare your Active Directory forest and domainsThis preparation will be done through the following 3 steps:
Extend the Active Directory schema
The first step in getting your organization ready for Exchange 2016 is to extend the Active Directory schema by running the following command:“Setup.exe /PrepareSchema /IAcceptExchangeServerLicenseTerms”The account you’re logged in as needs to be a member of the Schema Admins and Enterprise Admins security groups
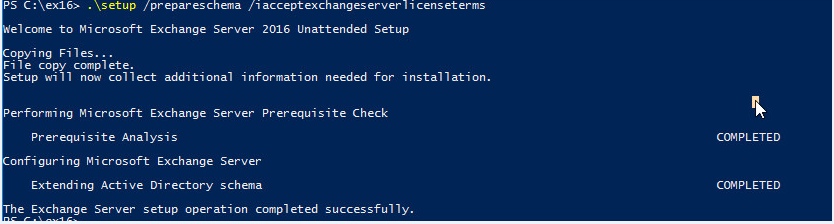
Prepare Active Directory
The second step that Exchange will create containers, objects, and other items in Active Directory that it’ll use to store information by running the following command:
“Setup.exe /PrepareAD /OrganizationName:”<organization name>” /IAcceptExchangeServerLicenseTerms”
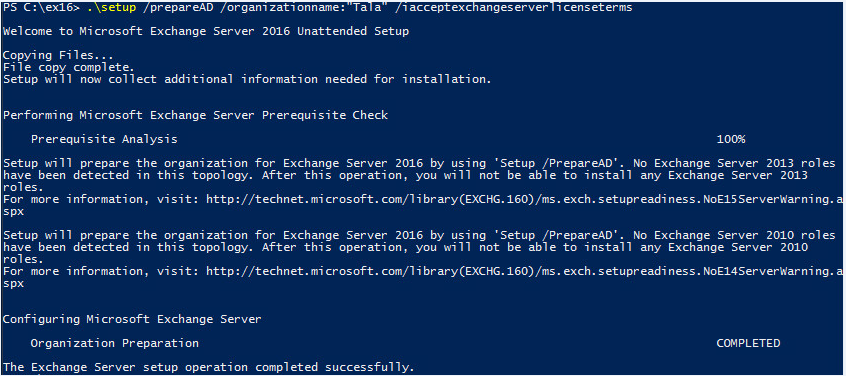
Prepare Active Directory domains
The final step
is to prepare each of the Active Directory domains where Exchange will be installed or where mail-enabled users will be located by running the following command:
“Setup.exe /PrepareAllDomains /IAcceptExchangeServerLicenseTerms”
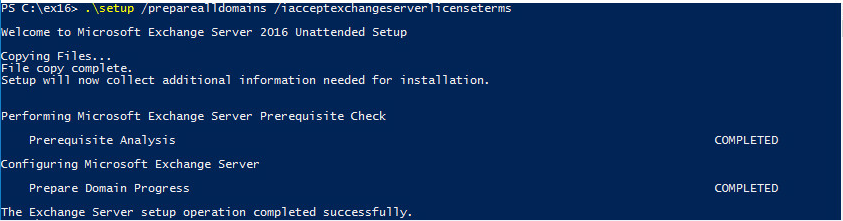
Finally after these 3 steps; your Active Directory environment will be ready for exchange installation.
Then we will install the first Mailbox server to our environment.
These steps should be implemented after the active directory preparation.
- Open the Setup.exe
-
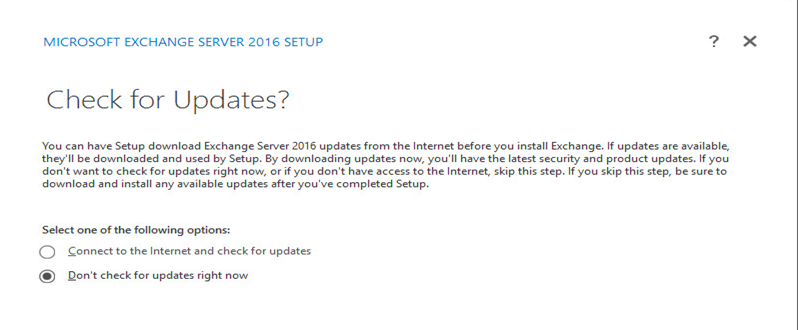
Check “Don’t check for update right now” and press next


-
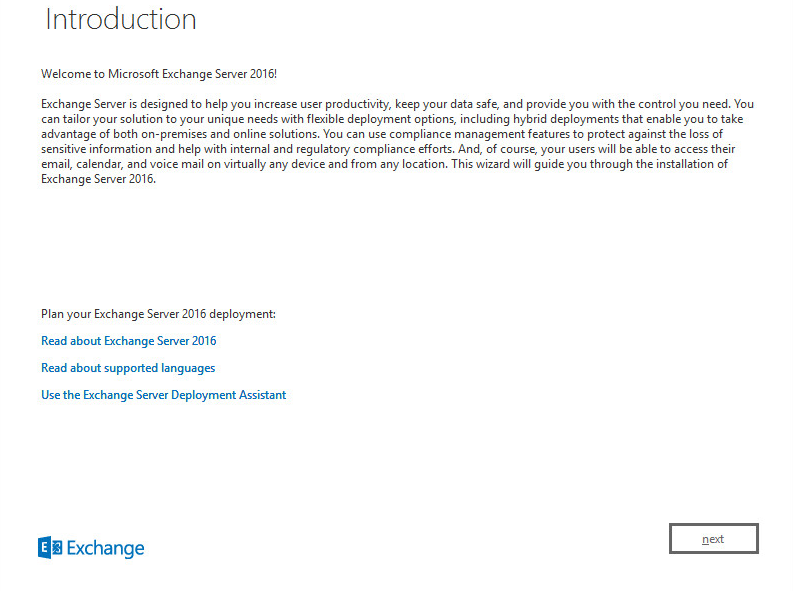
In Introduction window press next

-
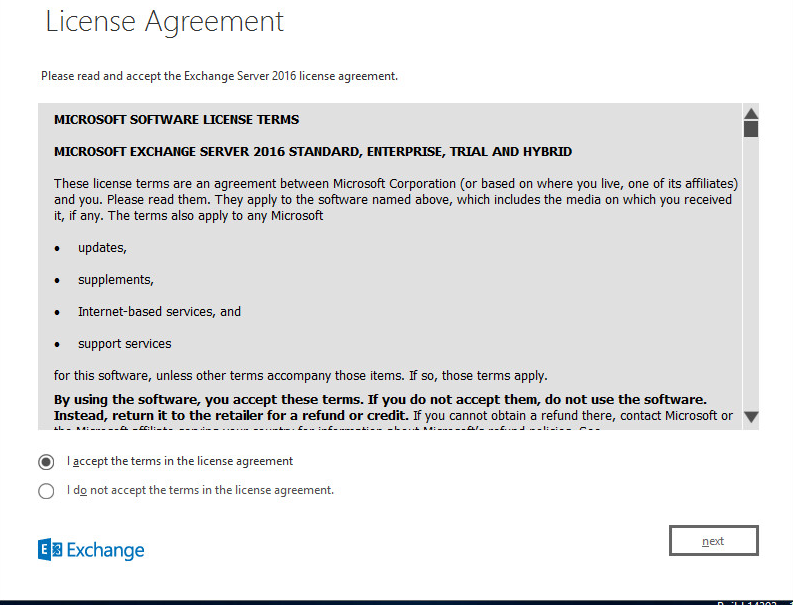
Then check “I Accept the terms in the license agreement” and press next

-
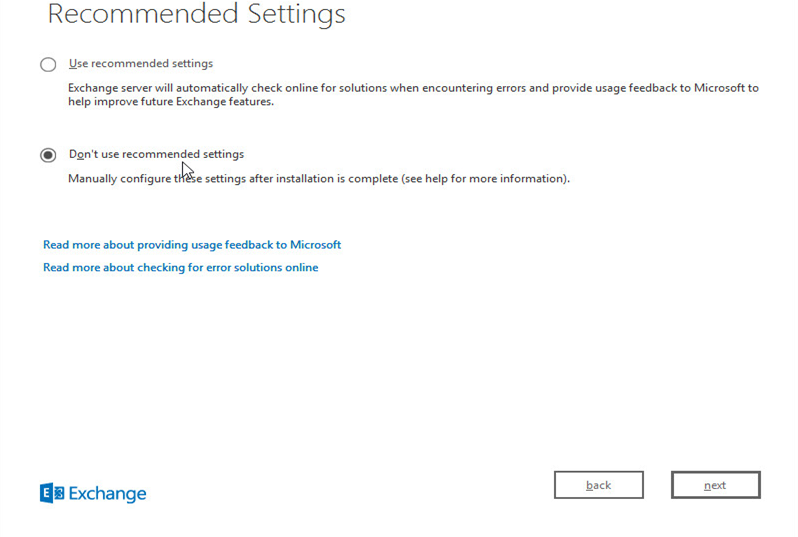
Check “Don’t use recommended settings”

-
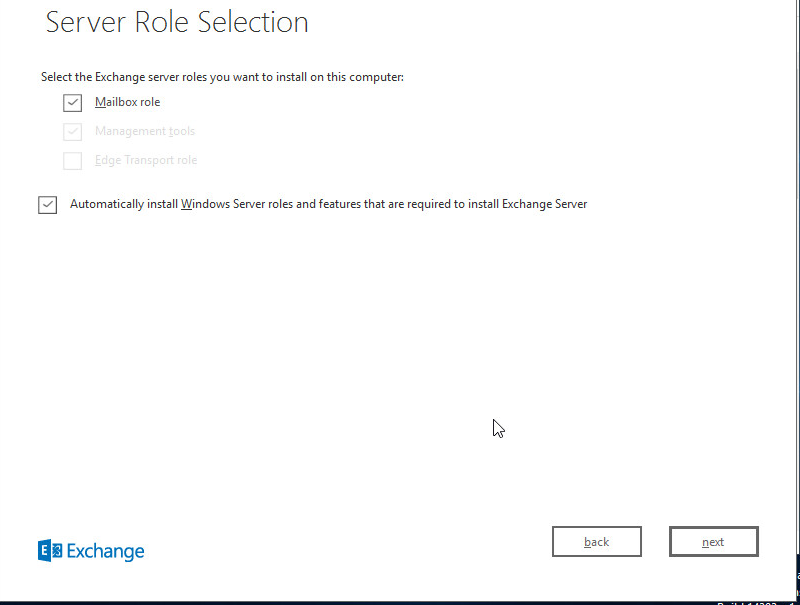
Check “Mailbox role” and “Automatically install windows server…” and press next

-
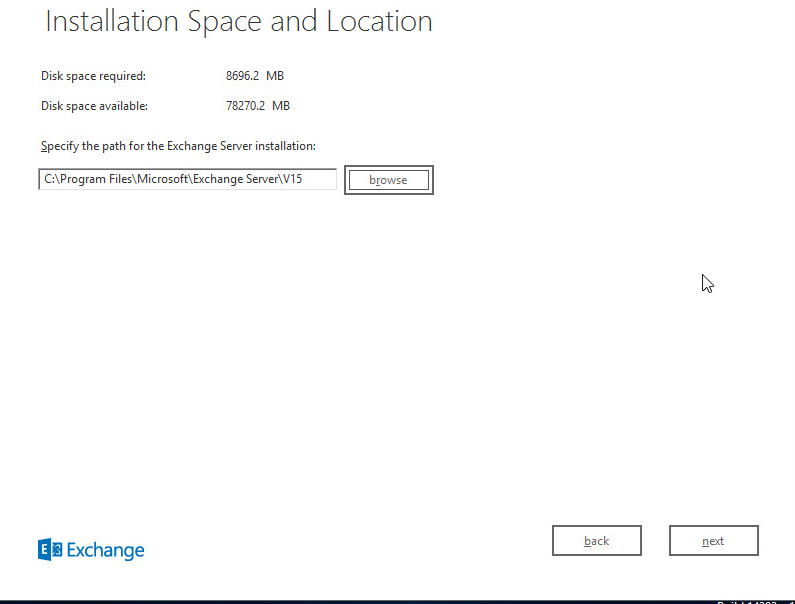
Leave installation path and press next

-
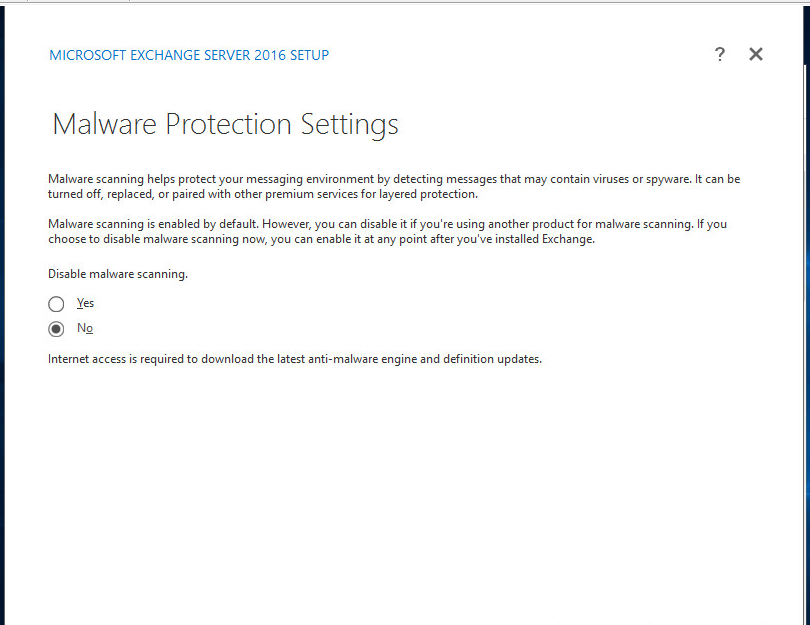
You can choose not to apply malware protection and can be configured later

-
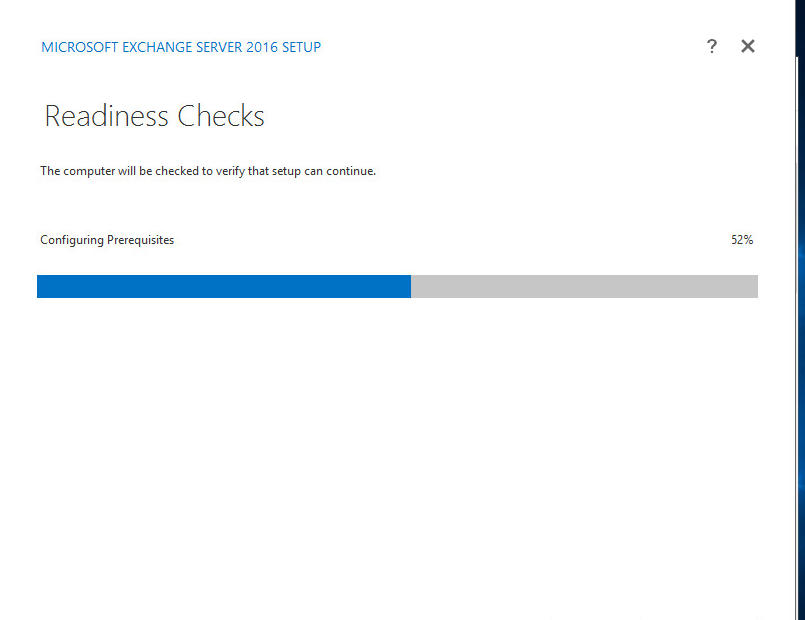
Now the prerequisite will be checked

-
The last step will be the installation of the exchange server through 15 steps:

-
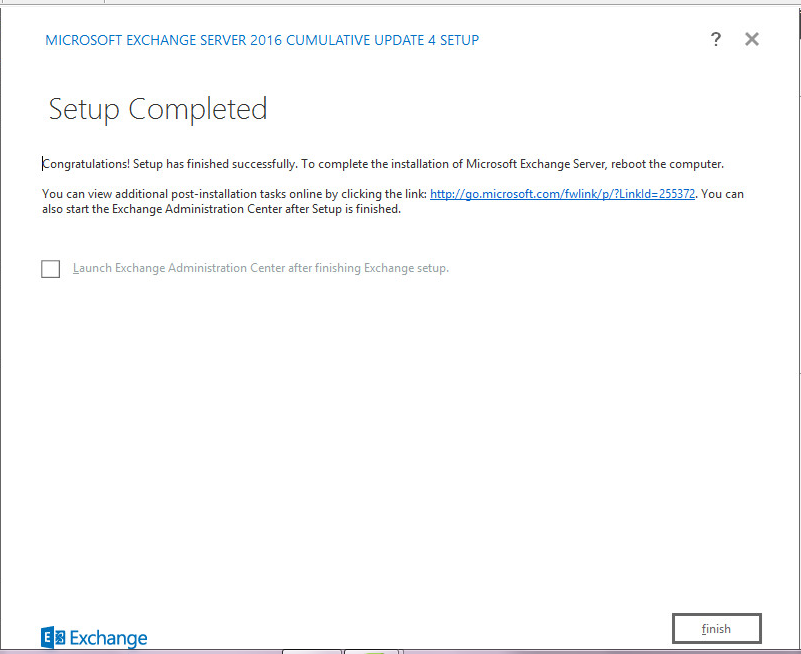
Then you should receive the completion screen.

If you try to install Exchange 2016 on windows server 2016 you may receive the below error:
Error: The Windows component Server-Gui-Mgmt-Infra isn’t installed on this computer
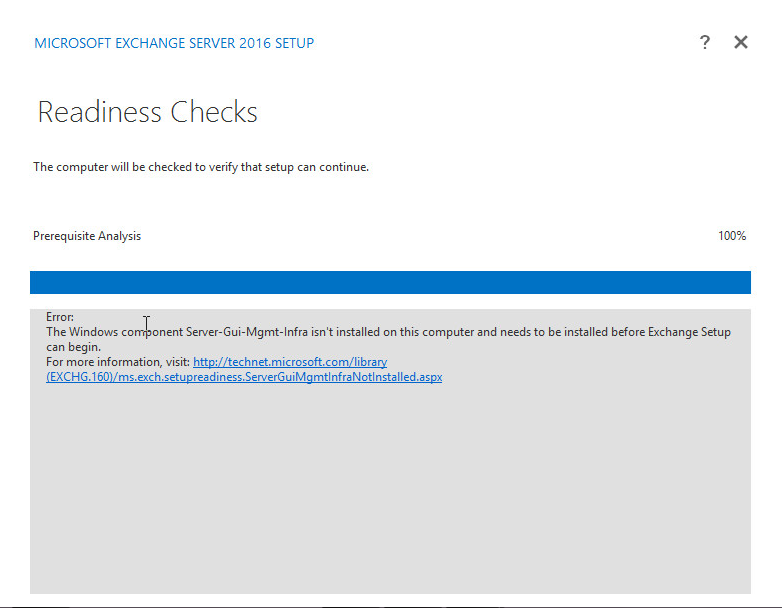
This error is related change on the operating system features of Windows server 2016 which can be solved by installing the cumulative update 4 for exchange server 2016:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54450
After you install the CU4 of Exchange server 2016 it will be installed successfully normally as below:

Exchange Server On-Premise
Advantages of On-Premise Server
- Full Control of all activities
- The Hardware and Email Platform are only used by the particular organization with full control.
- The organization will decide on the configuration, the upgrades and changes and timing. It can be applied to the infrastructure at the time convenient to business.
- Maintenance of the server, installation of the updates and hardware related problems needs to be monitored by the organization.
- While using On-premise Exchange Server, organization can decide the desired size of the mailboxes.
- Freedom to implement as many services as desired to its users with ActiveSync, transport rules, Webmail, public folders, etc.
- Options like Server-updates, backups, restarts or shutdowns can be controlled & performed at any time convenient by the organization.
- Flexibility for customizations
- The On-Premise Exchange Server supports more flexibility while providing integration to external systems or third party applications that will work with MS Exchange. It is easier to interconnect between Exchange & other application servers as long as both are hosted on same local network.
- Email for malfunction printers, notification messages for Customer Relationship management, Communication for receiving faxes through emails, etc. can be set as per requirements.
- Control of Exchange Data
- The integrity and longevity of the Exchange data depends on the organization.
- It is under the control of the business to decide when to take backup of the mailbox databases and how the backup can be stored or destroyed.
- Data is always stored on-premises even if it is using online drives, backup tapes or own remote storage.
- Other Benefits
- Using On-Premise Exchange Server enables ability to configure multi-level and high-level security and supports efficiency in use of storage by providing Public folders that allows sharing of one mailbox to all users.
- Due to end user proximity to Server Performance and information access without internet helps in improving Performance and access times as long as Exchange Server is well configured and setup.
Disadvantages of On-Premise Server
- Threat of Losing Data
- As the data is stored in the organization’s hardware, any disaster may lead to loss of email and servers.
- Losing data might affect business continuity and rebuilding it can be costly.
- Security of data loss is main concern. To ensure that, organization needs to configure networks, systems and Exchange platform against possible threats.
- High Expense Involved
- Setting up Exchange Server On-Premise not only involves initial cost in Licensing but also involves maintenance cost of hardware and applications.
- Update of new version of Exchange involves different configurations than the earlier one.
- Hardware used may require replacement after every few years.
- Availability
- The two main factors for the better reliability & Uptime of internally hosted Exchange Server depends on Exchange Server configuration and the level of investment the organization is willing to provide for hosting the Exchange Server On-Premise Environment.
-Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 brings a new set of technologies, features, and services to Exchange Server, the messaging platform that provides email, scheduling, and tools for custom collaboration and messaging service applications. Its goal is to support people and organizations as their work habits evolve from a communication focus to a collaboration focus. At the same time, Exchange 2016 helps lower the total cost of ownership whether you deploy Exchange 2016 on-premises or provision your mailboxes in the cloud.
1.Smarter Inbox
Exchange 2016 helps you get more done through faster search and an inbox that is more personalized, more helpful, and more intelligent.
2.Simplified Architecture
A simplified architecture, originally forged in the cloud, combines the mailbox and client access roles, so it’s easier to plan and scale your deployments. Streamlined coexistence with Exchange 2013 means easier upgrading.
3.Better Collaboration
With its new approach to attachments that eliminates versioning headaches, plus other enhancements, Exchange Server 2016 makes working together on documents easier.
4.Mobile Productivity
Exchange Server 2016 powers the latest Outlook experiences on phones, tablets, desktops, and the web so you can get more done, wherever you are.
Features
Exchange Server 2016 introduced innovations through changes in the architecture. These changes have brought more advantages and features to the users, such as:
1. Improved search experience
Thanks to the asynchronous and decentralized architecture. Not only making it more fault-tolerant, it also allows more efficient load distribution using multiple servers and make the search process faster. As the result, Exchange 2016 search capability has been increased to 10k mailboxes per search, while the previous version ‘only’ capable of searching 5k mailboxes per search. This new improvement applies to both mailboxes and archived mailboxes, so that means you can search 20k mailboxes at once using the console.Search suggestions also able to better anticipate what you are about to look for and search refiners will help you to find the information you need with easier by providing the context-aware filters such as date, sender name, etc.
2. New cloud-focused architecture that supports mobility
Cloud computing growth looks more promising each year. More companies are considering the cloud as the solution to help lower the TCO of IT infrastructure. With this shifting in trend, Exchange 2016 also supports mailbox provisioning in the cloud beside the regular on-premise deployment.On the client side, Outlook on the web (formerly known as OWA – Outlook Web App) user interface has been enhanced and optimized to support more tablets and smartphones, including iOS and Android. The protocol that Outlook client uses to communicate with Exchange also changed to MAPI over HTTP, increasing the connection reliability and stability. These improvements allow greater mobility experience, as it is now easier to access Exchange mailbox from anywhere and using almost any device.
3. Easier collaboration on SharePoint and OneDrive
Exchange 2016 comes up with the capability of integration with SharePoint 2016. When Exchange 2016 user received an email with document attachment, it will be saved automatically to OneDrive for Business or an on-premise SharePoint server. Users can easily share the documents using a link instead of attaching files to the email. Exchange 2016 also improves the way users saving and uploading files to OneDrive for Business, and it supports editing of the attachment directly if it’s integrated with Office Online Server.
4. Faster failover and failure isolation
Exchange 2016 uses Database Availability Group (DAG) where they split up the process for each database so they can isolate issue on a single database. DAG still relies on Windows Server clustering and continuous replication, but Exchange 2016 has reduced the time required for failover due to improvements in transaction log code and on the passive database. All monitoring and recovery features are now more than just to keep up the component uptime, instead, it focuses on the user experience by alerting the administrator to proactively restore services or with the automatic server failover.
5. Outlook on the web and Outlook app feature enhancement
Other than the features that have been mentioned above, Outlook has improved the way it handles user activities for the best of their experience. The inbox panel now has the most optimized view for reading and easily take actions such as archiving, deleting or moving a message, all with a single click of a button. It also now has the capability to quickly undo the last mailbox action taken by the user with just a single click on the undo button.
-Major Features of Microsoft Exchange Server 2016
1.Faster Searches
Almost 20% of user time is spent in searching items that you already know or have. So MS Exchange 2016 has lent a helping hand there and cut it short for you. Microsoft has researched users’ searching patterns from Exchange Online and used the info to reduce the time you spend in searching by introducing:
- Quicker searches
- Helpful search suggestions
- More accurate and complete results
- Built-in search refiners
2.Simplified Architecture
Architecture wise too, Exchange 2016 is seeing a major change. The old Client Access server role and Mailbox server role are now combined into the Exchange 2016 Mailbox Server role. Usage-wise you don’t need to worry since it’s the same old multi-server role, just enforced. However, this means that you cannot install dedicated Client Access server roles anymore. Plus, you won’t be able to use Windows NLB anymore if your servers and configured in Database Availability Group. It is now recommended to use a 7-layer solution and a hardware load balancer for load balancing purposes.
3.OWA and Email Attachments
The new version has introduced side-by-side document editing and viewing to make the user experience better, which means that you can now see a sent email in OWA, the reply you are currently writing and the document in read / edit mode, simultaneously. Plus, attaching documents is now easier with the last modified documents from email drafts directly available for inclusion. It is also easier to upload documents to OneDrive and change their permissions on the go. Enclosed attachments are displayed larger, with more descriptive content and are directly editable by the recipient.
4.Storage Improvements
The working of the Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) or the Exchange database engine has been improved and Microsoft now recommends using the ReFS (Resilient File System) instead of NTFS.
5.Storage Improvements
The working of the Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) or the Exchange database engine has been improved and Microsoft now recommends using the ReFS (Resilient File System) instead of NTFS.
6.Access on Mobile Devices
Thankfully (and after much waiting), Outlook is arriving on Windows 10, iOS and Android devices and that too with much better productivity. Key highlights include:
- 2 tabs for email reading
- Windows 10 gestures
- Quick filter to find emails faster
- Calendar improvements and more.
7.Default protocol – MapiHttp
The default protocol for Outlook clients to connect to Exchange 2016 is MapiHttp. Moreover, Outlook Anywhere has been deprecated. However, you can still use it for Outlook 2010 (SP2 or higher). For MapiHttp, Outlook 2013 SP1 or higher is needed.
8.Extremely easy coexistence with Exchange 2013
This one is obvious. It has already been established that the two Exchange versions are very close together; so naturally, coexistence between the two is very easy. Exchange 2013 Client Access can proxy requests to Exchange 2016 Mailbox and vice versa is directly possible. All you need to do is add Exchange 2016 servers to an existing array of Exchange 2013 Client Access server that is load balanced and continue working as usual. The location of the user’s mailbox won’t matter; everything is fully transparent.
Other Hybrid Improvements
A number of hybrid improvements have also been added to remove Hybrid hassles. These include:
- Secure mail routing
- Unified address list
- Free/Busy calendar sharing
- Single OWA URL
- Mailbox move
- Unified message tracking
- Cross-org MailTips
- Multi-mailbox search
- Additional Features
- Additionally, new features also include options to use some specific features from the Cloud while staying on-premise. For instance, Advanced threat protection and Predictive coding for eDiscovery.
9.Remain in Control
Exchange lets you tailor your solution based on your unique needs and ensures that your communications are always available, while you remain in control. Move to the cloud overnight, deploy on-premises, or manage a hybrid deployment with mailboxes that are both online and on-premises. Manage powerful capabilities, including data loss prevention and Office 365 Groups Tooltip with requirements for Office 365 Groups, from the easy-to-use, web-based Exchange admin center. Role-based access helps you manage Exchange efficiently and delegate tasks. With Exchange archiving, large mailboxes, and retention policies, your users can keep important data in one place and you can take control of your storage and compliance demands.
10.Protect your Organization
Exchange helps protect business communication and sensitive information, simplifying internal and regulatory compliance. Built-in defenses against viruses, spam, and phishing attacks actively protect your communications. Data loss prevention features identify, monitor, and protect sensitive data through deep content analysis, and Policy Tips in Outlook inform users about policy violations before sensitive data is sent. Your compliance officers can run In-Place eDiscovery across Exchange, SharePoint, and Skype for Business from the eDiscovery Center Tooltip with availability of eDiscovery in select Office 365 plans to identify, hold, and analyze your organization’s data. The data always remains in place, so you never have to manage a separate store of data.
AWS
A) Template Deployment: Please choose appropriate options for deployment of template.
Choose your Domain FQDN and other details for AD deployment which the template does and take a note of the Domain username and password.
After deploying the template which takes about 3 hours, check the Output of the template.
You will get RDGW1ElasticIP and RDGW2ElasticIP
After you connect to one of the RDC of Remote Desktop Gateway you shall be able to connect to the Exchange servers.
If you have used the default values
Exchange Server 1 IP:10.0.0.150
Exchange Server 1 IP:10.0.64.150
Please note that username for EDGE server is Administrator and password is same as what you chose for your domain login.

Please note For EDGE server user name is Administrator and the password is the password which was set by the user for StackAdmin during template deployment.
B) RDP Connection: To connect to the operating system of Remote Desktop Gateway:
1) Connect to virtual machine using following RDP credentials :
- Hostname: PublicDNS / IP of machine
- Port : 3389
Username: To connect to the operating system, use RDP and the username is Administrator.(or your domain login)
Password : Please Click here to know how to get password .
C) Other Information:
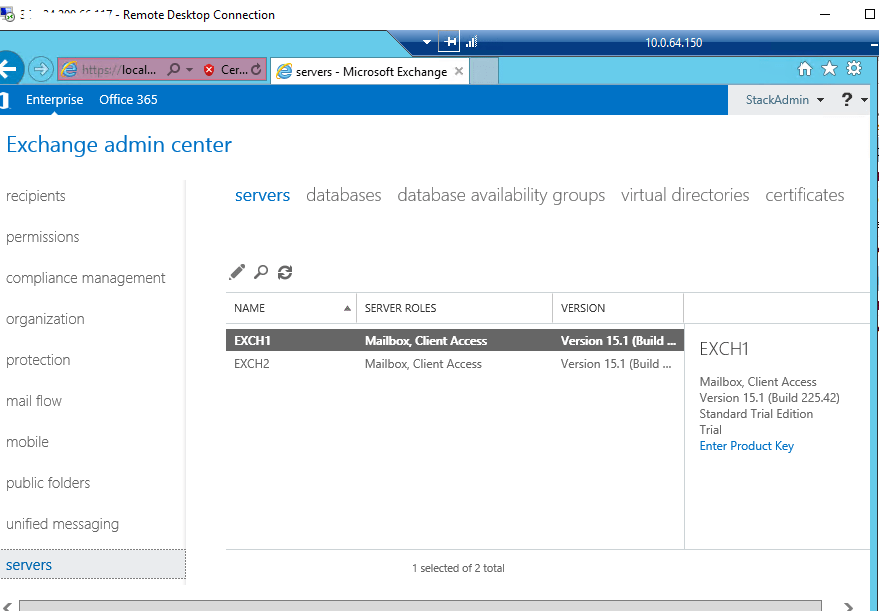
Once you connect to the RDC of your exchange servers via Remote Desktop Gateway you can access the toolbox and admin panel of exchange server. Go to start and search for Exchange 2016
You shall be able to see server setting as shown below:
Topology Diagram AD Exchange 2016 Design